Weekly Current Affairs (22nd to 31st December 2024) Part - 2 | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
20 Years of Indian Ocean Tsunami 2004
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- December 26, 2024, marks the anniversary of the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami, a significant historical event that reshaped disaster preparedness protocols worldwide.
Key Takeaways
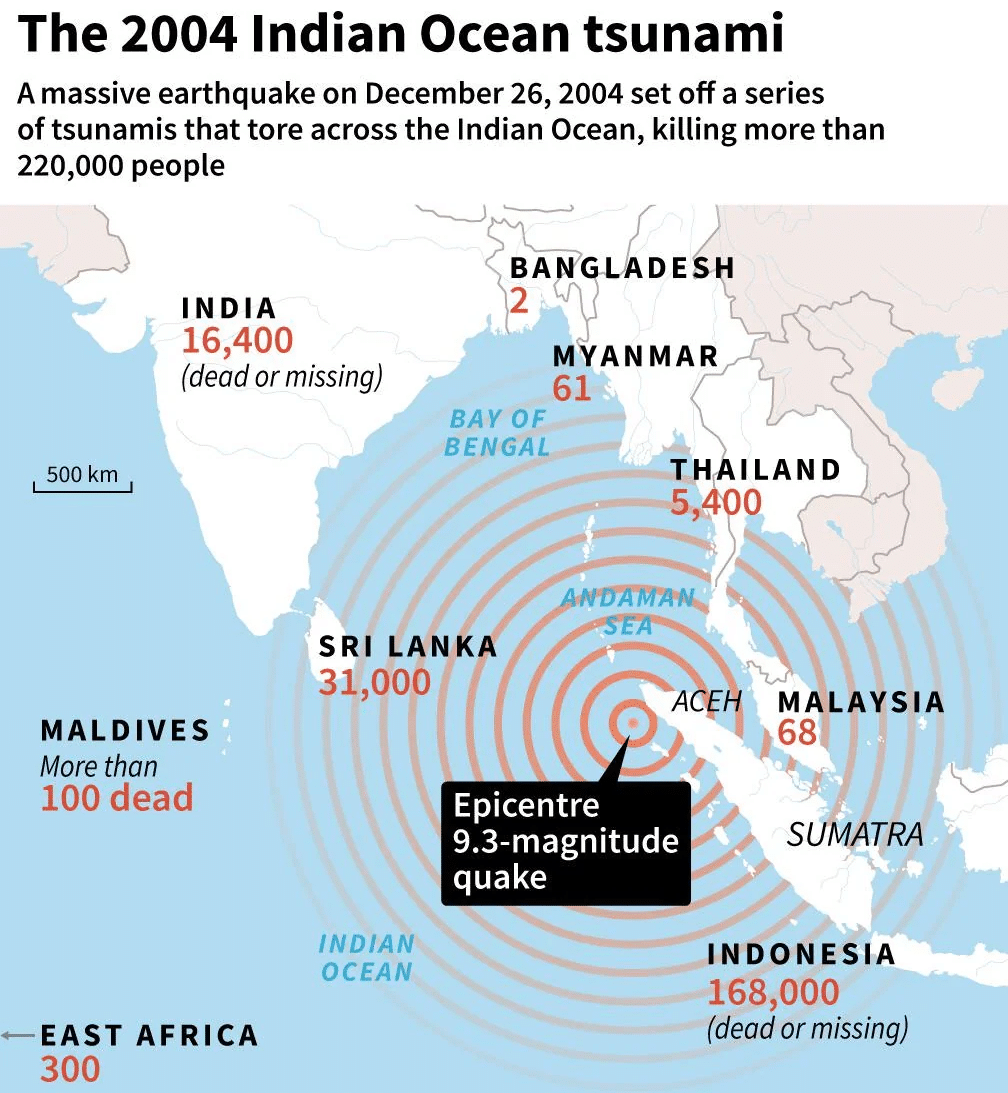
- The 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake had a magnitude of 9.1, making it the third-largest earthquake recorded globally since 1900.
