Weekly Current Affairs (1st to 7th February 2025) - 1 | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
Economic Survey 2024-25 Overview
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman tabled the Economic Survey 2024-25 in Parliament. This document outlines a roadmap for reforms and growth, setting the stage for the upcoming Union Budget 2025-26.
Key Takeaways
- Projected GDP growth for India is between 6.3% to 6.8% for FY26 (2025-26).
- Global economy is expected to grow by 3.2% in 2024, with manufacturing facing challenges.
- Inflation remains a concern, particularly in the services sector.
Additional Details
- State of the Economy: The International Monetary Fund (IMF) forecasts 3.2% global growth in 2024 amidst manufacturing slowdowns due to supply chain disruptions.
- India's Economic Growth: India's GDP is projected to grow by 6.4%in FY25, with sector-wise growth as follows:
- Agriculture: 3.8% growth driven by record Kharif production.
- Industry & Manufacturing: 6.2% growth, affected by weak global demand.
- Services: Leading at 7.2% growth, particularly in IT, finance, and hospitality.
- Monetary Developments:
- Gross Non-Performing Assets (GNPA) decreased to 2.6%, a 12-year low.
- Return on Assets (RoA) rose to 1.4%.
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI) held the repo rate at 6.5%.
- Climate & Environment Initiatives: India aims to enhance its forest carbon sink and increase renewable energy sources, targeting 50% of power capacity by 2030 being non-fossil.
In conclusion, while India's economic fundamentals remain strong, challenges from global uncertainties, inflation, and investment hesitancy must be addressed through effective policy interventions and reforms.
Jurisdiction and the State
Why in News?
- In the case of S. Shobha vs. Muthoot Finance Ltd (2025), the Supreme Court (SC) ruled that private companies, including scheduled banks and Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs), are not subject to writ jurisdiction as they do not perform public functions or duties. The SC determined that NBFCs do not qualify as a "State" under Article 12, and that a 'function' test should be applied to decide the maintainability of a writ application.
Key Takeaways
- The SC verdict established that NBFCs, while regulated, do not automatically fall under writ jurisdiction.
- Writ jurisdiction applies only if an entity performs public duties defined by statutes or statutory rules.
- Writs can be enforced against private bodies only if they deny rights related to a public duty.
Additional Details
- Writs: A writ is a legal order issued by constitutional courts under Articles 32 and 226 of the Indian Constitution to protect citizens' rights, derived from English "prerogative writs."
- Authority to Issue Writs:
- Supreme Court (Article 32): Can issue writs only for the enforcement of Fundamental Rights (FRs).
- High Courts (Article 226): Can issue writs for the enforcement of other legal rights.
- Prior to 1950, only the High Courts of Calcutta, Bombay, and Madras had the power to issue writs.
- Parliament can empower other courts to issue writs under Article 32, but no such provisions have been made yet.
Types of Writs and Their Scope
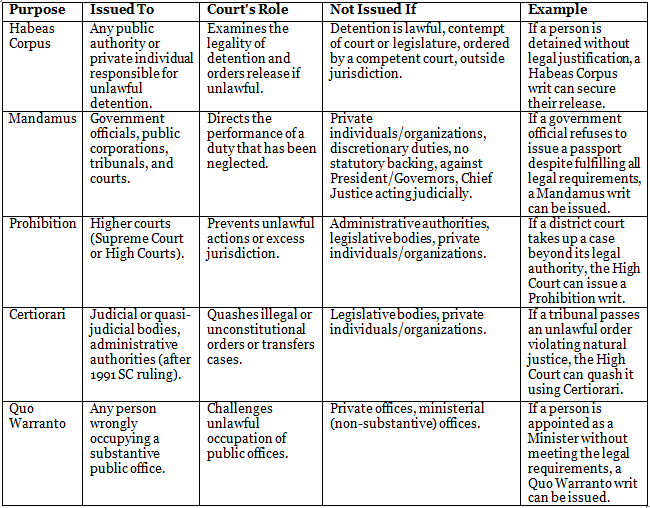
Differences in Writ Jurisdiction of SC and HC
- Scope of Enforcement: SC's jurisdiction applies only for Fundamental Rights violations, while HC's encompasses FRs and other legal rights.
- Territorial Jurisdiction: SC can issue writs throughout India; HC's jurisdiction is limited to its territorial area unless the cause of action arises within its jurisdiction.
