Class 4 Science - Adaptations in Plants - CBSE Worksheets Solutions - 1
Q1: Give two examples of the following.
(i) Underwater plants _______________ _______________
Ans: tape grass, hydrilla
 HydrillaUnderwater plants are aquatic and grow in the water. The plant's roots anchor it to the muddy soil. They have thin, narrow leaves that lack stomata. Carbon dioxide and oxygen are absorbed straight through the leaves' surface. The stems are pliable and contain air holes between them. Tape grass, hydrilla, and pond weed are examples.
HydrillaUnderwater plants are aquatic and grow in the water. The plant's roots anchor it to the muddy soil. They have thin, narrow leaves that lack stomata. Carbon dioxide and oxygen are absorbed straight through the leaves' surface. The stems are pliable and contain air holes between them. Tape grass, hydrilla, and pond weed are examples.
(ii) Plants in mountains _______________ _______________
Ans: pine, fir, spruce 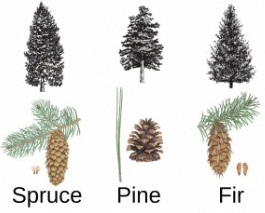 They're fashioned like cones to readily shrug off snow. Conifers have needle-shaped leaves that are extremely robust and can withstand cold weather. Conifers include trees like pine, fir, spruce, and cedar.
They're fashioned like cones to readily shrug off snow. Conifers have needle-shaped leaves that are extremely robust and can withstand cold weather. Conifers include trees like pine, fir, spruce, and cedar.
(iii) Floating plants _______________ _______________
Ans: duckweed, water hyacinth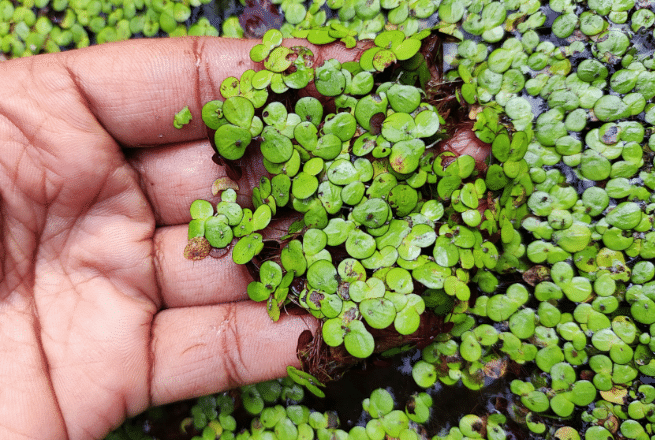  DuckweedFloating plants have a sponge-like texture. There are a lot of empty places in their body that are filled with air. The plant is now light enough to float in water. Duckweed and water hyacinth, for example.
DuckweedFloating plants have a sponge-like texture. There are a lot of empty places in their body that are filled with air. The plant is now light enough to float in water. Duckweed and water hyacinth, for example.
(iv) Plants in deserts _______________ _______________
Ans: Cactus, Brittlebush  CactusDesert plants have used both physical and behavioural mechanisms to adapt to the extremes of heat and aridity in order to thrive.
CactusDesert plants have used both physical and behavioural mechanisms to adapt to the extremes of heat and aridity in order to thrive.
(v) Plants in heavy rainfall areas _______________ _______________
Ans: teak, rice, cotton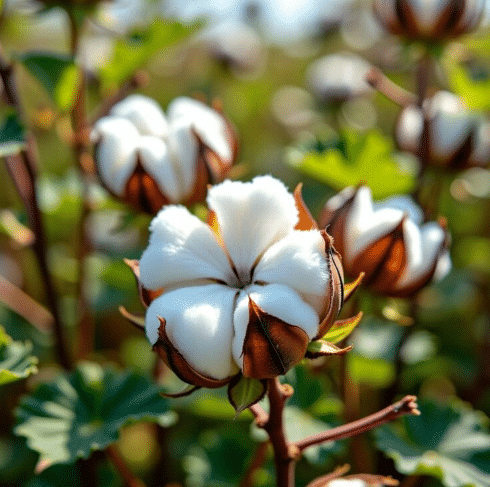  Cotton plantThey are evergreen plants that stay green for virtually the entire year. Rubber, teak, rice, cotton, and sugarcane are just a few examples.
Cotton plantThey are evergreen plants that stay green for virtually the entire year. Rubber, teak, rice, cotton, and sugarcane are just a few examples.
Q2: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
(i) Coconut trees grow well in ______ areas. Coconut Tree(a) swampy
Coconut Tree(a) swampy
(b) hilly
(c) desert
(d) coastal
Ans: (d)
Coconut trees are found in coastal regions because of water availability generally, around these coastal areas, hence the cold winter or warm and humid climate is just a perfect deal for them.
