Class 7 Social Science Chapter 3 Worksheet Solutions - Climates of India
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1: What is the main difference between weather and climate?
a) Weather is the average condition over many years, while climate is the short-term condition.
b) Weather is the short-term condition, while climate is the average condition over many years.
c) Weather occurs only in tropical areas, while climate is for the entire planet.
d) Weather and climate are the same thing.
Ans: b) Weather is the short-term condition, while climate is the average condition over many years.
Weather refers to daily atmospheric conditions, while climate is the long-term average of weather patterns in a region.
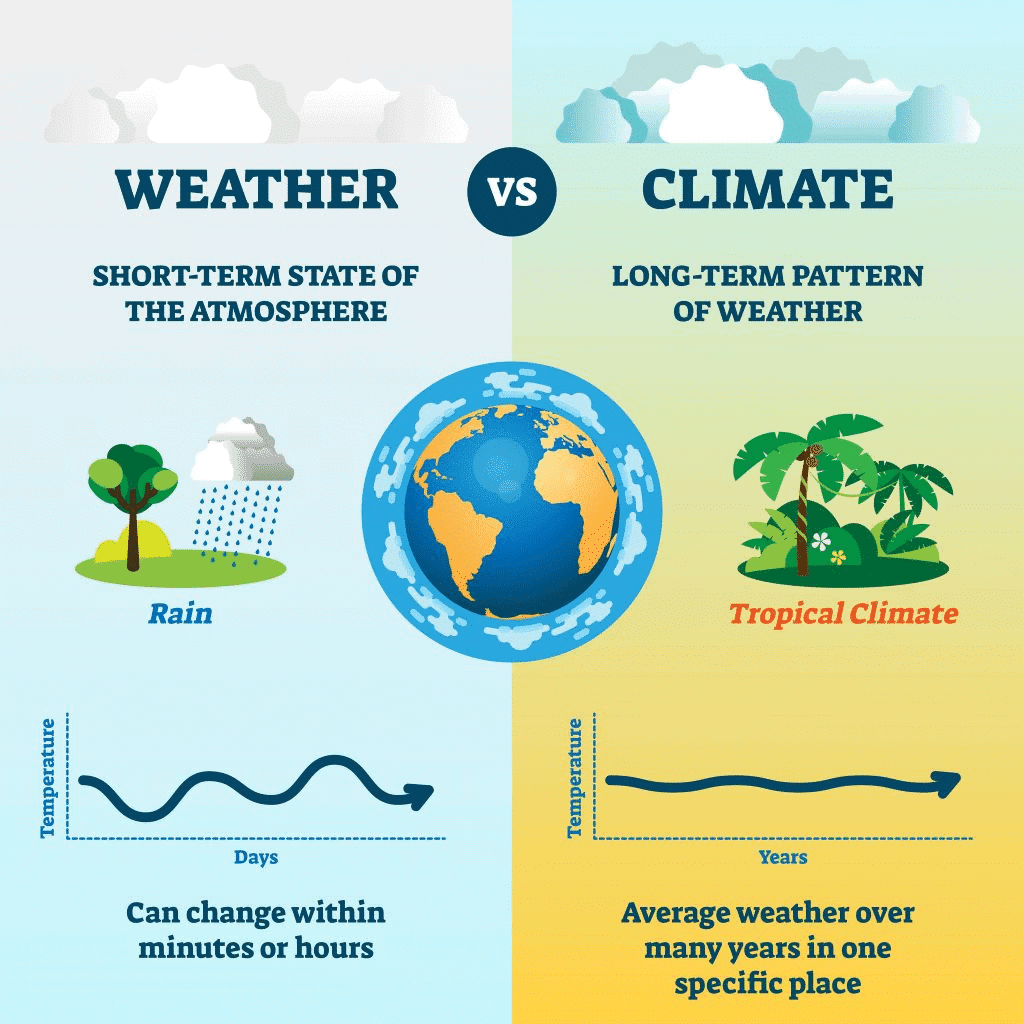 Difference between Weather and Climate
Difference between Weather and Climate
Q2: Which region of India experiences an alpine climate?
a) Western Ghats
b) Himalayan region
c) Ganga Plains
d) Thar Desert
Ans: b) Himalayan region
The Himalayan region experiences an alpine climate with cold winters and cool summers.
