Weekly Current Affairs (1st to 7th September 2024) | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
FAA Grounds SpaceX’s Falcon 9 After Landing Failure
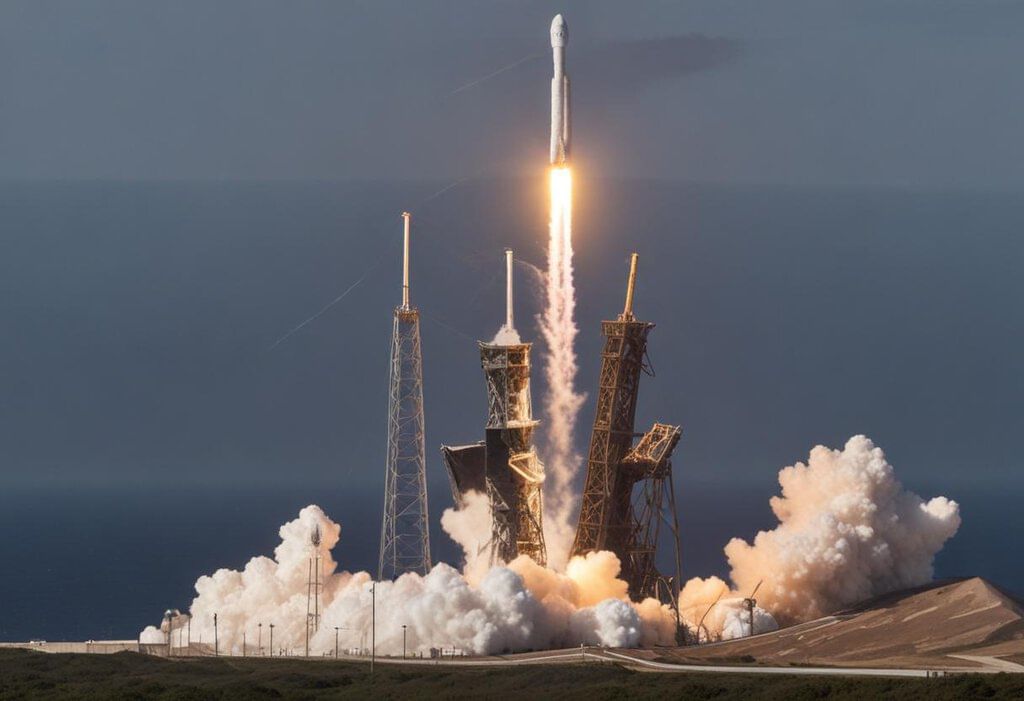

- FAA Order: The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) told SpaceX to stop using its Falcon 9 rocket on August 28, 2024. This happened after the rocket did not land correctly after launching Starlink satellites.
- Previous Incident: This was the second time the FAA had to intervene due to technical issues; a similar problem occurred in July 2023.
What is Falcon 9?
- Developer: The Falcon 9 was created by SpaceX, a company run by Elon Musk.
- Name Origin: It is named "Falcon 9" because it has nine engines in its first stage.
- Reusability: The rocket is special as it can be used multiple times.
Parts of Falcon 9:
- First Stage: Contains nine engines and is designed to land back on Earth for reuse.
- Second Stage: Has one engine and puts payloads like satellites or astronauts into orbit.
- Main Uses: Falcon 9 mainly sends satellites into space and transports astronauts to the International Space Station (ISS).
- Landing Failure: On August 28, 2024, after successfully launching satellites, the first stage of Falcon 9 tipped over and fell into the ocean instead of landing correctly.
- Previous Launch Issues: In July, another Falcon 9 mission faced problems with an engine failure, which left satellites in a bad orbit.
- FAA Investigation: The FAA is now investigating the landing failure but may still let SpaceX continue launching rockets while they find out what happened.
- Upcoming Missions: This is crucial because SpaceX has many launches planned, including one carrying NASA astronauts in September 2023.
Falcon 9's Achievements:
- In 2023, Falcon 9 completed 96 launches, more than any other country’s rockets.
- Comparison: For context, China completed 67 launches in the same year.
- Future Missions: Falcon 9 is set to take NASA astronauts to space in September and bring them back in February 2024.
History of Falcon 9:
- First launched in June 2010.