- It caused over 227,000 deaths and displaced more than 1.7 million people, highlighting the devastating impact of tsunamis.
- Post-tsunami, India established the Indian Tsunami Early Warning Centre (ITEWC) to improve disaster response.
Additional Details
- Origin and Cause: The earthquake originated in the Sunda Trench, where the Indo-Australian plate subducts beneath the Burma microplate, affecting a vast area of 1,300 km from Sumatra to the Coco Islands.
- The tsunami's tremors were felt across multiple countries, including Indonesia, India, and Thailand, with significant destruction reported at the Indian Air Force base in Car Nicobar.
- Lessons for India: India was unprepared for such a large-scale tsunami event, as past occurrences in 1881 and 1883 were minor. This prompted significant advancements in disaster risk reduction.
- Despite progress in reducing mortality rates from cyclones, the infrastructural damage remains a concern, such as the estimated Rs 616 crore damage caused by Cyclone Dana in 2024.
What Initiatives Were Taken After the 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami to Minimise Damages?
- Early Warning Systems: Established in 2007, the ITEWC operates from Hyderabad, using a network of seismological stations and tidal gauges to issue early tsunami warnings.
- Real-time Monitoring: India developed advanced real-time ocean monitoring systems capable of issuing alerts in as little as 10 minutes.
- Technological Advancements: The early warning systems now utilize better algorithms and supercomputers for rapid and accurate modeling of tsunami behavior.
- Tsunami Geology Research: Research has been conducted to uncover historical tsunami events, enhancing understanding of past occurrences and risks.
- Global Cooperation: The tsunami warning system has improved global coordination, with UNESCO tasked with establishing global tsunami warning services across ocean basins.
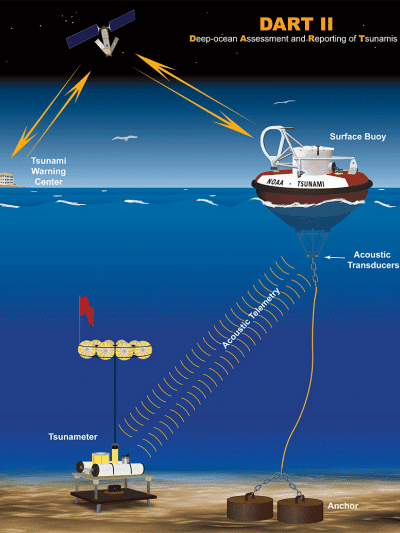
The 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami underscored critical gaps in early warning systems, leading to significant advancements in both global and regional preparedness. The establishment of the ITEWC and enhanced monitoring systems have drastically improved disaster responses, although challenges remain, especially in developing nations.
Mains Question:
- Discuss the initiatives taken post-2004 Indian Ocean tsunami to improve early warning systems.
EAC-PM Report on Domestic Migration
 Why in News?
Why in News?
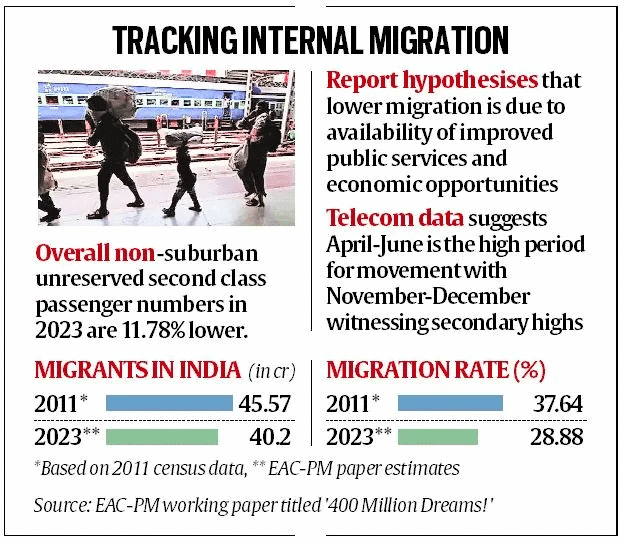
- The Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM) has released a working paper titled "400 Million Dreams!" which highlights a significant 12% decline in domestic migration since 2011. This change is indicative of broader socio-economic shifts and is largely attributed to improved economic opportunities and infrastructure in traditionally high migration areas.
