Worksheet Solutions: Era of One Party Dominance | Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The first Chief Election Commissioner of India was ________.
Ans: Sukumar Sen
Sukumar Sen served as the inaugural Chief Election Commissioner of India, overseeing the country's first general election in 1952.
Q2: India's first general election was held in the year ________.
Ans: 1952
The landmark first general election in India took place in 1952, marking a significant step in the country's democratic history after independence.
Q3: The party that won the second largest number of seats in India's first general election was ________.
Ans: Communist Party of India
In the inaugural general election of 1952, the Communist Party of India emerged as the second-largest party, securing a notable position in the newly formed Indian Parliament.
Q4: The Congress Socialist Party was formed within the Congress in the year ________.
Ans: 1934
The Congress Socialist Party, established within the Indian National Congress in 1934, advocated for socialist principles and played a crucial role in shaping the political landscape of the time.
Q5: The Bharatiya Jana Sangh was founded in the year ________.
Ans: 1951
Founded in 1951, the Bharatiya Jana Sangh was a prominent political party in India, emphasizing cultural nationalism and traditional Indian values.
Q6: The Swatantra Party was critical of the development strategy involving ________ intervention in the economy.
Ans: state
The Swatantra Party, established in 1959, opposed state intervention in the economy, advocating for a free private sector and market-driven economic policies.
Q7: India's Constitution came into force on ________.
Ans: January 26, 1950
India's Constitution, a significant document outlining the country's governance and fundamental principles, was implemented on January 26, 1950, marking the official establishment of the Republic of India.
Match the Column
Q1:
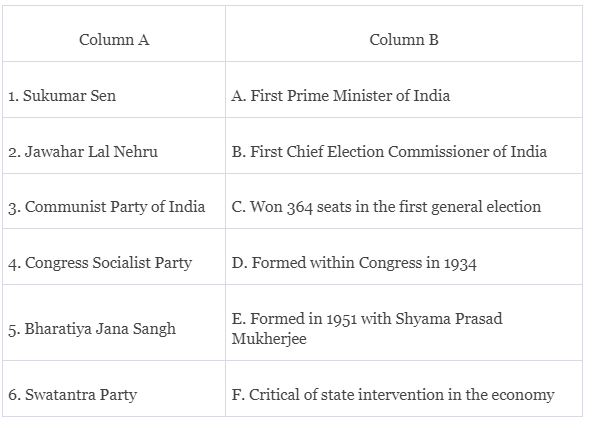 Ans: 1. Sukumar Sen - B. First Chief Election Commissioner of India:
Ans: 1. Sukumar Sen - B. First Chief Election Commissioner of India:
Sukumar Sen was the first Chief Election Commissioner of India. He played a crucial role in conducting India's first general election in 1952, overseeing the massive electoral process.
2. Jawahar Lal Nehru - A. First Prime Minister of India:
Jawahar Lal Nehru was India's first Prime Minister, serving from 1947 to 1964. He played a key role in shaping India's political and economic policies in the early years after independence.
3. Communist Party of India - C. Won 364 seats in the first general election:
The Communist Party of India (CPI) won 16 seats in the first general election held in 1952. While they were a significant presence, they did not win 364 seats. This statement is incorrect.
4. Congress Socialist Party - D. Formed within Congress in 1934:
The Congress Socialist Party (CSP) was indeed formed within the Congress party in 1934. It was a group of leaders who wanted a more radical and egalitarian Congress, advocating for socialist principles.
5. Bharatiya Jana Sangh - E. Formed in 1951 with Shyama Prasad Mukherjee:
Bharatiya Jana Sangh was founded in 1951 with Shyama Prasad Mukherjee as its founder president. It emphasized the idea of one country, one culture, and one nation, aligning with the cultural and nationalistic ethos of India.
6. Swatantra Party - F. Critical of state intervention in the economy:
The Swatantra Party, formed in 1959, was indeed critical of state intervention in the economy. It advocated for a free private sector and was against central planning and nationalization, aligning with the principle mentioned in Column F.
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: The dominance of the Congress party in India was a result of its diverse social coalition.
Reason: The Congress party represented various classes, castes, religions, languages, and interests.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Ans: (a)
Both the assertion and the reason are true, and the reason correctly explains the assertion. The diverse social coalition of the Congress party, encompassing a wide range of classes, castes, religions, and interests, indeed contributed to its dominance. The ability to represent such a varied demographic helped the Congress party maintain its influence in Indian politics, making option (a) the correct choice.
Q2: Assertion: The Congress Socialist Party (CSP) criticized the Congress for favoring capitalists and landlords.
Reason: CSP wanted a more radical and egalitarian Congress.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Ans: (a)
Both the assertion and the reason are true, and the reason correctly explains the assertion. The CSP indeed criticized the Congress for its policies favoring capitalists and landlords, advocating for a more radical and egalitarian approach. Thus, option (a) is the correct choice.
Q3: Assertion: The Swatantra Party favored expansion of a free private sector.
Reason: Swatantra Party believed in complete state control over the economy.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Ans: (c)
The assertion is true, but the reason is false. The Swatantra Party was critical of state intervention in the economy and favored an expanded free private sector. They did not believe in complete state control over the economy. Therefore, option (c) is the correct choice.
Q4: Assertion: The dominance of Congress in India was largely unchallenged in the initial general elections.
Reason: Opposition parties were weak and disorganized during that period.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Ans: (a)
Both the assertion and the reason are true, and the reason correctly explains the assertion. The Congress party's dominance in the initial general elections can be attributed to the weakness and disorganization of opposition parties during that period. This lack of strong opposition contributed to Congress's unchallenged position, making option (a) the correct choice.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Who was the first Chief Election Commissioner of India?
