Worksheet: Rights in the Indian Constitution | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answers Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The list of rights protected by the Indian Constitution is known as the ___________.
Q2: Fundamental Rights are listed in ___________ of the Indian Constitution.
Q3: The Indian Constitution grants the right to equality in ___________.
Q4: The Constitution of India ensures that Fundamental Rights are not violated by the ___________.
Q5: The judiciary has the power to protect Fundamental Rights from violations by the ___________.
Q6: Fundamental Rights may only be changed by ___________.
Q7: Article 21 of the Constitution provides protection of ___________.
Q8: Right against exploitation is covered under ___________ of the Constitution.
Q9: Cultural and Educational Rights are mentioned in Articles ___________.
Q10: The right to move to the court to enforce Fundamental Rights is granted by ___________.
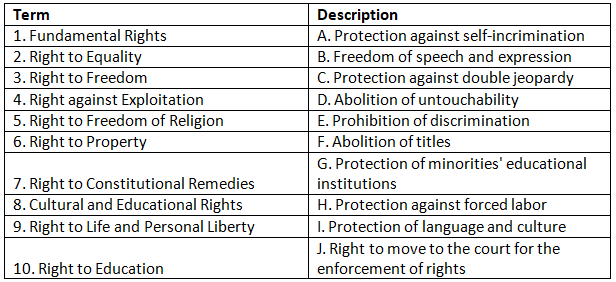
Match the Column
Q1: Match the terms on the left with their corresponding descriptions on the right.
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: Fundamental Rights can be changed by ordinary lawmaking.
Reason: Fundamental Rights are protected and guaranteed by the Constitution.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Q2: Assertion: Cultural and Educational Rights protect the right of minorities to establish educational institutions.
Reason: Cultural and Educational Rights are listed in Articles 29 and 30 of the Indian Constitution.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Q3: Assertion: Preventive detention allows the government to arrest a person without any reason.
Reason: Preventive detention can be up to three months.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Q4: Assertion: Freedom of religion includes the right to forcibly convert others to one's own religion.
Reason: Freedom of religion allows individuals to spread information about their religion.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Q5: Assertion: The NHRC has prosecution powers to punish violators of human rights.
Reason: The NHRC can issue recommendations to the government or courts based on its inquiries.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Q6: Assertion: The 44th Amendment in 1978 reclassified the right to property from a Fundamental Right to a Legal right
Reason: It was necessary to make the right to property a legal right so that the government could implement land reforms without being challenged under Fundamental Rights.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What is Habeas corpus?
Q2: Where are Fundamental Rights listed in the Indian Constitution?
Q3: Give one example of a Fundamental Right related to equality.
Q4: Who has the power to protect Fundamental Rights from violations?
Q5: Can Fundamental Rights be changed by ordinary lawmaking?
Q6: What does Article 21 of the Constitution protect?
Q7: Which articles in the Constitution cover the right against exploitation?
Q8: What does Cultural and Educational Rights protect?
Q9: How can citizens enforce their Fundamental Rights?
Q10: What is the role of the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)?
Short Answers Type Questions
Q1: Explain the difference between Fundamental Rights and Cultural and Educational Rights in the Indian Constitution.
Q2: Discuss the concept of preventive detention and its purpose.
Q3: Describe the rights of the accused to ensure a fair trial in courts.
Q4: Explain the limitations on the freedom of religion as mentioned in the Constitution.
Q5: How do Cultural and Educational Rights protect minorities' educational institutions?
Q6: Why is the right to constitutional remedies considered the "heart and soul of the constitution"?
Q7: Explain the historical context and significance of the 44th amendment regarding the right to property.
Q8: What is the Directive Principles of State Policy, and how do they differ from Fundamental Rights?
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: From where our constitution makers took the Fundamental Rights and with what difference?
Q2: Explain the role and functions of the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) in India.
Q3: Analyze the relationship between Directive Principles of State Policy and Fundamental Rights in the Indian Constitution.
Q4: Trace the evolution of the right to property in the Indian Constitution, from its original status as a Fundamental Right to its reclassification.
|
43 videos|268 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: Rights in the Indian Constitution - Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What are the fundamental rights guaranteed by the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 2. How do fundamental rights impact the citizens of India? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the Right to Constitutional Remedies? |  |
| 4. Can fundamental rights be suspended? If so, under what circumstances? |  |
| 5. How do the Directive Principles of State Policy relate to fundamental rights? |  |
