Key Takeaways
- The number of domestic migrants in India has decreased by 11.78%, with the estimated number of migrants in 2023 standing at 40.20 crore, down from 45.58 crore reported in Census 2011.
- The migration rate has fallen from 37.64% of the total population in 2011 to 28.88% in 2023, indicating a slowdown in migration.
Migration Dynamics
- Growing Migrant States: States like West Bengal, Rajasthan, and Karnataka have seen the highest growth in attracting migrants.
- Declining States: Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh have experienced a reduction in their share of total migrants.
- Urban Concentration: Major urban agglomerations such as Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Bengaluru, and Kolkata remain primary destinations for migrants.
- Top Districts: Bengaluru Urban and Howrah are among the districts attracting the most migrant arrivals.
- Emerging Migration Routes: Key migration corridors include Uttar Pradesh-Delhi, Gujarat-Maharashtra, Telangana-Andhra Pradesh, and Bihar-Delhi.
Seasonal Migration Trends
- Migration peaks occur from April to June, with secondary peaks in November-December, likely due to festivals and marriages.
- January sees the lowest levels of migration, indicating a seasonal pattern.
Reasons for Decline in Migration
The decline in domestic migration is attributed to improved local economic conditions through schemes like:
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY)
- Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY)
- Ayushman Bharat - Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY)
- Digital India initiatives enhancing education and connectivity
Implications of Decreased Domestic Migration
Economic Implications:
- Labor shortages may arise in certain regions, particularly in sectors reliant on migrant workers.
- Increased wages in these areas could lead to higher production costs, affecting competitiveness.
- Improved opportunities in smaller cities may help reduce income inequality between urban and rural areas.
- Local economies may benefit as the workforce remains in their home regions.
Social Implications:
- Increased demand for quality education, healthcare, and infrastructure in rural and semi-urban areas.
- Limited access to better employment and education opportunities in urban centers.
- Women may face prolonged economic dependence if male family members have fewer migration opportunities.
Demographic Implications:
- Reduced migrant inflow could slow urbanization, impacting economic dynamism in cities.
- Declines in population growth in metro areas may affect their consumer base and economic activities.
Policy and Governance Implications:
- Lower migration rates may ease urban pressures, reducing issues like overcrowding and strain on public services.
- National employment schemes like Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) may need scaling up to address reduced employment migration.
- Increased rural residency may heighten pressure on local land and water resources, leading to unsustainable agricultural practices.
Mains Question:
- Critically analyze the socio-economic implications of declining domestic migration in India. How does it affect regional development and urbanization trends?
Ken-Betwa Link Project
 Why in News?
Why in News?