Q3: Which of the following is not a factor affecting India's climate?
a) Latitude
b) Altitude
c) Longitude
d) Proximity to the sea
Ans: c) Longitude
Latitude, altitude, and proximity to the sea all influence India’s climate, but longitude doesn’t have a direct effect.
Q4: What does the term 'microclimate' refer to?
a) A region with a climate similar to the surrounding areas.
b) A small area with a unique climate different from its surrounding areas.
c) A type of tropical climate.
d) A specific seasonal weather pattern.
Ans: b) A small area with a unique climate different from its surrounding areas.
Microclimates are localized weather conditions that differ from the overall climate of the region.
Q5: Which of the following is a primary characteristic of the Thar Desert?
a) Cold winters with snowfall
b) Hot days with cool nights
c) Tropical wet climate
d) Mild summers and winters
Ans: b) Hot days with cool nights
The Thar Desert experiences extreme temperature variations, with hot days and cool nights.
 Thar Desert
Thar Desert
Q6: What is the main reason for the monsoon rains in India?
a) Winds from the Arctic
b) Wind patterns caused by pressure differences between land and sea
c) Heavy snowmelt from the Himalayas
d) Winds from the Bay of Bengal only
Ans: b) Wind patterns caused by pressure differences between land and sea
The monsoon rains are caused by low-pressure systems over land, which draw in moisture-laden winds from the ocean.
Q7: Which climate type is found in the Western Coast of India?
a) Arid climate
b) Tropical wet climate
c) Alpine climate
d) Temperate climate
Ans: b) Tropical wet climate
The Western Coast experiences a tropical wet climate, with heavy monsoon rainfall ideal for growing rice and spices.
Q8: What is the role of the Himalayas in India’s climate?
a) They block cold desert winds from Central Asia.
b) They warm the air in the northern plains.
c) They prevent rainfall in the southern parts.
d) They help control the monsoon winds.
Ans: a) They block cold desert winds from Central Asia.
The Himalayas act as a barrier, preventing cold desert winds from reaching India’s northern plains.
Q9: Which region of India is most affected by the Northeast Monsoon?
a) Western Ghats
b) Deccan Plateau
c) Eastern India and Southern Peninsula
d) Himalayan region
Ans: c) Eastern India and Southern Peninsula
The Northeast Monsoon brings rain to parts of eastern India and the southern peninsula)
Q10: Which of the following cities experiences a larger range of temperatures between summer and winter?
a) Mumbai
b) Delhi
c) Chennai
d) Kolkata
Ans: b) Delhi
Delhi, being inland, experiences extreme temperatures, with hot summers and cold winters, unlike coastal cities.
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The weather of India is greatly influenced by the __________ system.
Ans: Monsoon
The monsoon system brings seasonal rains to India, significantly impacting its weather.
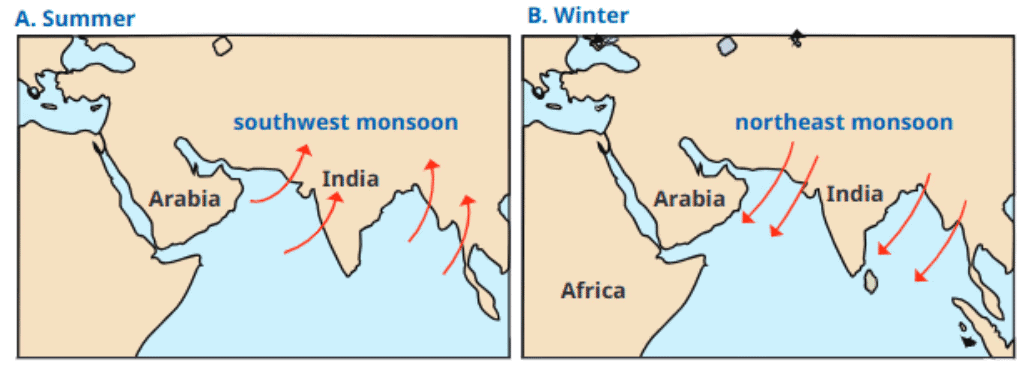 Monsoons
Monsoons
Q2: The __________ climate is found in the Himalayan region, where temperatures stay below freezing in the highest peaks.
Ans: Alpine
The alpine climate in the Himalayas is characterized by cold winters and cool summers.
Q3: __________ is the term for the small area’s unique climate that differs from its surrounding region.