- Has completed over 180 missions.
- Name inspired by the Millennium Falcon from Star Wars and the nine engines in its first stage.
- Notable for being the first commercial rocket to reach orbit and carry astronauts to space.
Activists Urge Review of EU’s 2030 Emission Goals
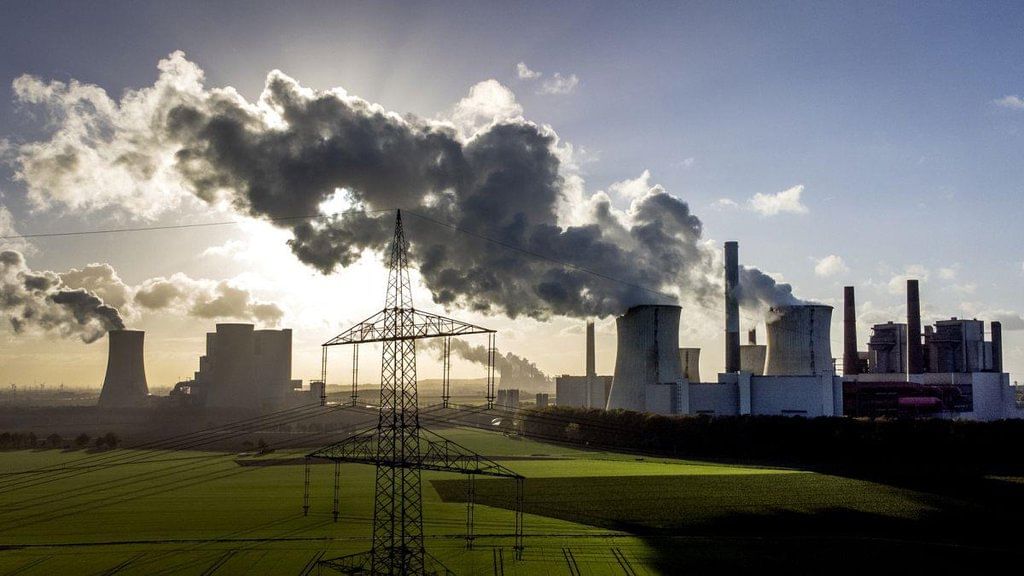

- Environmental activists, such as Climate Action Network and the Global Legal Action Network, are taking legal action against the European Commission. They argue that the European Union (EU) plans to cut emissions by 2030 are not sufficient to achieve the goals of the Paris Agreement.
- The Paris Agreement aims to keep global warming below 1.5°C, and the activists believe the EU's targets do not meet this crucial objective.
Background of the Case
- This case is important because it is the first time EU courts will assess if the EU's climate targets are adequate.
- Previously, the European Court of Human Rights has stated that countries need to set emission targets based on science to stay within the 1.5°C limit.
- This case will examine if the EU's targets are genuinely based on scientific evidence and if they meet the required standards to protect the environment.
What Legal Steps Have Been Taken?
- On August 23, 2024, the two non-profit groups requested the European Commission to review its Annual Emissions Allocations (AEA), which are the emission reduction goals for each EU country.
- After the Commission declined their request on December 14, 2023, the NGOs chose to bring the issue to the EU Court on February 27, 2024.
- The court has acknowledged the urgency of the climate crisis and has prioritized this case, with a hearing scheduled for 2025.
Emission Targets and Regulations
- The Annual Emissions Allocations are part of the EU Effort-Sharing Regulation, which mandates each EU nation to cut emissions by a certain amount by 2030.
- This regulation includes sectors such as transport, buildings, and agriculture.
- However, the activists claim that these targets have not been properly assessed through scientific research, raising concerns that they may not be adequate to meet climate goals.
Implications of Insufficient Targets
- The activists warn that the current EU emission targets could result in a global temperature rise of 3°C by 2100 if other nations adopt similar weak measures.
- Such a temperature increase could have severe impacts on the planet.
- To prevent this, the activists are advocating for a 65% reduction in emissions by 2030, believing this is essential for the EU to lead in the battle against climate change.
Navratna Status Granted to NHPC, SJVN, RailTel PSUs

Three major public sector companies in India, NHPC, SJVN, and RailTel, have been granted the prestigious “Navratna” status by the Government of India. They are the 18th, 19th, and 20th companies to receive this honor, which is a significant milestone for them. This status provides these companies with greater independence and authority to make decisions and grow their operations.