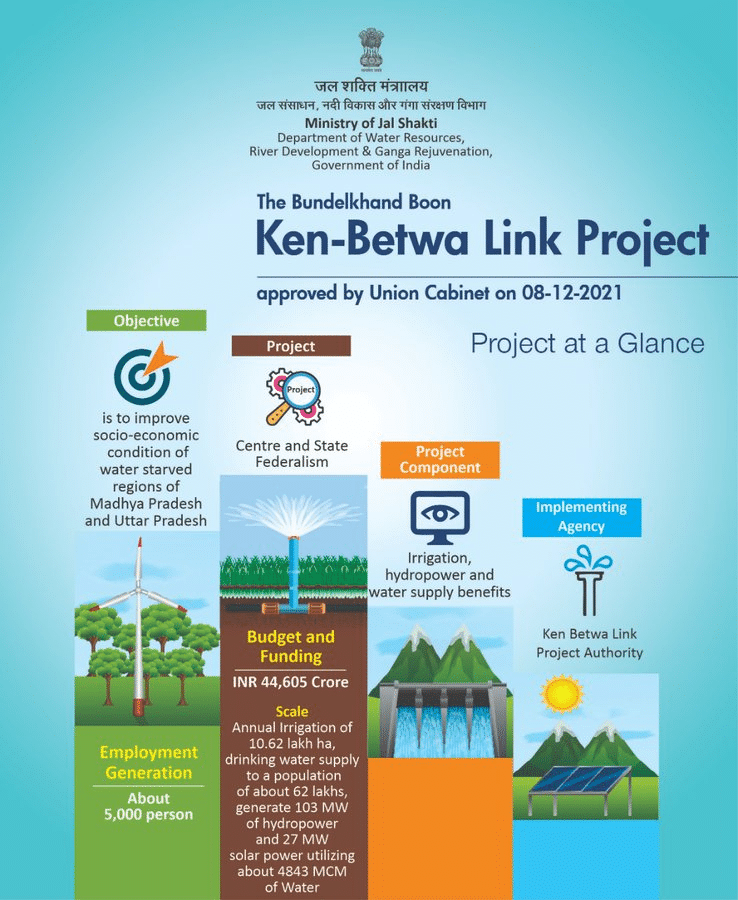
- Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone for the Ken-Betwa Link Project (KBLP) in Khajuraho, Madhya Pradesh. This Rs 45,000 crore initiative is part of the National Perspective Plan (NPP) for interlinking rivers, aimed at addressing water scarcity in Bundelkhand.
Key Takeaways
- The KBLP is India's first initiative under the NPP, formulated in 1980.
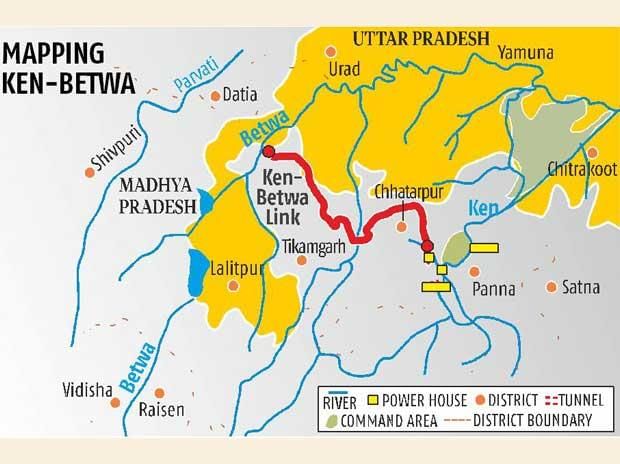
- It aims to transfer surplus water from the Ken River in Madhya Pradesh to the Betwa River in Uttar Pradesh.
- The project consists of two phases: Phase I focuses on the Daudhan Dam complex, while Phase II involves the Lower Orr Dam and related projects.
- Benefits include irrigation for 6.3 lakh hectares and drinking water supply for 62 lakh people.
- Environmental concerns have been raised regarding the impact on the Panna Tiger Reserve.
Additional Details
Phases of the Project:
- Phase I: Construction of the Daudhan Dam complex, low-level and high-level tunnels, Ken-Betwa link canal, and powerhouses.
- Phase II: Development of the Lower Orr Dam, Bina Complex Project, and Kotha Barrage.
Benefits:
- Irrigation for 6.3 lakh hectares annually.
- Drinking water supply for 62 lakh people.
- Includes provisions for hydropower generation (100 Megawatt) and solar energy (27 Megawatt).
Importance for Bundelkhand: The project enhances drinking water access, boosts agriculture, and fosters regional development, reducing migration pressures.
Environmental Concerns: The project may submerge over 10% of the Panna Tiger Reserve, leading to loss of wildlife habitats and the felling of over 23 lakh trees.