Ans: Microclimate
Microclimates are areas with weather conditions that vary from those of the surrounding region.
Q4: The __________ Desert has hot days and cool nights, with very little rainfall.
Ans: Thar
The Thar Desert is an arid region with extreme temperature fluctuations and minimal rainfall.
Q5: The __________ Monsoon brings rain to the eastern and southern parts of India during winter.
Ans: Northeast
The Northeast Monsoon is responsible for rainfall in the southeastern regions of India.
Q6: The __________ climate in India is ideal for growing rice and spices due to heavy monsoon rainfall.
Ans: Tropical wet
The tropical wet climate on the western coast of India supports rice and spice farming.
Q7: The __________ Plateau experiences a semi-arid climate with hot summers and mild winters.
Ans: Deccan
The Deccan Plateau, in central India, has a semi-arid climate and moderate rainfall during the monsoon season.
Q8: __________ is the term for the rise in global temperatures caused by the accumulation of greenhouse gases.
Ans: Global warming
Global warming is the result of increased levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which trap heat.
 Global Warming
Global Warming
Q9: The __________ ranges influence rainfall by blocking moist air coming from the sea.
Ans: Western Ghats
The Western Ghats play a crucial role in rainfall patterns by blocking moist winds from the Arabian Sea.
Q10: __________ refers to the average weather pattern in an area over many years.
Ans: Climate
Climate is the long-term average of weather conditions in a region, measured over many years.
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1: What does the word "monsoon" mean?
Ans: Monsoon comes from the Arabic word "mausim," meaning season.
Q2: What is a microclimate?
Ans: A small area’s unique climate different from its surrounding region.
Q3: Which climate is found in the Deccan Plateau?
Ans: Semi-arid climate.
Q4: What causes the monsoon rains in India?
Ans: Seasonal winds are the primary cause of monsoon rains in India.
Q5: Which region has the coldest climate in India?
Ans: The Himalayan region.
Short Answer Questions
Q1: What is the difference between weather and climate?
Ans: Weather refers to the short-term conditions of the atmosphere, while climate is the long-term average of these conditions over many years.
Q2: How does altitude affect India’s climate?
Ans: Higher altitudes, like hill stations, have cooler climates, while lower areas experience warmer temperatures.
Q3: Why are the Western Ghats important in determining the climate of India?
Ans: The Western Ghats influence monsoon rainfall by blocking moist air from the sea, leading to heavy rainfall on the western side.
Q4: What role does latitude play in India’s climate?
Ans: Areas closer to the Equator, like Kanyakumari, remain warm year-round, while regions further north, like Srinagar, experience cooler climates.
Q5: How does proximity to the sea influence the climate?
Ans: Coastal areas have milder temperatures due to the sea's ability to moderate both summer and winter temperatures.
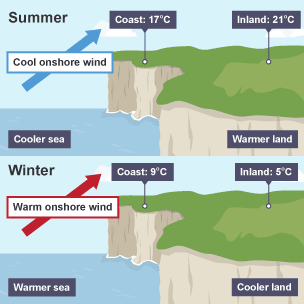 Proximity to Sea
Proximity to Sea
Match the Following
(Match Column A with the correct option in Column B)
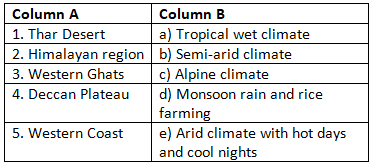
Ans: Matched Pairs and Explanations:
- 1 → e: The Thar Desert is an arid region with extreme temperature fluctuations.
- 2 → c: The Himalayan region has an alpine climate with cold temperatures year-round)
- 3 → a: The Western Ghats receive heavy monsoon rains, supporting tropical wet climates.
- 4 → b: The Deccan Plateau experiences a semi-arid climate with hot summers.
- 5 → d: The Western Coast has a tropical wet climate, ideal for rice farming due to heavy monsoon rains.
|
1 videos|107 docs
|
FAQs on Class 7 Social Science Chapter 3 Worksheet Solutions - Climates of India
| 1. What are the main factors that influence the climate of India? |  |
| 2. How do the seasons in India differ from each other? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the monsoon season in India? |  |
| 4. How does altitude affect the climate in different regions of India? |  |
| 5. What role does the Himalayas play in India's climate? |  |