- Nature of the Right: SC's writ jurisdiction is a Fundamental Right (Article 32) that cannot be refused, while HC's is discretionary (Article 226) and may refuse to issue a writ.
Definition of a State under Article 12
- Article 12 defines "State" for the purpose of Part III (Fundamental Rights). It includes:
- Government and legislature of the Union and States.
- Local authorities such as municipalities and panchayats.
- All statutory or non-statutory authorities.
- The definition of "State" is broad, covering all its agencies whose actions can be challenged in court for violating Fundamental Rights.
The Supreme Court and High Courts issue writs to address violations of fundamental and legal rights, focusing on entities that perform public duties. Writ jurisdiction is contingent upon whether an entity provides governmental functions, as only such entities are subject to writs.
Strengthening Regulatory Bodies
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- Recent discussions among experts highlight the necessity of examining the role and impact of regulatory bodies, such as the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), to improve decision-making processes. It is emphasized that these bodies need to effectively communicate their decisions to ensure that stakeholders are satisfied, both in reality and in perception.
Key Takeaways
- Regulatory bodies are crucial for ensuring fair practices in various sectors.
- There are two main types: statutory regulatory bodies and self-regulatory bodies.
- Issues such as lack of independence and ineffective appointment processes hinder their effectiveness.
Additional Details
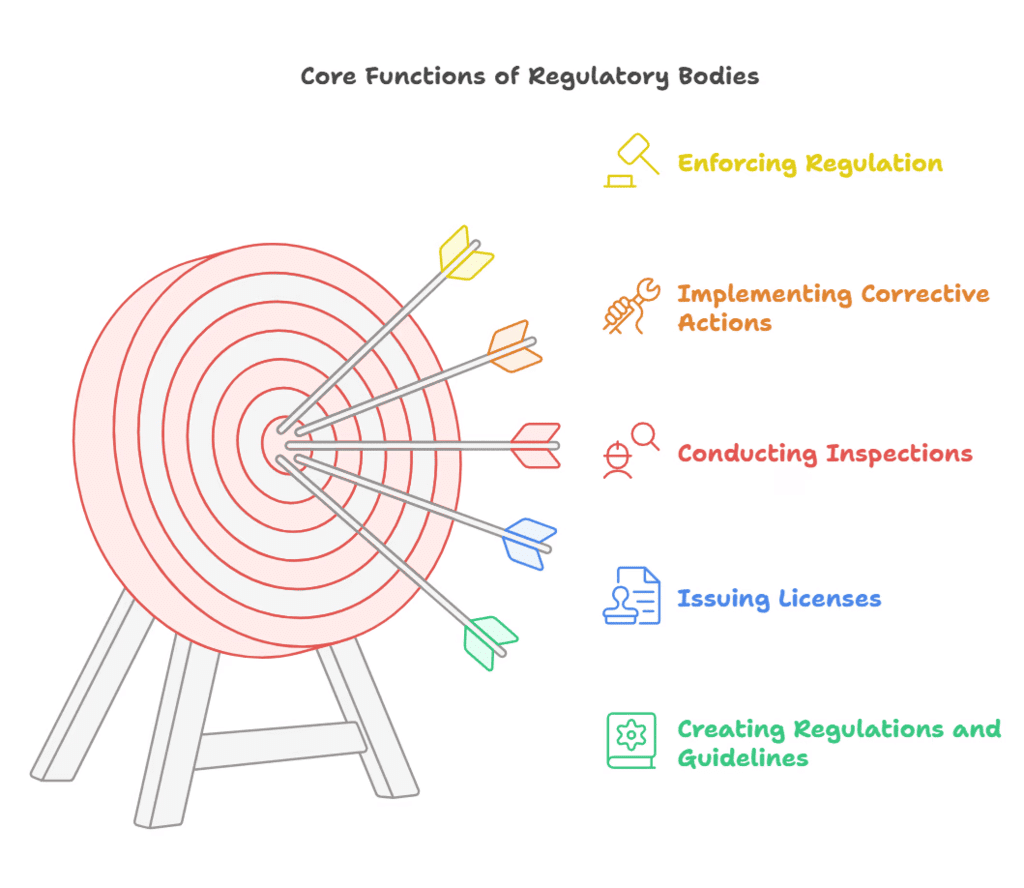
- What are Regulatory Bodies? Regulatory bodies are organizations established to monitor and regulate specific sectors of the economy, ensuring fair practices and protecting public interests. Since 1991, following the LPG reforms, numerous authorities have been established to prevent monopolies in critical sectors like banking, insurance, and capital markets. Most of these bodies are quasi-judicial in nature.