Government Response: Assurances have been made regarding wildlife preservation and mitigation measures for the local ecosystem.
What is the National Perspective Plan (NPP) for Interlinking Rivers?
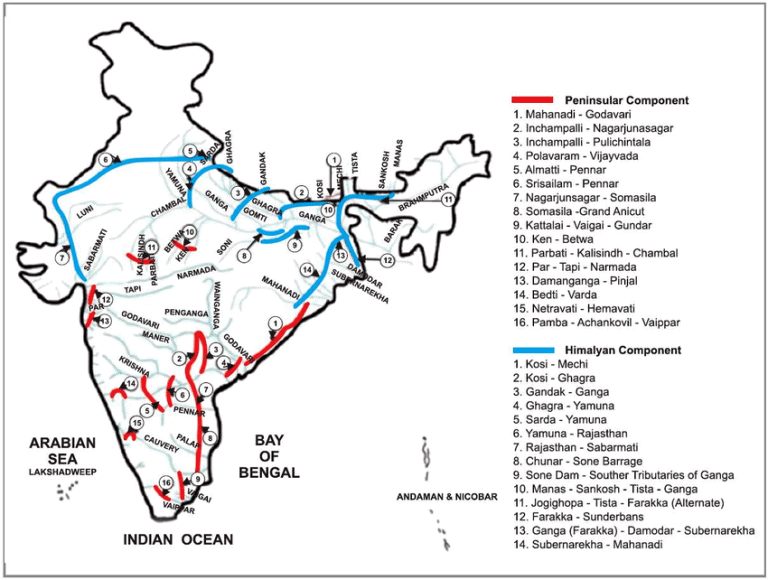
Formulated in 1980 by the Ministry of Irrigation (now Ministry of Jal Shakti), the NPP aims to develop water resources through the inter-basin transfer of water. The National Water Development Agency (NWDA) has been entrusted with the work of interlinking rivers under the NPP.
Components
- The plan has two main components:
- Himalayan Rivers Development
- Peninsular Rivers Development
Link Projects: There are 30 link projects proposed, with 16 under the Peninsular Component and 14 under the Himalayan Component.
Significance
- Addresses water shortages in states like Rajasthan, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
- Improves irrigation, boosts agricultural productivity, and enhances food security.
- Promotes inland waterways for freight movement and helps reduce groundwater depletion.
 Mains Question:
Mains Question:
- Evaluate the National Perspective Plan for river interlinking in India and its implications for sustainable water management.
Tau Protein and Alzheimer's Disease
Why in News?
- A recent study has indicated that inhibiting the stress response pathway in the brain could potentially reverse symptoms of Alzheimer's disease by preventing the accumulation of tau proteins.
Key Takeaways
- Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder leading to memory loss, cognitive decline, and behavioral changes.
- It is the leading cause of dementia, accounting for 60-80% of dementia cases.
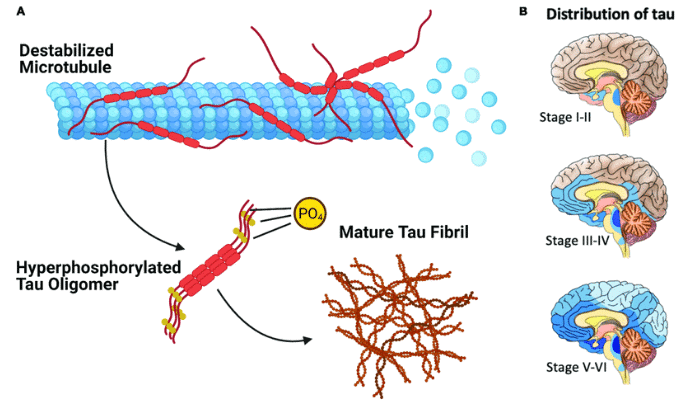
- Tau proteins play a crucial role in stabilizing neurons, but their accumulation leads to the formation of neurofibrillary tangles, disrupting neuron communication.
