Worksheet: Challenges of Nation Building | Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: India became independent on the midnight of __________, 15 August 1947.
Q2: The speech given by Jawaharlal Nehru on independence day is known as __________.
Q3: India was divided into three parts: British India, Pakistan, and __________.
Q4: The leader of the North-West Frontier Province during partition was __________, popularly known as "Frontier Gandhi."
Q5: The Memorandum of Understanding for the merger of princely states is called __________.
Q6: The first Home Minister of India was __________.
Q7: The creation of linguistic states in India was implemented through the __________ Act.
Q8: The government appointed the __________ in 1953 for state reorganization.
Match the Column
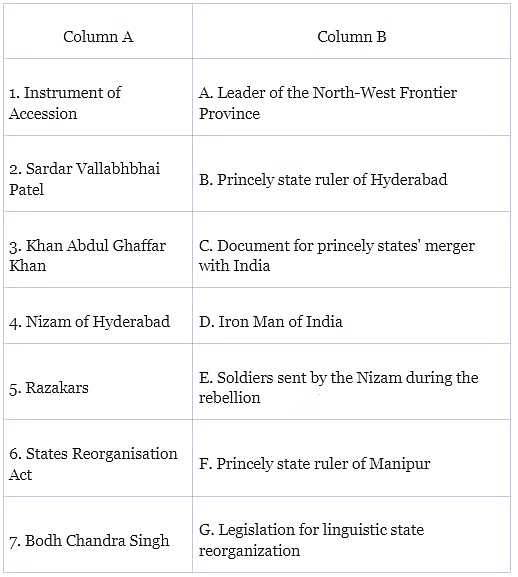
Q1:
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: The partition of India led to one of the largest population transfers in human history.
Reason: Communal violence was at its peak during the partition, forcing millions to abandon their homes.
(a) True for both Assertion and Reason
(b) True for Assertion, but False for Reason
(c) False for Assertion, but True for Reason
(d) False for both Assertion and Reason
Q2: Assertion: Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel played a crucial role in integrating princely states into India.
Reason: Most princely states willingly joined the Indian Union.
(a) True for both Assertion and Reason
(b) True for Assertion, but False for Reason
(c) False for Assertion, but True for Reason
(d) False for both Assertion and Reason
Q3: Assertion: The creation of Andhra Pradesh in 1952 marked the beginning of state reorganization in India.
Reason: Princely states were already reorganized based on linguistic lines.
(a) True for both Assertion and Reason
(b) True for Assertion, but False for Reason
(c) False for Assertion, but True for Reason
(d) False for both Assertion and Reason
Q4: Assertion: The reorganization of states in India was a smooth and uncontroversial process.
Reason: The States Reorganisation Act was passed in 1956, leading to the formation of 14 states and 6 Union Territories.
(a) True for both Assertion and Reason
(b) True for Assertion, but False for Reason
(c) False for Assertion, but True for Reason
(d) False for both Assertion and Reason
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What were the three challenges in nation-building after India's independence?
Q2: Who was Khan Abdul Ghaffar Khan, and why was he significant during partition?
Q3: What was the Instrument of Accession, and why was it crucial for princely states?
Q4: Who was the Nizam of Hyderabad, and what did he want for Hyderabad?
Q5: What were the Razakars, and why did the Indian Army intervene in Hyderabad?
Q6: Why did the Indian government put pressure on the king of Manipur?
Q7: What was the significance of the creation of Andhra Pradesh in 1952?
Q8: Why did the government appoint the States Reorganisation Commission in 1953?
Q9: What was the main consideration of the government in dealing with princely states?
Q10: Why was the reorganization of states in India necessary after independence?
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Describe the process of partition between India and Pakistan in 1947.
Q2: Who was Khan Abdul Ghaffar Khan, and what was his role in the partition?
Q3: What were some of the consequences of the partition, particularly in terms of population transfers and communal violence?
Q4: How did the Indian government approach the integration of princely states into the newly independent India?
Q5: What was the "Instrument of Accession," and who played a crucial role in getting princely states to join India?
Q6: Explain the significance of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel in the integration of princely states.
Q7: Describe the events that led to the integration of Hyderabad and Manipur into India.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Discuss the challenges of building a united India in the aftermath of independence. How did the Indian government address these challenges in terms of princely states' integration?
Q2: Analyze the consequences of the partition in 1947, focusing on the human and social impact, as well as the failures of political and administrative machinery.
Q3: Explain the significance of the States Reorganisation Commission and the reorganisation of states based on linguistic lines. How did this impact the map of India in the 1950s?
Q4: Describe the role of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel in the integration of princely states, with a particular focus on his involvement in the cases of Hyderabad and Manipur.
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
34 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: Challenges of Nation Building - Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What were the main challenges faced during the process of nation building? |  |
| 2. How did the leaders of newly independent nations address the challenge of nation building? |  |
| 3. What role did colonial legacy play in the challenges of nation building? |  |
| 4. How did nation building contribute to social and political changes in the newly independent nations? |  |
| 5. What were the long-term impacts of successful nation building on the development of the newly independent nations? |  |
