- Types:
- Statutory Regulatory Bodies (e.g., SEBI)
- Self-Regulatory Bodies (e.g., Bar Council of India)
- Functions: Regulatory bodies perform essential functions, including protecting consumer interests, enforcing standards, ensuring market stability, promoting economic growth, and upholding legal compliance.
- Examples:Over 30 regulatory bodies exist in India, including:
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI): Oversees credit supply and banking operations.
- Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI): Regulates the insurance sector.
- Central Electricity Regulatory Commission: Regulates tariffs for government-owned electricity generating companies.
- Issues:
- Lack of independence due to governmental interference.
- Financial autonomy issues, as regulators depend on ministry approval for budgets.
- Ineffective appointment processes leading to a lack of expertise.
- Inadequate parliamentary accountability affecting transparency.
- Fragmented regulatory frameworks across different sectors, hindering efficiency.
- Way Forward:
- Enhance accountability to Parliament's Standing Committee.
- Audit annual expenditures by the CAG and present reports to Parliament.
- Foster regular reviews with input from experts to assess effectiveness.
- Build research capacity through collaboration with academic institutions.
- Implement international best practices for regulatory coherence and efficiency.
In summary, addressing the challenges faced by Indian regulatory bodies is vital for enhancing their accountability, transparency, and effectiveness. By implementing suggested measures, these organizations can better fulfill their roles in protecting public interests and ensuring market stability.
Gender Budget 2025-26
Why in News?
- The Gender Budget Statement (GBS) represents a crucial advancement in gender-responsive budgeting (GRB), featuring increased financial allocations and broader participation from various ministries.
Key Takeaways
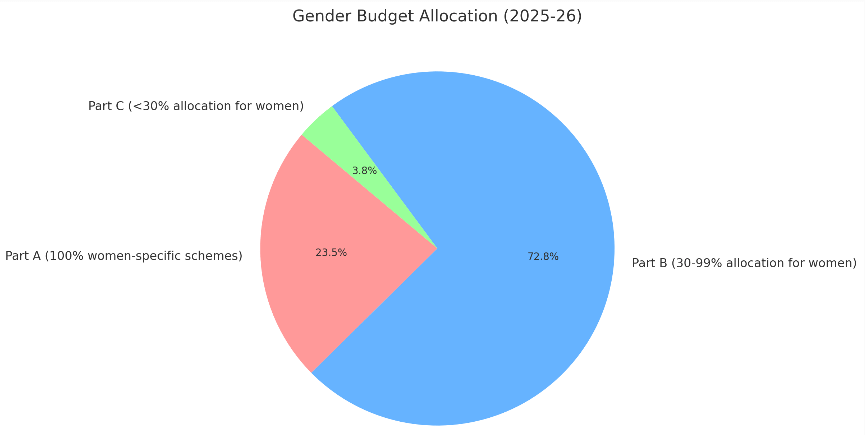
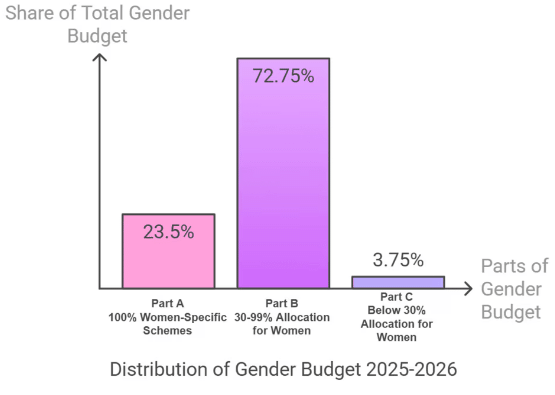
- The Gender Budget for FY 2025-26 is set at Rs 4.49 lakh crore, which constitutes 8.86% of the total Union Budget, marking a 37.5% increase from Rs 3.27 lakh crore in FY 2024-25.
- This GBS is the largest in India's history, focusing on enhancing women's welfare, education, and economic empowerment, with 49 ministries reporting gender-specific allocations.