- Blocking the synthesis of toxic lipids may prevent tau buildup and offer a potential reversal of symptoms.
Additional Details
- Tau Proteins: These proteins are essential for maintaining the structure of neurons. In Alzheimer's, they misfold and accumulate, forming tangles that are detrimental to neuron function.
- Role of Microglia: Microglia are brain immune cells that can either protect neurons or contribute to neurodegeneration by producing toxic lipids, especially when activated by stress response pathways.
- Current treatments for Alzheimer's primarily delay cognitive decline but do not stop the progression of the disease.
- Targeting the microglial stress response pathway may lead to more effective therapies in the future.
This emerging research highlights the potential for new therapeutic strategies aimed at the stress response mechanisms in the brain, which could lead to significant advancements in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Impact of Covid-19 Pandemic
Why in News?
- Recently, the world marked five years since the outbreak of a pandemic that caused millions of deaths, unprecedented economic disruptions, and significant social challenges. Although much of the immediate crisis has passed, its lingering effects on global economies, policies, and societies continue to shape the world profoundly.
Key Takeaways
- The pandemic led to a sharp contraction in economic growth and significant public debt increases.
- Trust in institutions declined globally, impacting political dynamics and governance.
- Work models have shifted towards hybrid and gig work, emphasizing flexibility and work-life balance.
Additional Details
Economic Impact:
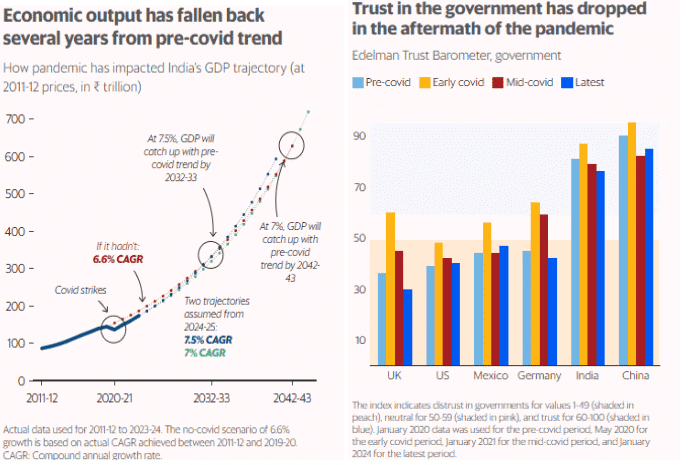
- India's GDP growth rate contracted to -5.8% during 2020-21, down from a pre-Covid average of 6.6%.
- Post-pandemic recovery showed growth rates of 9.7%, 7%, and 8.2% from 2021 to 2023, yet the economy remains behind its pre-pandemic trajectory.
- Global GDP contracted by 3.1% in 2020, with a USD 4.7 trillion shortfall projected in 2023.
Debt Explosion:
- Governments worldwide saw the largest spike in public debt in two decades during the pandemic.
- High debt burdens are limiting fiscal flexibility and diverting resources from essential sectors like health and education.
Social and Political Dynamics:
- The Edelman Trust Barometer showed a significant decline in public trust in institutions.
- A 2023 Pew survey found that 74% of respondents felt disconnected from elected officials.
- Anti-incumbency sentiment surged, resulting in losses for incumbents in 40 out of 54 elections in 2024.
Changing Work Models:
- Hybrid work became popular, with 42% of Indian job seekers in 2024 prioritizing flexible hours.
- Gig work and e-commerce platforms have allowed workers to monetize hobbies and explore alternative income streams.
To navigate the post-pandemic landscape effectively, countries must focus on strategic investments and collaboration.
Way Forward
- Economic Recovery: Invest in key growth sectors, such as green energy and technology, to stimulate GDP recovery.
- Global Collaboration: Strengthen international trade alliances to enhance supply chain resilience and reduce protectionism.