Eligibility Criteria
- Miniratna-I Status: The company must already hold the Miniratna-I status, which is an initial recognition for profitable public sector firms.
- Excellent Performance: The company must have earned an “Excellent” or “Very Good” rating in its performance evaluations (MoU rating) for at least three out of the last five years.
- Strong Financial Performance: The company must achieve at least 60 points in six important financial indicators, including Net Profit, Net Worth, and Earnings Per Share.
Investment Autonomy
With the Navratna status, NHPC, SJVN, and RailTel now enjoy enhanced freedom in making investment choices:
- Investment Autonomy: These companies can invest up to ₹1,000 crore or 15% of their net worth in a single project without needing government approval. They can also invest up to 30% of their net worth in a year as long as it does not exceed the ₹1,000 crore limit.
- Expanded Operational Capabilities: The Navratna status allows these companies to establish subsidiaries abroad, create joint ventures, and reorganize their structures to enhance efficiency and performance.
Overview of the Companies
- SJVN (Satluj Jal Vidyut Nigam Limited): SJVN, which became a Miniratna in 2008, oversees a large portfolio of 56,802 MW across 75 energy projects, including hydroelectric, solar, and wind power.
- NHPC (National Hydroelectric Power Corporation): Founded in 1975, NHPC is one of India's leading hydropower companies, with an installed capacity of 7,144.2 MW. The company aims to increase this capacity to 23,000 MW by 2032 and 50,000 MW by 2047, focusing on major projects in northeastern states like Assam and Arunachal Pradesh.
- RailTel: Established in 2000, RailTel provides telecom infrastructure and broadband services across India. The company manages over 55,000 kilometers of optical fiber networks along railway tracks, making it one of the largest telecom infrastructure providers in the country. RailTel also offers Wi-Fi services at railway stations and supports various government initiatives like Smart Cities and e-governance.
The announcement of the Navratna status has attracted attention to the shares of these companies. However, despite this positive development, the shares of SJVN, NHPC, and RailTel have recently seen significant drops, with SJVN and NHPC shares down by 18% and RailTel shares down by 21% from their highest values.
Who is Vithya Ramraj, Breaks 39-Year 400m Hurdles Meet Record?
63rd National Open Athletics Championships

- At the 63rd National Open Athletics Championships, held at the Sree Kanteerava Stadium in Bengaluru, Vithya Ramraj made history by breaking a 39-year-old record in the women’s 400m hurdles.
- She finished the race in 56.23 seconds, beating the old record of 56.80 seconds set by the famous Indian athlete P.T. Usha in 1985.
Significance of the Record
- Vithya’s achievement is important not only for herself but also in the history of Indian athletics.
- P.T. Usha, known as the Queen of Indian Track and Field, set a high standard, and by breaking her record, Vithya has increased her own reputation and highlighted Indian athletics.
Outstanding Performances in Men’s Events
- The championships showcased impressive performances in the men’s events.
- Nithin from Tamil Nadu broke the men’s 200m meet record with a time of 20.66 seconds, surpassing the record held by Animesh Kujur.
Other notable performances included:
- 800m: P. Mohammed finished in 1:48.10.
- 10,000m: Abhishek completed the race in 29:48.18.
- 400m hurdles: Aman clocked in at 50.52 seconds.
Highlights from the Women’s Events
- In the women’s events, Ancy Sojan shone in the long jump with a leap of 6.71 meters, earning the title of the best woman athlete of the championships.
Other key performances included:
- 200m: Nithya Gandhe finished in 23.51 seconds.
- 800m: Chanda clocked in at 2:01.16.
- 10,000m: Seema completed the race in 33:56.86.
Awards and Overall Achievements
- The championships concluded with several athletes being recognized for their exceptional performances.
- Vithya Ramraj (400m hurdles) and Nithin (200m) were highlighted as standout athletes of the event.
- The team championships were claimed by the Railways in the women’s category and by Services in the men’s category.
- Railways also won the overall title.
West Bengal’s ‘Aparajita’ anti-rape Bill

The West Bengal Assembly has recently approved the Aparajita Woman and Child Bill. This new law aims to provide better protections for women and children, especially due to increasing worries about sexual crimes. The bill received full support from all members of the assembly, including the opposition, highlighting the importance and urgency of these actions.
