Weekly Current Affairs (15th to 21st June 2024) Part - 1 | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
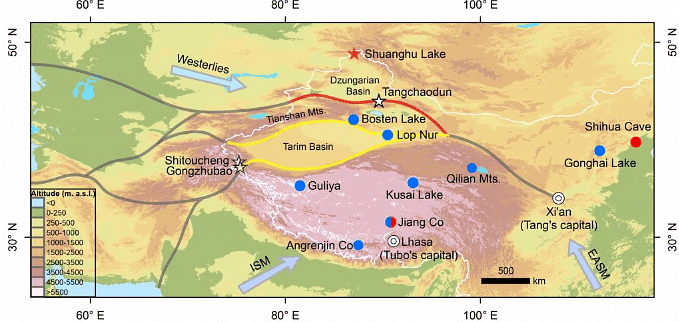
Shifting of Route of the Silk Road
Why in News?
- A recent study by Chinese scientists published in the journal Science Bulletin revealed that due to climate change, the primary route of the ancient Silk Road shifted northward.
- This study offers valuable insights into how climate change can impact the spatial evolution of human societies.
What is the Silk Road?
- The Silk Road was an extensive network of trade routes connecting Europe's Atlantic coast with Asia's Pacific coast over 1,500 years.
- It got its name from the profitable silk trade originating in China at the eastern end of the route.
- Aside from silk, the route was utilized for transporting spices, gold, and precious stones.
Route and History
- The Silk Road passed through significant cities and kingdoms like Samarkand, Babylon, and Constantinople.
- Its history dates back over 1,500 years, starting around the 2nd century BCE when trade between Europe and China intensified.
- Emperor Wu of the Han Dynasty sent Zhang Qian to explore the "Western Regions," leading to the establishment of the Tarim Basin route.
- Zhang Qian, known as the "Father of the Silk Road," paved the way for caravans traveling from China.
- Caravans from China's capital used the Tarim Basin route, eventually heading west towards the Levant and Anatolia for further trade.
Shift in Silk Road Route
- Originally, the Silk Road's main route circumvented the Tarim Basin due to harsh desert conditions.
- Between 420-850 CE, caravans shifted to the northern slopes of the Tianshan Mountains, establishing the "New Northern" route.
Consequences and Reasons Behind the Shift
- The new route fostered the Turco-Sogdian cultural sphere and improved communication between Chinese dynasties and nomadic empires.
- Climate change, marked by cooling and drying in the Tarim Basin, led to the shift due to water scarcity.
- Geopolitical factors, like conflicts with the Tubo Kingdom, also influenced the route change.
Historical Significance of the Silk Route
- The Silk Road facilitated trade of luxury goods, cultural exchange, and technological advancements between East and West.
- It played a pivotal role in economic prosperity, cultural diffusion, and geopolitical influence across Eurasia.
- Technological innovations and the exchange of ideas along the route shaped civilizations for centuries.
End of Silk Route and Revival Efforts
- The original Silk Route vanished in 1453, prompting the discovery of alternative sea routes for trade.
- In 2013, China launched the "One Belt, One Road" initiative to revive the Silk Route, enhancing connectivity across multiple regions.
50th G7 Summit

Why in News?
- Recently, the Prime Minister attended the 50th G7 summit in Italy from June 13 to 15, 2024. This marked the group's 50th anniversary.
- This summit was the Prime Minister's first foreign trip after beginning his third consecutive term in office.
Key Highlights of the 50th G7 Summit in Italy
Promotion to G7 PGII (Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment):
- Leaders decided to advance concrete G7 PGII initiatives, aiming to bridge the infrastructure gap in developing nations.
- This initiative, launched in 2022, seeks to mobilize $600 billion by 2027 for infrastructure projects in low and middle-income countries.
Support and Promotion to India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC):
- G-7 nations pledged support for IMEC, a network linking India, the Middle East, and Europe through various transportation modes.
- IMEC, signed in 2023, involves rail, road, and sea routes, along with energy and data cables.
Support to Infrastructure Projects:
- G7 extended support for infrastructure projects like the Lobito Corridor, Luzon Corridor, and Middle Corridor.
- These projects aim to enhance transportation and economic connectivity in Africa and Asia.
The Great Green Wall Initiative:
- A project combating desertification in Africa by planting trees to prevent the spread of the Sahara Desert.
- It aims to improve biodiversity and create economic opportunities.
Enhancing Interoperability of AI Governance:
- G7 leaders commit to improving AI governance to ensure transparency and accountability while fostering innovation.
