Worksheet: Constitution as a Living Document | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answers Type Questions |

|
| Short Answers Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The Soviet Union had ______ constitutions during its existence.
Q2: The Constitution of India was adopted on __________.
Q3: The Indian Constitution is considered a ______ document.
Q4: Article 368 pertains to the ______ power of the parliament.
Q5: The Indian Constitution is both ______ and ______.
Q6: To amend the Constitution, ______ types of special majorities are required.
Q7: In cases related to the distribution of powers, it is mandatory to consult with the ______.
Q8: The theory of basic structure emerged from ______ interpretation.
Q9: Democracy is not only about electing representatives but also about the ______.
Q10: Political institutions must be ______ to the people.
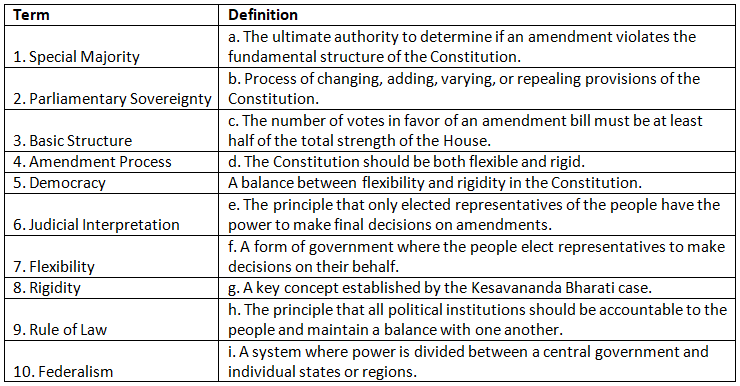
Match the Column
Q1: Match the following terms to their definitions:
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: The Indian Constitution is considered a living document.
Reason: It can be easily modified to accommodate changes.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Q2: Assertion: Amendments to the Indian Constitution require broad consensus and the participation of states.
Reason: States are not involved in the amendment process.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Q3: Assertion: Judicial interpretation has impacted our understanding of the Indian Constitution.
Reason: The Constitution explicitly defines the basic structure.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Q4: Assertion: Democracy is better than the old feudal system.
Reason: Democracy ensures more equality among the people.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Very Short Answers Type Questions
Q1: How many constitutions did the Soviet Union have?
Q2: When was the Constitution of India adopted?
Q3: What is the primary question raised about the Indian Constitution's longevity?
Q4: Explain the concept of a "living document" in the context of the Indian Constitution.
Q5: What does Article 368 pertain to?
Q6: Define the terms "flexibility" and "rigidity" in the context of constitutions.
Q7: Why is it important for the Constitution to be amendable?
Q8: In what cases is it mandatory to consult with the states for amendments?
Q9: How many types of special majorities are required to amend the Constitution?
Q10: What is the fundamental principle underlying the amending process of the Constitution?
Short Answers Type Questions
Q1: Explain the balance between flexibility and rigidity in the Indian Constitution.
Q2: Describe the process of amending the Indian Constitution, including the role of the Parliament.
Q3: Why is the protection of fundamental rights important in the amendment process?
Q4: What is the theory of basic structure, and how has it affected the Constitution's evolution?
Q5: Discuss the role of judicial interpretation in shaping the Constitution.
Q6: How does parliamentary democracy relate to the Constitution as a living document?
Q7: Explain the significance of involving states in amendments related to federalism and fundamental rights.
Q8: Why has the Indian Constitution undergone a high number of amendments, and what are some significant amendments in recent years?
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Describe the concept of a "living document" in the context of constitutions and provide examples of how the Indian Constitution has demonstrated its adaptability.
Q2: Discuss the need for a balance between flexibility and rigidity in the Constitution, and how the Indian Constitution achieves this balance.
Q3: Explain the significance of the Kesavananda Bharati case and its impact on the Indian Constitution's basic structure.
Q4: Analyze the challenges and criticisms related to the high number of amendments to the Indian Constitution and provide insights into the reasons behind these amendments.
|
44 videos|202 docs|40 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: Constitution as a Living Document - Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the Constitution as a Living Document? |  |
| 2. How does the Constitution act as a Living Document? |  |
| 3. Why is it important for the Constitution to be a Living Document? |  |
| 4. Is the Constitution as a Living Document a controversial concept? |  |
| 5. Are there any limitations to the concept of Constitution as a Living Document? |  |





