Additional Details
- Parts of GBS 2025-26: The Gender Budget is divided into three components, as illustrated in the accompanying image.
- What is Gender Budgeting in India? Gender budgeting is a strategic approach adopted by governments to allocate resources effectively, addressing the unique needs of different genders, ensuring that policies are gender-sensitive.
- Background: India's commitment to gender equality began with the ratification of the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) in 1993, leading to the first GBS in 2005-06.
- Need: Gender budgeting is essential not only as a financial strategy but also as a moral imperative to combat gender inequality, especially as India ranks 129 out of 146 countries in the 2024 Gender Gap Report.
- Implementation: At the central level, the Ministry of Women and Child Development (MWCD) oversees gender budgeting, while state-level responsibilities lie with various departments, and district-level coordination is managed by the Hub for Empowerment of Women (HEW).
Gender budgeting plays a vital role in promoting gender equality, addressing discrimination, and supporting Sustainable Development Goal 5, which aims for global gender equality and women's empowerment.
Challenges Facing Gender Budgeting in India
- Ambiguities in Allocation: Unclear methodologies for fund allocation lead to discrepancies, such as the underreporting of significant schemes like MGNREGS.
- Concentration of Funds: Approximately 90% of the gender budget is concentrated in a few ministries, limiting its broad impact across various sectors.
- Long-term Schemes: Long-term funding for schemes may divert resources from immediate-impact programs that focus on women's empowerment.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Insufficient tracking mechanisms and a lack of gender-segregated data impede the accurate assessment of policies and their outcomes.
- Political Will: Gender budgeting may not always align with prevailing political priorities, resulting in inadequate support.
Way Forward
- Integration: Gender budgeting should be integrated across all ministries to ensure gender-sensitive allocations in every government initiative.
- Invest in the collection and analysis of gender-specific data to better understand women's needs and the impact of current policies.
- State GBS: Encourage state governments to increase their share in gender-responsive budgeting to include vulnerable women in the planning process.
- Clarification of Reporting Methods: Transparency in allocation and reporting processes is necessary for accountability, including public disclosure of funding methodologies.
- Conduct regular gender audits across ministries to evaluate the effectiveness of the allocated funds.
- Capacity Building: Training for government officials and stakeholders on gender budgeting will enhance expertise in incorporating gender perspectives into budget processes.
In conclusion, the Gender Budget 2025-26 signifies a pivotal move towards enhancing gender equality in India, while addressing the existing challenges and promoting women's empowerment effectively.
Mutual Credit Guarantee Scheme for MSMEs
Why in News?
- The Government of India has recently approved the launch of the Mutual Credit Guarantee Scheme for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MCGS-MSME).
Key Takeaways
- The scheme aims to enhance access to credit for MSMEs by providing guarantees for loans, thus lowering the perceived risk for lenders.
- Eligible borrowers are MSMEs with a valid Udyam Registration Number.
- The loan limit can go up to Rs 100 crore specifically for the purchase of equipment and machinery.
- The National Credit Guarantee Trustee Company Ltd (NCGTC) offers a 60% guarantee coverage to Member Lending Institutions (MLIs).
- At least 75% of the project costs must be allocated for the scheme.
- The scheme is applicable for four years or until a cumulative guarantee of Rs 7 lakh crore is issued, whichever comes first.
Significance
- Boost to Manufacturing: The scheme enhances credit availability for MSMEs, which contribute 17% to India's GDP.
- Support for Make in India: It aligns with the vision to raise the manufacturing sector's share to 25% of GDP.
- Credit Access: The scheme facilitates collateral-free loans, allowing MSMEs to expand their operations.
- Employment Growth: It is expected to create significant job opportunities in the manufacturing sector, which employs over 27 million people.
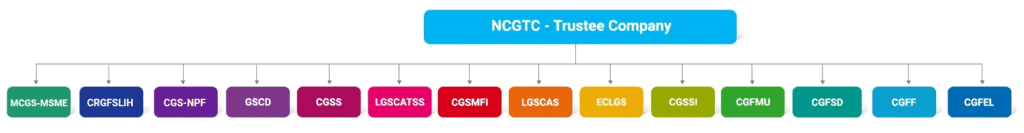
What is National Credit Guarantee Trustee Company Ltd (NCGTC)?
