Worksheet Solutions: Atoms Structure | Chemistry Class 7 ICSE PDF Download
Section A: Multiple Choice Questions
Q1. Which scientist gave the first scientific theory about atoms?
a) J.J. Thomson
b) John Dalton
c) Niels Bohr
d) Rutherford
Answer: (b) John Dalton
Reasoning: Dalton proposed that all matter is made of indivisible atoms – the first scientific atomic theory.
Q2. Which particle has no charge?
a) Proton
b) Neutron
c) Electron
d) Positron
Answer: (b) Neutron
Reasoning: Protons are positive, electrons negative, but neutrons are neutral.
Q3. According to Thomson’s model, the atom looks like:
a) A solar system
b) A solid sphere
c) A sphere with positive charge in which electrons are embedded
d) A dense nucleus surrounded by electrons
Answer: (c) A sphere with positive charge in which electrons are embedded
Reasoning: This is called the “plum pudding model.”
Q4. Rutherford’s gold foil experiment proved that:
a) Atoms are solid
b) Most of an atom is empty space
c) Electrons are stationary
d) Neutrons are present in the nucleus
Answer: (b) Most of an atom is empty space
Reasoning: Most alpha particles passed through, showing emptiness inside the atom.
Q5. Two atoms having the same atomic number but different mass numbers are called:
a) Isotopes
b) Isobars
c) Ions
d) Molecules
Answer: (a) Isotopes
Reasoning: Isotopes differ in neutrons, hence mass number changes.
Section B: Short Answer Questions
Q6. State two postulates of Dalton’s Atomic Theory.
Answer:
All matter is made of tiny indivisible atoms.
Atoms of the same element are identical in mass and properties.
Q7. Differentiate between atomic number and mass number.
Answer:
Atomic number (Z): Number of protons in an atom.
Mass number (A): Sum of protons and neutrons.
Q8. Define an electron. Where is it located in an atom?
Answer:
Electron is a negatively charged particle, revolving around the nucleus in fixed orbits.
Q9. Name the three subatomic particles of an atom and state their charges.
Answer:
Proton: +1 charge
Neutron: 0 charge
Electron: –1 charge
Q10. Explain Rutherford’s gold foil experiment and its conclusions.
Answer:
Thin gold foil bombarded with alpha particles.
Most passed through → atom mostly empty.
Few deflected → dense, positive nucleus.
Conclusion: Nucleus is small, dense, positively charged.
Section C: Long Answer Questions
Q11. Describe Bohr’s model of the atom.
Answer:
Electrons revolve in fixed circular orbits (shells).
Each orbit has a fixed energy.
Electrons don’t lose energy in these orbits.
Energy is absorbed or released when electrons jump shells.
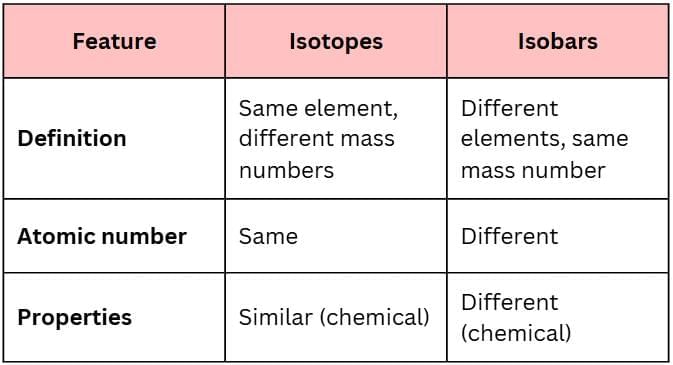
Q12. What are isobars? Give one example.
Answer:
Isobars are atoms of different elements having the same mass number but different atomic numbers.
Example: Calcium-40 and Argon-40.
Q13. Write three differences between isotopes and isobars.
Answer:
|
33 videos|58 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Atoms Structure - Chemistry Class 7 ICSE
| 1. What is the basic structure of an atom? |  |
| 2. Who proposed the atomic theory and what are its key points? |  |
| 3. What are isotopes and how do they differ from each other? |  |
| 4. How do the properties of electrons influence the behavior of atoms? |  |
| 5. What role do protons play in determining the identity of an atom? |  |
















