Worksheet: Legislature | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: Parliament is the center of all democratic ____________ processes.
Q2: A genuine democracy is inconceivable without a representative, efficient, and effective ____________.
Q3: The Indian Parliament consists of two houses, the Rajya Sabha and the ____________.
Q4: The Constitution allows states to have either a ____________ or bicameral legislature.
Q5: Rajya Sabha represents the states indirectly, with members elected by State ____________.
Q6: In Rajya Sabha, one-third of the members complete their term every ____________ years.
Q7: The Rajya Sabha is also known as the ____________ House of Parliament.
Q8: Lok Sabha is the lower house and represents the people directly through universal ____________.
Q9: Parliament plays a crucial role in controlling taxation and government ____________.
Q10: Parliament has the power to discuss and enact changes to the ____________.
Match the Column
Q1: Match the term on the left with its correct definition on the right.
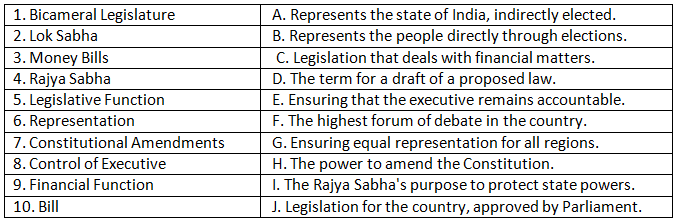
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: Parliament is essential for democratic governance.
Reason: It represents the diverse interests of the people and holds the government accountable.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Q2: Assertion: The Rajya Sabha represents the states of India and is indirectly elected.
Reason: Members of the Rajya Sabha are elected by residents of the states.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Q3: Assertion: A bicameral legislature ensures a double check on every decision.
Reason: Bills and policies are discussed and voted on in both houses.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What is the role of a Parliament in a democracy?
Q2: What are the two houses of the Indian Parliament?
Q3: What is the purpose of Rajya Sabha?
Q4: How often do one-third of Rajya Sabha members complete their terms?
Q5: What is the main function of Lok Sabha?
Q6: What is the significance of financial functions in Parliament?
Q7: Explain the concept of representation in Parliament.
Q8: What is a money bill according to the Constitution?
Q9: How can a deadlock be resolved in Parliament?
Q10: What happens if the President withholds assent to a bill?
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Describe the advantages of having a bicameral legislature in a diverse country like India.
Q2: Explain the role of Rajya Sabha in representing the states and protecting their powers.
Q3: Detail the legislative functions of Parliament and how laws are enacted.
Q4: How does Parliament ensure accountability of the executive branch of government?
Q5: Discuss the different types of bills and their significance in the legislative process.
Q6: Describe the procedures involved in the enactment of ordinary bills in Parliament.
Q7: What is the significance of money bills, and how are they processed in Parliament?
Q8: Explain the role of the President in the legislative process, including the use of discretionary powers.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Discuss the essential functions of Parliament, including its role in controlling the executive and ensuring transparency and accountability.
Q2: Explain how Parliament ensures the representation of diverse interests in a democratic society, considering regional, social, economic, and religious factors.
Q3: Describe the powers and functions of both Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha, highlighting their roles in the legislative process and control of the executive.
Q4: Outline the procedures involved in the enactment of constitutional amendment bills and the significance of such amendments in the Indian Constitution.
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
43 videos|278 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: Legislature - Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the role of the legislature in a democratic system? |  |
| 2. How does the legislative process work? |  |
| 3. What are the differences between the upper and lower houses of a legislature? |  |
| 4. Why is the separation of powers important in a legislature? |  |
| 5. What are some common challenges faced by legislatures today? |  |