- NCGTC: This is a common trustee company responsible for managing various credit guarantee trust funds that assist borrowers in accessing finance by sharing lending risks with lenders.
- It provides loan guarantees to banks and financial institutions, promoting credit extension to underserved sectors including MSMEs, startups, and vulnerable groups.
- Establishment: NCGTC was established in March 2014 under the Indian Companies Act, 1956, with a paid-up capital of Rs 10 crore. It is a private limited company fully owned by the Government of India and operates under the Department of Financial Services, Ministry of Finance.
- Coverage: NCGTC currently manages 14 dedicated credit guarantee trust schemes, including MCGS-MSME, Credit Guarantee Fund for Micro Units (CGFMU), and Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS), among others.
This initiative is a significant step towards improving financial support for MSMEs, thereby enhancing their capabilities and contributions to the economy.
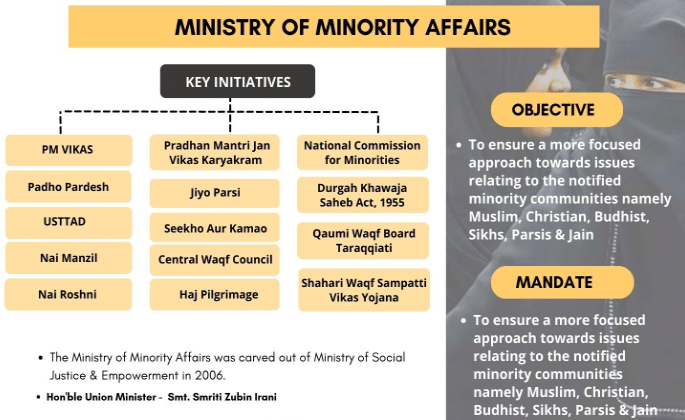
Initiatives by the Ministry of Minority Affairs
Why in News?
- The Ministry of Minority Affairs (MoMA) has recently highlighted India's persistent efforts aimed at empowering minority communities across the country.
Key Takeaways
- Post-Matric Scholarship Scheme (2007) enhances higher education opportunities for meritorious students from economically weaker sections of minority communities.
- Pre-Matric Scholarship Scheme (2008) encourages school attendance among children from minority communities by alleviating financial burdens.
- National Minorities Development and Finance Corporation (NMDFC) provides concessional credit for self-employment initiatives aimed at socio-economic development.
- Haj Pilgrimage Support (2016) facilitates low-income individuals' pilgrimage to Mecca.
- Jiyo Parsi Scheme (2013) aims to reverse the declining Parsi population through scientific measures.
- Pradhan Mantri Virasat Ka Samvardhan (PM VIKAS) consolidates various schemes to promote skill development and cultural preservation among minorities.
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK) focuses on enhancing community infrastructure in minority-concentrated areas.
Additional Details
- Post-Matric Scholarship Scheme: This scheme provides financial assistance to deserving students from economically disadvantaged minority backgrounds, with the allocation increasing significantly from Rs 70.63 crores in 2008-09 to Rs 1000 crores in 2023-24.
- Pre-Matric Scholarship Scheme: Aimed at encouraging parents to send their children to school, this scheme has seen its allocation rise from Rs 62.21 crores in 2008-09 to Rs 400 crores in 2023-24.
- National Minorities Development and Finance Corporation (NMDFC): Established in 1994, it focuses on providing credit for self-employment, with an allocation increase from Rs 2 crores in 2014-15 to Rs 3 crores in 2023-24.
- Haj Pilgrimage Support: This initiative has seen a significant increase in expenditure from Rs 9.75 crores in 2014-15 to Rs 83.51 crores in 2023-24, facilitating the pilgrimage for low-income individuals.
- Jiyo Parsi Scheme: This scheme aims to counteract the decline in the Parsi population, resulting in over 400 births since its inception, with Rs 3 crores allocated in 2023-24.
- Pradhan Mantri Virasat Ka Samvardhan (PM VIKAS): This program integrates five existing schemes to promote skill development and the preservation of cultural heritage among minority communities.
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK): Focused on community infrastructure in areas with high minority populations, covering health, skill development, women's projects, water supply, sanitation, and sports.
These initiatives reflect a comprehensive approach towards fostering the growth and development of minority communities in India, ensuring their participation in various socio-economic spheres.
|
201 videos|842 docs|2245 tests
|





