Key Provisions of the Bill
- Life Sentence Without Parole: Individuals found guilty of rape will face life imprisonment with no opportunity for parole, meaning they will remain in prison for their entire lives. They will also be required to pay a financial penalty.
- Capital Punishment: The bill establishes the death penalty for offenders whose actions result in the death of the victim or cause severe, permanent disabilities.
- Revisions to the POCSO Act: The bill introduces strict changes to the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, which protects children from sexual abuse, aiming to enhance the safety and rights of minors.
- Aparajita Task Force: A special task force will be formed to accelerate the legal process in sexual crime cases. This task force aims to ensure that charges are filed within 21 days of the initial investigation and that trials are completed within 30 days.
- Enhanced Security for Medical Personnel: The bill allocates ₹120 crores to improve safety for doctors and nurses, particularly during their commutes, in response to the growing violence against medical staff.
- Acid Attack Convictions: Those convicted of acid attacks will also face life imprisonment without the chance of parole, underscoring the seriousness of these offenses.
Background to Legislation
The need for this bill became clear after a tragic event where a female medical worker was brutally raped and killed. This horrific crime sparked widespread public anger and prompted the assembly to act quickly. The bill was introduced by Law Minister Moloy Ghatak as a strong reaction to the ongoing violence against women and children in West Bengal.
Punjab Assembly Passes Law to Control Illegal Colonies

The Punjab State Assembly approved a new law called the Punjab Apartment and Property Regulation (Amendment) Act, 2024 on September 3, 2024. This law was created to tackle the increasing issue of illegal colonies in Punjab. Illegal colonies are places where homes or buildings are constructed without the necessary government permission. The main goal of this new law is to improve the management of these areas and stop the further growth of illegal colonies.
Reasons for the Amendment- Control Illegal Colonies: The law introduces new rules to prevent the establishment of unauthorized developments, or colonies built without following the correct procedures.
- Support Small Property Owners: The law simplifies the process for small landowners to register their properties, giving them legal protection.
Punjab's Chief Minister, Bhagwant Mann, commended the new law, describing it as a crucial step in safeguarding the interests of ordinary citizens. He highlighted that this amendment is essential for public welfare, especially given the ongoing issues with illegal colonies in the state.
Penalties for Law Violations- The amendment includes strict penalties for those who violate property regulations. This means that anyone attempting to build or sell property in an illegal colony could face serious consequences.
- This enforcement will make it more difficult for illegal colonies to expand.
The original Punjab Apartment and Property Regulation Act was established in 1995 to regulate real estate activities in Punjab. It requires builders and developers to register with the government and creates a regulatory authority to ensure transparency in property transactions. The law also protects buyers by ensuring that common areas and facilities are maintained properly.
- Additionally, it provides a mechanism for resolving disputes over property ownership and management, which helps to boost consumer confidence in the real estate market.
Himachal Pradesh Assembly Introduces Zero Hour

The Himachal Assembly is set to introduce Zero Hour, as announced by Speaker Kuldeep Singh Pathania. This decision comes after discussions about the need to create Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) before implementing it.
What is Zero Hour?
- Zero Hour is a time during parliamentary sessions when members can discuss urgent public issues that are not on the official agenda.
- This period occurs after Question Hour and gives lawmakers a chance to address important matters that need immediate attention.
How Are Issues Raised During Zero Hour?
- Members can bring up urgent issues during Zero Hour, but they must receive approval from the Speaker.
- The Speaker decides which issues can be discussed, and the government is not obligated to respond immediately to these concerns.
Government and Opposition Views on Zero Hour
- Government’s Position: The Parliamentary Affairs Minister, Harshwardhan Chauhan, expressed worries that the decision to introduce Zero Hour was made without consulting the government.
- Chief MinisterSukhvinder Singh Sukhu agreed with introducing Zero Hour but emphasized the need for clear SOPs to keep discussions orderly.
- Opposition’s Viewpoint:Leader of the OppositionJai Ram Thakur supported Zero Hour but pointed out the necessity for clear rules to ensure that every member has a chance to raise public issues.