(iii) These trees usually have waxy coating to prevent evaporation and loss of water.
(a) Hydrilla
(b) Mangrove
(c) Fir
(d) Coconut
Ans: (c)  Fir PlantsMountain plants have waxy coating on the leaves to prevent evaporation and loss of water.
Fir PlantsMountain plants have waxy coating on the leaves to prevent evaporation and loss of water.
(iv) Light and spongy water plants like ______ can float on the surface of the water.
(a) duckweed
(b) cactus
(c) mangroves
(d) lotus
Ans: (a)
Plants such as duckweed, mosquito fern, water hyacinth, and watermeal are free floating. These plants are anchored by roots to the bottom of the pond, but their leaves and flowers grow to and float on the water surface.
(v) ______ is an underwater plant.
(a) Water lily
(b) Duckweed
(c) Eelgrass
(d) Lotus
Ans: (c)  EelgrassThese plants provide a home and lots of food to marine organisms such as juvenile cod, crab, and snails.
EelgrassThese plants provide a home and lots of food to marine organisms such as juvenile cod, crab, and snails.
(vi) Plants in heavy rainfall areas are
(a) Sundew, pitcher plant
(b) Mango, pine
(c) Cotton, sugar cane
(d) Indian pipe, fir
Ans: (c)
They are the evergreen plants and remain green almost round the year. Example rubber, teak, rice, cotton and sugarcane.
Q3: Fill in the blanks.
(i) Underwater plants such as pondweed and eelgrass have narrow leaves without ______.
Ans: stomata
They have thin, narrow leaves that lack stomata. Carbon dioxide and oxygen are absorbed straight through the leaves' surface. The stems are pliable and contain air holes between them. Tape grass, hydrilla, and pond weed are examples.
(ii) Neem, peepal and sheesham are some trees that grow in ______.
Ans: plains
Sal, neem, peepal, teak, and sheesham are important trees that may be found in Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, Chattisgarh, Odisha, and Maharashtra.
 Neem Tree
Neem Tree
(iii) Roots of some plants that grow out of the soil to breathe from air are called ______ roots.
Ans: breathing
A specialised root that rises upwards out of the water or mud to reach the air and get oxygen for the root systems of marshy or tidal trees.
(iv) ______ plants like duckweed and Pistia have lots of empty spaces filled with air.
Ans: Floating
Duckweed, green algae, water hyacinth, and pistia are examples of floating plants that float freely on the surface of the water. Floating plants are what they're called. Their bodies are spongy. Duckweed(v) Long ______ systems in desert plants go deep into the ground to absorb the available water.
Duckweed(v) Long ______ systems in desert plants go deep into the ground to absorb the available water.
Ans: root
Far roots are developed by the plants in order to collect water deep beneath the earth's surface. The water evaporates much more slowly at such a depth than it does closer to the surface due to the desert heat.
Q4: True & False.
(i) Some terrestrial plants grow in water.
Ans: False
Terrestrial plants are defined as any plant that grows on, in or from the land. By contrast, aquatic plants are plants that thrive when their roots are submerged in water.
(ii) Evergreen plants do not shed their leaves at once.
Ans: True
Leaves do not have to fall off evergreen trees. Their leaves stay greener and stay linked longer than their deciduous counterparts because they have more water. The waxy covering on evergreen needles also helps to conserve water in the summer and winter.
(iii) The trees in heavy rainfall areas are called conifers.
Ans: False
The trees in heavy rainfall areas are called evergreen forest trees. Coniferous forests are found in the northern hemisphere, at high latitudes and altitudes, in areas with long, cold winters and short, cool summers.
(iv) The cactus plant stores water in its stem.
Ans: True
When it rains, water is stored in the thick, hard-walled, succulent stem of cacti. The stems are fleshy, green, and photosynthetic. The stem is either spongy or hollow on the inside (depending on the cactus). The water inside the cactus is kept from evaporating by a thick, waxy layer.
(v) Spines protect cactus from animals.
Ans: True
By shading the cactus, these spines also help prevent the cactus from losing water through evaporation. So all in all, spines are adaptations that protect and help cacti hide from animals that may want to eat them.
Q5: Match the following.
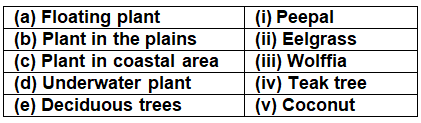
Ans: (a) Floating plant - (iii) Wolffia
Wolffia species are free-floating thalli, green or yellow-green, and without roots. The flower is produced in a depression on the top surface of the plant body.