Extraordinary Revenue Acceleration (ERA) Loans for Ukraine:
- The G7 will provide around $50 billion in additional funding to Ukraine by the end of 2024.
What is G7?
About:
- The G7 consists of the most advanced economies—France, Germany, Italy, the United Kingdom, Japan, the United States, and Canada.
- Summits are held annually, featuring discussions on global issues.
Origin:
- Formed in response to the 1973 oil crisis, the G7 has evolved into a key platform for economic and political coordination.
- Initially comprising six nations, it expanded to seven with Canada's inclusion in 1976.
Nature of Grouping:
- Operates informally, lacking a permanent bureaucracy.
- Decisions are based on consensus among member nations.
Purpose:
- Facilitates dialogue on global issues.
- Seeks to coordinate responses to challenges and influence international policies.
Significance:
- Controls a significant portion of global wealth and GDP.
- Represents a sizable portion of the world's population.
Why is India's Role in the G7 Important?
India's Economic Significance:
- India boasts a large economy, outstripping several G7 countries.
- It is recognized as one of the world's fastest-growing economies by the IMF.
India's Strategic Importance in the Indo-Pacific:
- India plays a vital role in balancing power dynamics in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Its partnerships with various G7 nations contribute to regional stability.
India's Role in Addressing the European Energy Crisis:
- India's involvement in supplying oil to Europe aids in mitigating the energy crisis caused by the Ukraine conflict.
India's Potential for Mediating the Russia-Ukraine Conflict:
- Given its relations with both Russia and the West, India could serve as a mediator in the Ukraine conflict.
Challenges to India in Balancing Power Conflicts
Defence Dependence:
- India's reliance on Russian military equipment poses challenges in the context of global power dynamics.
Economic Interdependence:
- Deepening ties with the US and China necessitate a delicate balance to avoid economic disruptions.
Divergent Approaches:
- India faces challenges in aligning with differing Western viewpoints on Russia and China.
Domestic Political Turmoil:
- Internal political divisions in Western nations could impact India's strategic decisions.
Border Disputes:
- Territorial conflicts with China and regional power struggles pose security concerns for India.
Geopolitical Rivalry:
- Growing US-China competition may compel India to make strategic choices that align with its national interests.
Conclusion
- India's participation in the G7 is crucial for addressing global challenges and shaping international cooperation.
- From economic strength to strategic significance, India's role is pivotal in the evolving global landscape.
Child Food Poverty
Why in News?
- A recent UNICEF report titled 'Child Food Poverty: Nutrition Deprivation in Early Childhood' examines child food poverty in early childhood.
Key Findings of the Report
- Approximately 181 million children under 5 live in severe child food poverty globally.
- In India, 40% of children face severe child food poverty.
- Progress is slow but some regions show improvement.
- Children from both poor and non-poor households are affected.
- Severe child food poverty leads to lack of nutrient-rich foods and unhealthy diet.
- Global food crisis and conflicts worsen the situation.
- Severe child food poverty drives child undernutrition.
- Prevalence is higher in countries with child stunting.
Definition of Child Food Poverty
- UNICEF defines it as children's inability to access nutritious diets under 5.
- Includes child undernutrition and child overweight.
- Childhood overweight results from excessive calorie intake.
Key Drivers of Child Food Poverty
- Poor Food Environments:
- Disruptions in rural areas affect food production.
- Unhealthy options are abundant in urban areas.
- Poor Feeding Practices in Early Childhood:
- Generational knowledge gaps and gender inequality impact child diets.
- Household Income Poverty:
- Unaffordability of nutritious foods due to rising prices.
- Failing Food and Health Systems:
- Insufficient food options and lack of health system support contribute.
Impacts of Child Food Poverty
- Impaired Growth and Development:
- Malnutrition affects physical and cognitive development.
- Weakened Immune System:
- Makes children vulnerable to diseases.
- Long-Term Health Issues:
- Linked to chronic diseases and reduced productivity.
- Perpetuating the Cycle of Poverty:
- Contributes to poverty cycles across generations.
Actions to End Child Food Poverty
- Making Policy-Based Targets:
- Transforming Food Systems for accessibility and affordability.
- Regulating the Food Industry for healthier options.
- Strengthening Health Systems with nutrition services.
- Data and Monitoring for informed interventions.
Indian Initiatives
- Mid-day Meal (MDM) scheme
- POSHAN Abhiyaan
- National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013
- Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY)
- Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) Scheme
Conclusion
This UNICEF report emphasizes the severity of child food poverty. Action through recommendations can ensure children access nutritious diets, breaking the poverty cycle.