Importance of SOPs
- Creating SOPs is crucial to manage what types of issues can be discussed during Zero Hour.
- These rules will help keep discussions focused, efficient, and brief.
- The SOPs for Himachal’s Zero Hour are expected to be similar to those in the Indian Parliament, making sure the practice runs well.
Duration and Structure of Zero Hour
- Some members, like Randhir Sharma, suggested that Zero Hour should last for one hour.
- This would provide lawmakers more time to discuss significant issues affecting the public.
- This proposal aims to ensure that enough time is available to address urgent concerns effectively.
Zero Hour in the Himachal Assembly will enable members to raise urgent public issues, but clear SOPs are being developed to ensure that discussions are orderly and productive. Both the government and the opposition recognize the importance of this practice while stressing the need for clearly defined rules.
India, South Africa Sign Submarine Rescue Cooperation Agreement
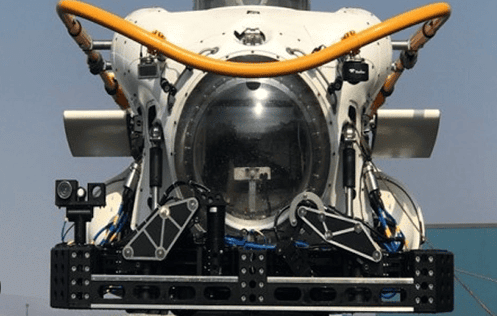
On September 4, 2024, the Indian and South African navies signed an agreement to enhance support for submarine rescues. This deal aims to protect South African submarine crews during emergencies and underscores the importance of collaboration between the two nations.
Key Features of the Agreement
- The agreement allows the Indian Navy to utilize its Deep Submergence Rescue Vehicle (DSRV) in submarine emergencies.
- The DSRV is a specialized vehicle capable of diving deep into the ocean to rescue individuals trapped inside submarines.
- This cooperation will improve both navies' readiness for emergencies and shows their dedication to maritime safety.
- In September 2023, three members of the South African navy lost their lives in an incident involving the submarine SAS Manthatisi.
- This tragic event highlighted the need for improved safety measures.
- As one of the few African nations with a submarine fleet, South Africa's agreement with India ensures access to essential tools and support to avoid similar tragedies in the future.
- India possesses two DSRVs, originally acquired from the UK, which became operational in 2018 and 2019.
- These vehicles can dive to depths of 650 meters and can rescue up to 14 people at a time.
- Each DSRV is equipped with a remotely operated vehicle (ROV) for underwater tasks.
- In 2018, one of India's DSRVs set a national record by diving 666 meters underwater.
- The DSRVs are designed for easy transport by road, sea, or air, ensuring quick deployment during emergencies.
- India has a history of sharing its submarine rescue expertise with other nations.
- For instance, it has a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Singapore to share submarine rescue techniques.
- India aims to enhance maritime security throughout the Indian Ocean Region by providing its rescue capabilities to neighboring countries.
- In April 2021, India deployed one of its DSRVs to assist in the search for the missing Indonesian submarine KRI Nanggala.
- Although the DSRV was called back after the Indonesian Navy located the wreckage, the mission demonstrated India's readiness to assist other nations in need.
The agreement between the Indian and South African navies strengthens their partnership and commitment to maritime safety, emphasizing their collaboration to protect submarines and enhance security in the Indian Ocean Region.
New Antarctic Dragonfish Species Discovered by Researchers
 Overview of Antarctic Waters
Overview of Antarctic Waters
- Antarctica's waters are home to a wide variety of marine life.
- Many species are still unknown to researchers.