(b) Plants in Plains - (i) Peepal
Peepal, banyan, mango, sal, Sheesham are some of the plants found in plains. They grow into trees having many branches.
(c) Plants in coastal area - (v) Coconut
Coconuts have a high water requirement. So it is easier for them to grow in those areas. In non-coastal regions the high necessity of water is matched by using coco peat near the roots of coconut trees, so that the water stays near the root for a long time.
(d) Underwater plant - (ii) Eelgrass
Eelgrass is a flowering underwater plant.
(e) Deciduous tree - (iv) Teak tree
Teak, (genus Tectona grandis), large deciduous tree of the family Verbenaceae, or its wood, one of the most valuable timbers. Teak has been widely used in India for more than 2,000 years.
Q6: Answer the following questions in brief.
(i) What is a habitat?
Ans: A habitat is the natural home or environment of a plant, animal, or other organism. It provides the organisms that live there with food, water, shelter and space to survive.
(ii) Why do mountain plants have waxy coatings on leaves?
Ans: Mountain plants have waxy coating on the leaves to prevent evaporation and loss of water.
(iii) What are breathing roots?
Ans: The roots of the plants that grow out of the soil to breathe from the air. Such roots are called Breathing roots.
(iv) How does long root system help desert plants?
Ans: Many desert plants have adapted to the harsh environment by growing deep roots that can gather water from several feet under the surface. Without these long roots, these desert plants could not stay alive, nor could the wildlife that depends on them for food, drink and shade.
(v) Define coniferous trees. Give two examples
Ans: Conifers are trees which produce cones. Almost all of them are evergreen. Examples include pine, fir, cypress. The larch is a deciduous conifer. Coniferous trees that do not bear flowers but have seeds in cones. Hence are called conifers and coniferous trees.
Q7: Answer the following questions in detail.
(i) How do plants in marshy areas survive? Explain.
Ans: The plants must be able to survive in wet mud with low oxygen levels. Many of these plants, therefore, have aerenchyma, channels within the stem that allow air to move from the leaves into the rooting zone. Marsh plants also tend to have rhizomes for underground storage and reproduction. They have sticky and clayey soil. It is difficult for plants to grow in such areas as air cannot reach the roots. Thus, roots of these grow out of the soil to breathe from the air. Such roots are called breathing roots. Trees growing in marshy areas are called mangroves.
(ii) Explain some adaptations in desert plants.
Ans: Some adaptations in desert plants are:
- Plants store food in their stems or leaves.
- Long root system to go deep in to the ground.
- Most plants are leafless hence help in reduce water loss.
- Prickly spines discourage animals from eating plants for water.
(iii) Draw a cactus plant and label its adaptations.
Ans: 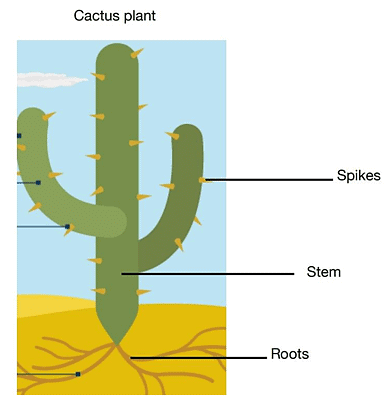
(iv) Choose the odd one out. State a reason for selection.
(a)
(b)
(c)
Ans: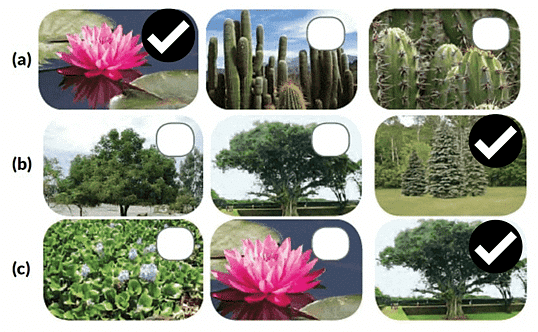
(a) First image is that of an aquatic plant whereas other two are cactus and desert plants.
(b) The third image is terrestrial plant whereas first two are not.
(c) First two images are aquatic plants but third is not.
|
48 videos|156 docs|34 tests
|
FAQs on Class 4 Science - Adaptations in Plants - CBSE Worksheets Solutions - 1
| 1. What are the main types of adaptations found in plants? |  |
| 2. How do desert plants adapt to their environment? |  |
| 3. Why do some plants have thorns or spines? |  |
| 4. How do aquatic plants adapt to living in water? |  |
| 5. What role do adaptations play in the survival of plants? |  |

