Ans: Sukumar Sen
Q2: Name the party that won the second largest number of seats in India's first general election.
Ans: Communist Party of India
Q3: Which party was formed within the Congress in 1934 and criticized the Congress for favoring capitalists and landlords?
Ans: Congress Socialist Party
Q4: Who was the founder President of Bharatiya Jana Sangh?
Ans: Shyama Prasad Mukherjee
Q5: In which year was the Swatantra Party formed?
Ans: 1959
Q6: When did India's Constitution come into force?
Ans: January 26, 1950
Q7: Which party believed in the idea of one country, one culture, and one nation?
Ans: Bharatiya Jana Sangh
Q8: Name one notable leader of the Communist Party of India.
Ans: AK Gopalan
Q9: What was the main criticism of the Swatantra Party regarding the economy?
Ans: Opposition to state intervention in the economy
Q10: Which state witnessed the Communist Party forming the government in 1957?
Ans: Kerala
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Describe the challenges faced during India's first general election in 1952.
Ans:
- Low literacy rate (only 16% educated population).
- Widespread poverty among the majority of the population.
- Lack of communication and technology infrastructure.
- The task of electing 3200 MLAs and 489 Parliament members by 17 crore voters.
Q2: Explain the nature of Congress dominance in post-independence India.
Ans:
- The Congress party represented a diverse social coalition, including various classes, castes, religions, languages, and interests.
- Tolerance and management of factions within the party allowed for diverse ideologies to coexist.
- Opposition parties like the Congress Socialist Party and Communist Party of India provided principled criticism, balancing the power dynamics within Congress.
Q3: What led to the formation of the Congress Socialist Party (CSP)?
Ans:
- CSP was formed within the Congress in 1934 by leaders seeking a more radical and egalitarian Congress.
- They criticized the Congress for favoring capitalists and landlords, advocating for a more equitable society.
Q4: Discuss the role of the Communist Party of India (CPI) in post-independence Indian politics.
Ans:
- CPI emerged in the 1920s, inspired by the Bolshevik Revolution in Russia.
- In 1951, CPI chose to participate in general elections, abandoning the path of violent revolution.
- Leaders like AK Gopalan, SA Dange, and EMS Namboodripad played key roles in the party.
Q5: What were the core principles of the Bharatiya Jana Sangh (BJS)?
Ans:
- BJS, founded in 1951, emphasized the idea of one country, one culture, and one nation.
- They believed in India's progress based on its traditional culture and heritage.
Q6: Explain the ideology of the Swatantra Party regarding the economy.
Ans:
- Swatantra Party, formed in 1959, opposed state intervention in the economy.
- They criticized central planning, nationalization, and advocated for an expanded free private sector.
Q7: Describe the significance of the first general election in India held in 1952.
Ans:
- The first general election established the democratic process in India.
- It witnessed active participation, with a voter list prepared for every person above 21 years.
- Congress won 364 seats, becoming the single largest party, and Jawahar Lal Nehru became the first Prime Minister.
Q8: Discuss the influence and controversy surrounding the Communist Party of India (CPI) in Kerala in 1957.
Ans:
- In 1957, CPI formed the government in Kerala, showcasing its influence in the state.
- However, in 1959, the Congress-led Central Government dismissed the CPI government using Article 356, sparking controversy and debates over state autonomy.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the challenges faced by India during its first general election in 1952 and how these challenges were overcome.
Ans: Challenges:
- Low literacy rate (16% educated population).
- Widespread poverty and lack of resources.
- Limited means of communication and technology.
- 3200 MLAs and 489 Parliament members to be elected by 17 crore voters.
Overcoming Challenges:
- Extensive voter education and training programs conducted for nearly 3 lakh people.
- Demarcation of constituencies and preparation of voter lists for individuals above 21 years.
- Massive election campaigns mobilized public participation.
- Despite criticisms, the elections were held successfully, establishing the democratic process in India.
Q2: Discuss the coalition-like character of the Congress party and its significance in India's political landscape.
Ans:
- Congress represented diverse groups in terms of classes, castes, religions, languages, and interests.
- Tolerance and management of factions allowed various ideologies to coexist within the party.
- The party's ability to balance these diverse interests gave it strength, ensuring broad representation and a stable government.
- Opposition parties, emerging from factions within Congress, provided principled criticism, maintaining a checks-and-balances system in Indian politics.
Q3: Analyze the role of the Communist Party of India (CPI) in post-independence India, focusing on its evolution and contributions.
Ans: Evolution:
- Emerged in the 1920s, inspired by the Bolshevik Revolution in Russia.
- Initially pursued violent revolution but shifted focus to democratic participation in 1951.
Contributions:
- Provided a voice to the working class and peasants in Indian politics.
- Offered principled criticism, challenging Congress policies.
- Leaders like AK Gopalan and EMS Namboodripad played pivotal roles, influencing state politics, especially in Kerala.
Q4: Evaluate the impact of the first general election in India held in 1952 on the country's political landscape.
Ans: Establishment of Democracy:
- Marked the establishment of democracy in India, setting a precedent for subsequent elections.
- Active participation and acceptance of results silenced critics, reinforcing faith in democratic processes.
Congress Dominance:
- Congress emerged as the single largest party, forming the government.
- Nehru became the first Prime Minister, initiating India's post-independence political era.
Paving the Way for Opposition:
- Opposition parties like CPI and Congress Socialist Party emerged, offering critical perspectives and shaping Indian political discourse.
- The election's success laid the foundation for a multi-party democratic system in India, promoting political pluralism.
|
34 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|