E-flow Monitoring System
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Jal Shakti Ministry introduced an innovative Environmental flows (E-flows) Monitoring System to monitor river water quality in real-time and support river ecosystem projects.
Key Features of the E-flow Ecological Monitoring System
- About: Developed by the National Mission for Clean Ganga under the Jal Shakti Ministry.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous analysis of water quality in the Ganga, Yamuna, and their tributaries.
- Centralised Oversight: Monitoring activities under the Namami Gange program, especially Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs).
- Comprehensive Data Analysis: Tracking in-flow, out-flow, and mandated E-flow across 11 projects along the Ganga Mainstream using quarterly reports from the Central Water Commission.
The Namami Gange Programme
About: Integrated Conservation Mission initiated in June 2014 by the Union Government to clean and rejuvenate the Ganga River.
Main Pillars:
- Sewerage Treatment Infrastructure
- River-Front Development
- River-Surface Cleaning
- Biodiversity Conservation
- Afforestation
- Industrial Effluent Monitoring
- Ganga Gram
- Public Awareness
Challenges Facing the Namami Gange Programme
- Delays in Project Execution
- Funding and Budget Allocation
- Insufficient Sewage Treatment Capacity
- Persistence of Industrial Pollution
Measures for Ganga River Conservation
- Leverage Technology for Monitoring and Data Management
- Adopt-a-Ghat Initiative
- Riverine Economy Incentives
- Floodplain Restoration
- Waste-to-Wealth Handicrafts
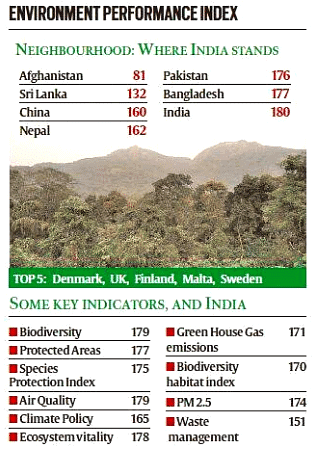
Environmental Performance Index 2024
Why in News?
- The Yale Center for Environmental Law and Policy and the Columbia Center for International Earth Science Information Network released the Environmental Performance Index (EPI) for 2024.
Key Highlights of EPI 2024
Global Scenario:
- Estonia leads the index by reducing its greenhouse gas emissions by 59% from 1990 levels.
- Only five countries - Estonia, Finland, Greece, Timor-Leste, and the United Kingdom - cut their GHG emissions at the rate needed to reach net zero by 2050.
- Sub-Saharan Africa and Southern Asia rank lowest among the eight regions assessed.
- India ranks 176th out of 180 countries with 27.6 points, performing poorly in Air quality, Emissions, and Biodiversity Conservation.
- India is the largest emitter of transboundary pollution in South Asia.
- India ranks 133rd in the climate change category.
- The 2024 EPI introduces pilot indicators to measure the effectiveness of protected areas.
Issues Related to EPI
Projected GHG Emissions Calculation:
- India criticizes the calculation based on the average rate of change in emissions.
- Measurement challenges include biodiversity loss, ecosystem health, and lack of standard methodologies.
- India's carbon sinks like forests are not considered in emissions trajectory calculation.
- India faces issues in balancing national priorities and implementing EPI recommendations.
What is the Environmental Performance Index?
- The EPI evaluates nations' efforts to meet international environmental targets.
- It consists of 58 performance indicators grouped into 11 categories.
- Factors like governance, financial resources, and human development are crucial in environmental sustainability.
Way Forward
- Enhance methodology by incorporating longer time frames for GHG emissions calculation.
- Expand indicators to include relevant measures for developing countries like India.
- Ensure transparent weighting of indicators and engage stakeholders for feedback.
Base Erosion and Profit Shifting
Why in News?
- Recently, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) welcomed the commitment of the 147 Members of the Inclusive Framework on Base Erosion and Profit-Shifting (BEPS) to keep working to resolve any remaining issues in the signing process of the Multilateral Convention (MLC).
What is Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS)?
About:
- The BEPS initiative is an OECD initiative, approved by the G20, to identify ways of providing more standardized tax rules globally.
- BEPS refers to tax strategies exploiting differences in tax rules across countries to minimize overall corporate tax payments.
Aim:
- This strategy aims to reduce overall corporate tax liability by making profits seem to vanish or by moving them to low-tax regions with minimal real economic activity.
- While often not illegal, BEPS tactics capitalize on variations in international tax regulations.
- Developing countries are particularly vulnerable to BEPS due to their strong dependence on corporate income tax, especially from multinational corporations.