Identification of the New Species
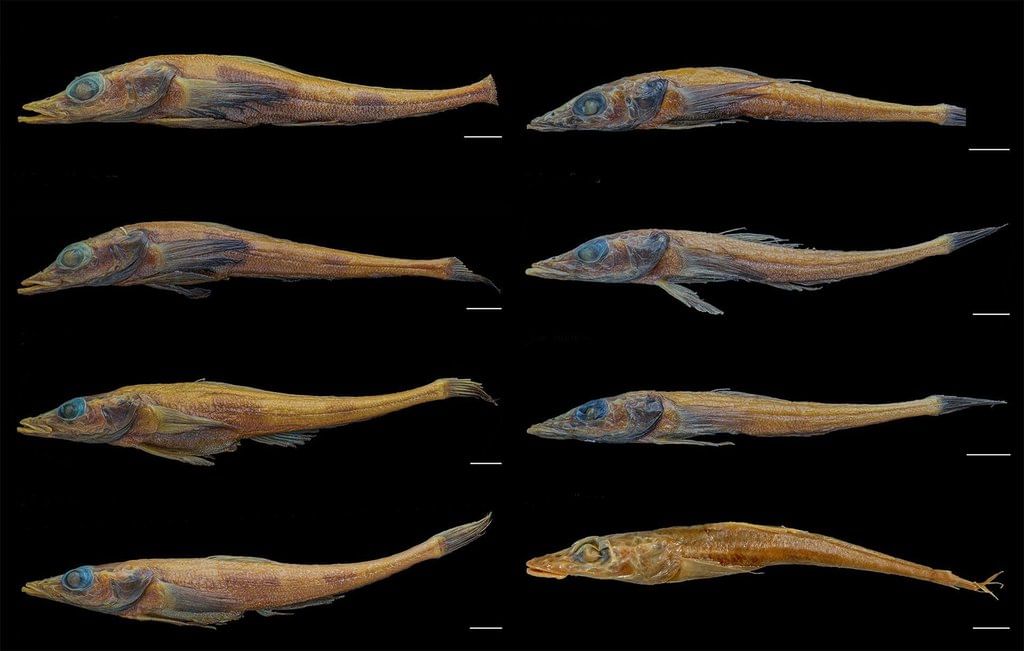
- Researchers from William & Mary’s Virginia Institute of Marine Science found a new fish species in the Antarctic Peninsula.
- This fish is called the Banded Dragonfish (Akarotaxis gouldae).
- The fish was discovered while studying small sea organisms known as zooplankton.
- Initially, scientists thought it was another species called Akarotaxis nudiceps.
As the fish grew, researchers noticed it had unique features:
- Two dark vertical bands.
- Other special traits that confirmed its identity.
Naming the New Species
- The Banded Dragonfish is named after the Laurence M Gould, an Antarctic research ship that contributed to scientific studies.
- This ship has been retired but played an important role in exploration.
- The fish has a slim body, a wide snout, a long mouth, and large, oval eyes.
- Its most noticeable features are the two dark bands on its sides.
Research Methods
- Scientists employed genetic testing and a technique called phylogenetic analysis to explore the fish's evolution.
- They discovered that Akarotaxis gouldae and Akarotaxis nudiceps became different species approximately 780,000 years ago.
- This separation likely happened due to isolated, icy conditions, leading them to evolve separately.
- The Banded Dragonfish is found only in the deep waters of the western Antarctic Peninsula.
- Studying this fish is difficult because it lives in very deep and remote ocean areas.
Importance of the Discovery
- The discovery of Akarotaxis gouldae shows the hidden diversity of life in Antarctic waters.
- It suggests that many more unknown species may still be waiting to be found as scientists continue their research in this less-explored region.
Facts About Antarctic Dragonfish
- Habitat: Resides in very deep Antarctic waters, reaching depths of up to 2,000 meters.
- Body: Features a transparent body to blend in with its surroundings and has special proteins in its blood to prevent ice formation.
- Diet: Feeds on small fish and krill.
- Size: Can grow up to 38 cm long.
- Bioluminescence: Its body can glow in the dark, aiding in communication and evasion from predators.
- Unique Features: Lacks scales and possesses long teeth for capturing prey.
Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC)

- Chinese President Xi Jinping announced that China will provide $51 billion to assist African nations during the Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC).
- The funding will be used to support 30 major infrastructure projects, which may include building roads, bridges, power plants, and other essential facilities in African countries.
- This decision shows China's current economic strategy as it deals with challenges at home while aiming to maintain its strong ties with Africa.
What is FOCAC?
- The Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC) was established in 2000 to enhance the partnership between China and African nations.
- The forum meets every three years, sometimes in China and other times in an African country.
- Currently, 53 African nations, except for Eswatini, are members of this forum.
- The African Union Commission is also involved, helping to guide discussions and future plans.
Significance of FOCAC
- FOCAC is a vital platform where African leaders can discuss important political and economic issues directly with China.