- Improving Trust in Governance: Promote transparency and accountability in policymaking to rebuild public trust.
- Workforce Adaptation: Encourage hybrid and gig work models through legal frameworks and social safety nets.
- Social Equity: Expand healthcare access and ensure equitable distribution of resources globally.
Mains Question:
- How has the Covid-19 pandemic influenced divergence in global GDP growth trajectories, and what policies should India adopt to ensure a sustainable recovery trajectory?
Trends and Progress of Banking in India 2023-24
Why in News?
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has raised alarms over the increasing reliance on unsecured lending and private credit, calling for enhanced vigilance in its annual Trends and Progress of Banking in India 2023-24 report. Despite the steady decline in gross non-performing assets (GNPA) and sustained profitability of banks, the central bank emphasized the need to address emerging risks in the financial ecosystem.
Key Takeaways
- Decline in NPAs: GNPAs reached a 13-year low of 2.7% in March 2024, further dropping to 2.5% by September 2024.
- Profitability: The return on assets (RoA) was 1.4% in the first half of 2024-25, and return on equity (RoE) at 14.6% in FY24.
- Rising Share of Unsecured Loans: The share of unsecured loans in SCBs' total credit rose to 25.5% in March 2023.
- High Employee Attrition: Employee attrition rates surged to 25% over the past three years.
- RBI’s Recommendations: Suggested strategies for banks to reduce attrition and improve compliance with credit appraisal processes.
Additional Details
- Return on Assets (RoA): Measures a business's profitability relative to its total assets.
- Return on Equity (RoE): Measures a company's annual return (net income) relative to its total shareholders' equity.
- Capital Adequacy Ratios (CRAR): Indicates a bank's ability to absorb losses and ensure stability.
- Dark Patterns: Unethical UI/UX tactics designed to deceive users into unintended actions, such as hidden costs and difficult cancellation options.
The rise of unsecured loans poses significant risks to both the banking sector and the broader economy. As defaults increase, financial strain on banks and non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) may escalate, potentially leading to higher inflation and reduced consumer confidence. To address these pressing challenges, the RBI must focus on tightening lending practices, enhancing consumer protection, improving regulatory oversight, and proactively managing asset quality.
India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement

Why in News?
The India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (Ind-Aus ECTA) has reached a significant milestone, completing two years of operation. This period has seen remarkable growth in bilateral trade and economic cooperation between the two nations. Both countries are now focused on further enhancing this collaboration, setting an ambitious target of reaching AUD 100 billion in trade by 2030.
Key Takeaways
- The Ind-Aus ECTA is a major trade agreement signed in April 2022 and ratified in November 2022.
- Over 85% of Australian goods can be exported to India tariff-free, increasing to 90% by January 2026.
- India benefits from tariff-free imports of 96% of its goods from Australia, projected to reach 100% by 2026.
- The agreement includes commitments across 135 sub-sectors in services, enhancing trade in various industries.
- It is expected to create 1 million jobs in India, facilitating skill exchange and employment opportunities.
Additional Details
- Tariff Reductions: The ECTA significantly reduces tariffs, benefiting both nations through cheaper raw materials and lower consumer costs.
- Access to Key Markets: India gains preferential access to Australia's market, while Australian businesses can tap into India's labor-intensive sectors like textiles and agriculture.
- Geopolitical Importance: The ECTA strengthens strategic partnerships in initiatives like the Quad and the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework, aligning both nations’ economic and geopolitical interests.
- Challenges: Despite progress, India faces low competitiveness in Australia and must address non-tariff barriers affecting trade.
The Ind-Aus ECTA marks a pivotal step in enhancing trade relations between India and Australia, fostering economic growth and collaboration. As both nations work towards the ambitious AUD 100 billion trade target by 2030, the agreement lays a strong foundation for a resilient and dynamic economic partnership.
|
164 videos|626 docs|1132 tests
|
