Inclusive Framework on BEPS
- Inclusive Framework was established by the OECD and G20 in 2016.
- It unites 147 countries and jurisdictions, to combat tax avoidance and promote equitable tax practices, and comprises two pillars.
- First Pillar: It addresses cross-border profit shifting by multinational and digital companies.
- Second Pillar: It proposes a global minimum corporate tax rate, currently suggested at 15%, to prevent harmful tax competition among countries.
What is the Significance of BEPS?
- Equitable Tax Contributions: It ensures multinational enterprises (MNEs) pay their fair share where they do business.
- Fiscal Healing: It helps governments raise crucial funds to mend public finances strained by various unforeseen conditions (Man-made or Natural disasters).
- Competitive Balance: It reduces the tax advantages of larger corporations over smaller, domestic businesses.
- Digital-Era Readiness: This tax systems catch up with online commerce.
- Worldwide Teamwork: It emphasizes an international commitment to solving cross-border tax challenges.
What is India's Position on Global Tax Reform?
- Signing Global Tax Reform: Indian multinational enterprises will have to start reviewing and accounting for any additional tax liability as per the global tax reform signed by India.
- Consensus-Driven Solution: The country supports a consensus-driven solution that's easy to implement and comply with.
- Abiding Market Jurisdiction: India emphasizes that the solution should allocate substantial and sustainable revenue to market jurisdictions, especially developing and emerging economies.
What are the Concerns Related to Global Tax Reform?
- Sovereignty Issues: The reform may infringe upon a nation's sovereign right to determine its own tax policies.
- Limiting Tax Competition: Some argue that the fear of tax competition restrains governments from imposing excessive taxes on citizens to finance extravagant spending.
- Effectiveness: Critics question the reform's potency, suggesting it may not eliminate tax havens as multinational companies continue to engage in aggressive tax planning strategies that exploit regulatory gaps and inconsistencies.
Way Forward
- Flexible Implementation: Allow countries to adapt the rules to their specific economic contexts while maintaining the spirit of the agreement.
- Strengthen International Cooperation: Enhance information sharing and joint audits to tackle complex cross-border tax issues.
- Public Transparency: Encourage or mandate public country-by-country reporting by large multinationals.
Ukraine "Path to Peace" Summit
Why in News?
- Recently, the "Path To Peace Summit" in Switzerland aimed to end the Russia-Ukraine war.
Key Highlights
- 80 countries called for Ukraine's territorial integrity as the basis for peace.
- Focus areas included nuclear safety, global food security, and humanitarian issues.
- Emphasis on releasing prisoners of war and displaced civilians.
- Russia was absent due to President Putin's indictment.
- India, along with others, didn't endorse the final statement, stressing proposals acceptable to both sides for peace.
India's Stand in the Conflict
- Non-Alignment: India's neutral stance aligns with its non-aligned foreign policy principles.
- Strategic Partnership: India values its ties with Russia due to military and energy cooperation.
- Humanitarian Diplomacy: India supports Ukraine with aid and calls for diplomatic resolutions.
- Global Balancing Act: India balances partnerships with Russia, the US, and the EU for economic and geopolitical interests.
Global Implications of the Conflict
- Geopolitical Shifts: Countries align differently, impacting alliances and global power dynamics.
- Strain on Global Institutions: The conflict questions the effectiveness of international bodies.
- Humanitarian Crisis: Millions displaced, especially children, facing trauma and education disruptions.
- Food Security Threat: War disrupts agriculture, risking food shortages globally.
- Energy Market Disruptions: Global energy markets affected by Russia's role, leading to price hikes and insecurity.
International Peace Efforts
- Ukrainian Peace Plan: Demands include Russian troop withdrawal, territorial restoration, and war crime accountability.
- Minsk Agreements (2015): Aimed to end conflict in eastern Ukraine with ceasefire and government control agreements.
- UN Calls for Peace: Emphasizes respecting Ukraine's sovereignty and territorial integrity for peace.
|
164 videos|800 docs|1157 tests
|
FAQs on Weekly Current Affairs (15th to 21st June 2024) Part - 1 - General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce
| 1. How will the shifting of the Silk Road route impact global trade and connectivity? |  |
| 2. What were the key highlights and outcomes of the 50th G7 Summit? |  |
| 3. How is the issue of child food poverty being addressed at the international level? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the E-flow Monitoring System in monitoring and managing water resources? |  |
| 5. How does the Base Erosion and Profit Shifting impact global taxation and corporate practices? |  |





