- It allows both sides to agree on joint projects and future actions.
- The upcoming 2024 FOCAC summit has the theme “Joining Hands to Advance Modernization and Build a High-Level China-Africa Community with a Shared Future,” aimed at improving collaboration between the two regions.
Evolution of China-Africa Relations
- China’s relationship with Africa began in the 1950s when it supported African nations in their fight for independence from colonial rule.
- One of its significant contributions was the construction of the Tanzania-Zambia railway in the 1970s.
- Over the years, China has become Africa's largest trading partner, with trade reaching $282 billion in 2023.
- This trade mainly involves raw materials from Africa and manufactured goods from China.
Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)
- Africa plays a crucial role in China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), which aims to build new economic and cultural connections between countries, similar to the ancient Silk Road.
- In the past decade, China has invested over $120 billion in African infrastructure projects through the BRI.
Concerns and Criticisms
- Although China’s investments in Africa are significant, some critics express concerns about debt trap diplomacy.
- This refers to the idea that some African countries may struggle to repay loans, leading to fears that China could take control of their assets.
- However, some believe these issues are more about how African governments manage their finances rather than a specific strategy by China.
FOCAC 2024’s Significance
- The 2024 FOCAC summit will be crucial as China addresses its slowing economy after the COVID-19 pandemic and loan defaults from countries like Zambia and Ghana.
- China may focus more on smaller projects and green technologies, while African nations are likely to request more loans despite their existing debt challenges.
[Intext Question]
India Commissioned Advanced Nuclear Submarine INS Arighaat
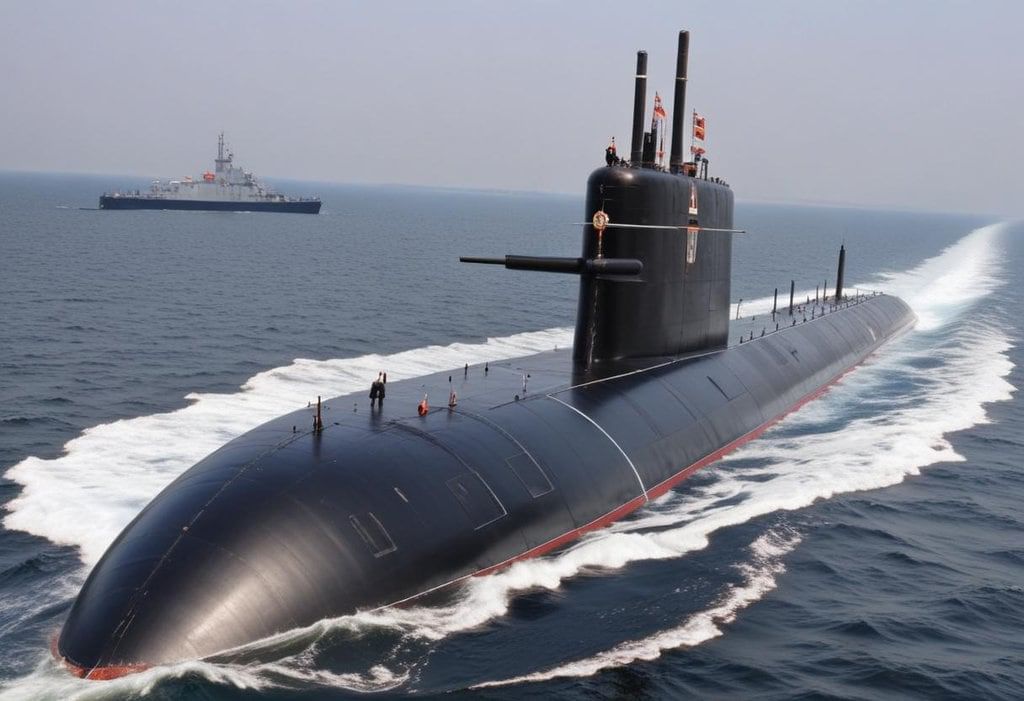

India has recently launched its second nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine (SSBN), known as INS Arighaat. This development significantly enhances India's naval strength, following the commissioning of its first SSBN, INS Arihant, in 2016.
India's Submarine Program:
The journey to build nuclear-powered submarines in India started with INS Arihant, which was the country's first of its kind. The introduction of INS Arighaat marks a major step forward, showcasing advancements in technology and local manufacturing abilities.
Key Features of INS Arighaat
- Enhanced Missile Range: INS Arighaat is armed with missiles that can reach targets over 3,500 km. This is a significant upgrade from the 750 km range of INS Arihant.
- Indigenous Content: A significant portion of INS Arighaat was designed and built in India, promoting the country's aim for greater self-sufficiency in defense technology.
- Advanced Technology: The submarine incorporates new and advanced designs, reflecting the progress India has made in naval technology.
Strategic Importance:
Both INS Arihant and INS Arighaat play vital roles in India's national security. They serve as crucial deterrents against potential threats, enhancing India's strategic position in regional waters.
The Indian Navy plans to expand its fleet of nuclear submarines further. A third submarine is set to be commissioned early next year, demonstrating India's ongoing commitment to strengthening its maritime defense and security.
More About INS Arihant:
- INS Arihant is India's first nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine, commissioned in 2016.
- It is 111 meters long and weighs around 6,000 tons.
- The submarine can carry 12 K-15 Sagarika missiles, with a range of 750 km.
- Designed for stealth, it features a double-hulled structure.
- Its nuclear reactor was developed under the Indian Navy's Advanced Technology Vessel program.
- INS Arihant is a key component of India's nuclear triad, which helps deter regional threats.
India Successfully Launches Agni-4 Ballistic Missile in Odisha
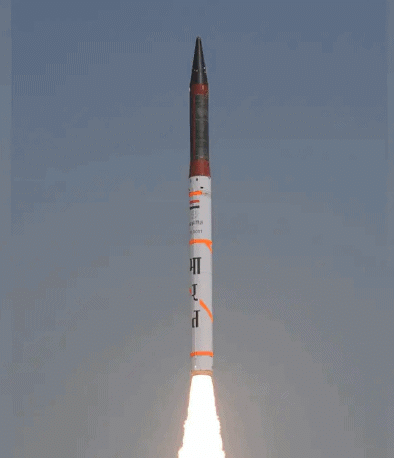
India recently achieved a successful test of the Agni-4 ballistic missile from the Integrated Test Range (ITR) located in Chandipur, Odisha. This test was conducted by the Strategic Forces Command (SFC), confirming the missile's performance and technical capabilities.
What is Agni-4?
- The Agni-4 is an Intermediate Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM) developed by India. It plays a crucial role in enhancing India's defense capabilities. The missile is crafted to improve India's ability to respond to threats with great accuracy and effectiveness. The successful launch of Agni-4 demonstrates that the missile functions as intended. This accomplishment showcases India's advancements in missile technology and its ability to carry out precise and dependable strikes.
Recent Developments in Missile Testing
Prior to the Agni-4 test, there were several significant missile tests:
- On April 4, 2024, India successfully tested the Agni-Prime missile, meeting all its goals and displaying reliable performance.
- In June 2023, India executed its first night launch of the Agni-Prime, proving its capabilities under different conditions.
These missile tests reflect India’s commitment to modernizing its defense systems and enhancing its strategic deterrence. This effort is vital for maintaining stability in the region and safeguarding against potential threats.
More About Agni-4
- Range: Agni-4 can travel between 3,000 to 4,000 kilometers.
- Payload: It can carry nuclear warheads weighing up to 1,000 kg.
- Design: It features a two-stage solid propellant system, which enhances its accuracy and effectiveness.
- Mobility: The missile is road-mobile, which improves its survivability.
- Guidance: It employs advanced systems, including inertial navigation and GPS, for precise targeting.
- Development: Agni-4 is part of India’s Integrated Missile Development Program, aimed at strengthening strategic deterrence. It was first tested in November 2011.
|
164 videos|800 docs|1156 tests
|
FAQs on Weekly Current Affairs (1st to 7th September 2024) - General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce
| 1. What led to the FAA grounding SpaceX's Falcon 9? |  |
| 2. What are the main goals of the EU's 2030 emission targets? |  |
| 3. What is Navratna status and why was it granted to NHPC, SJVN, and RailTel? |  |
| 4. Who is Vithya Ramraj and what record did she break? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of West Bengal’s ‘Aparajita’ anti-rape Bill? |  |
















