Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Worksheet Solutions - Heat Transfer in Nature
Q.1. True/False
(i) Metals are poor conductors of heat.
Ans: False
Metals are good conductors of heat.
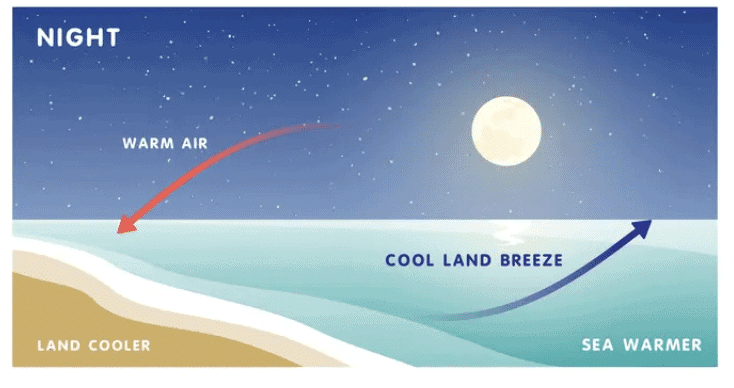
(i) Land breeze occurs during the night.
Ans: True
At night, cooler land air moves towards the warmer sea.
(i) Dark-colored clothes absorb less heat than light-colored clothes.
Ans: False
Dark-colored clothes absorb more heat.
(i) Water vapor released by plants is called transpiration.
Ans: True
It is a natural process where plants release water into the air.
(i) Radiation requires air or water to transfer heat.
Ans: False
Radiation can occur in empty space, such as sunlight.
Q.2. Fill in the blanks.
(i) The hotness of an object is determined by its ____.
temperature
(ii) Temperature is measured in degree ____.
celsius
(iii) A cold steel spoon is dipped in a cup of hot milk. It transfers heat to its other end by the process of ____.
conduction
(vi) Dark colored clothes are preferred during ____.
winter
(v) Poor conductors are known as ____.
insulators
Answer the following Questions
Q.3. Does the transfer of heat by radiation require any medium?
The transfer of heat by radiation does not require any medium.
Q.4. What is the concern associated with the use of mercury thermometers?
There is a lot of concern over the use of mercury in thermometers. Mercury is a toxic substance and is very difficult to dispose of if a thermometer breaks.
Q.5. How water get heated when kept on flame?
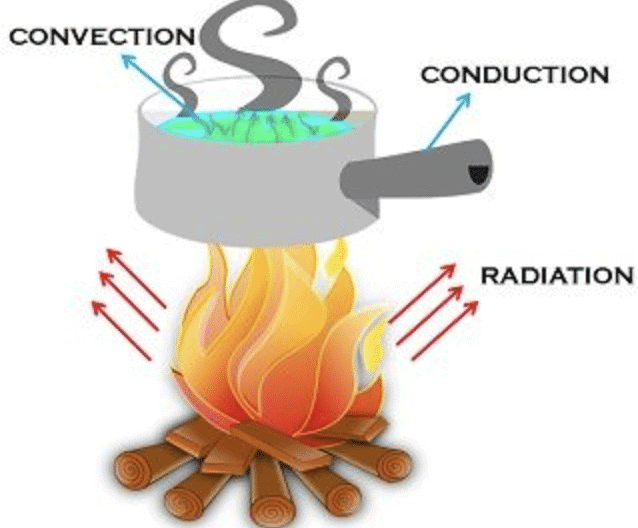
When water is heated, the water near the flame gets hot. Hot water rises up. The cold water from the sides moves down towards the source of heat. This water also gets hot and rises and water from the sides moves down. This process continues till the whole water gets heated. This mode of heat transfer is known as convection.
Q.6. Which device is used to measure temperature?
Thermometer is used to measure temperature.
Q.7. How does heat flow from one object to another?
Heat flows from a hotter object to a colder object.
Q.8. Do all hot bodies radiate heat?
Yes, all hot bodies radiate heat.
Q.9. How does heat transfer in solids?
In solids, generally, the heat is transferred by the process of conduction.
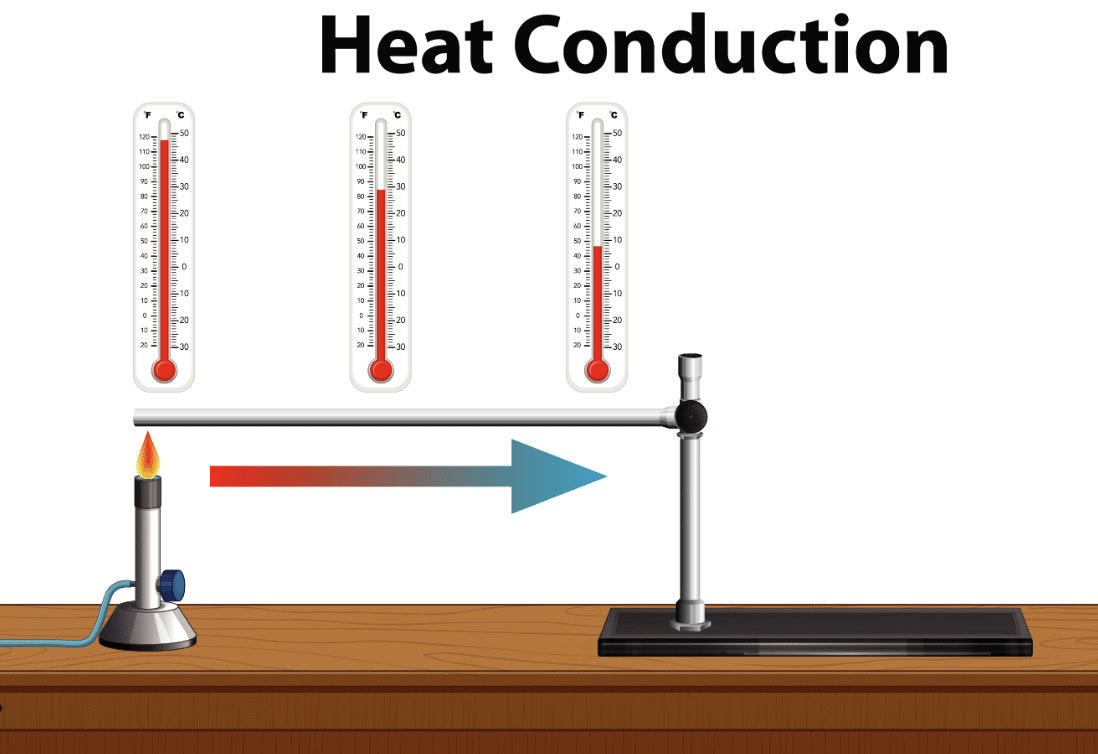
Q.10. What is Conduction?
The process by which heat is transferred from the hotter end to the colder end of an object is known as conduction.
Q.11. Explain the process of conduction with an example.
Conduction is the transfer of heat in solids through direct contact. In this process, heated particles vibrate and pass energy to nearby particles. For example, when a metal pan is placed on a flame, heat travels from the bottom to the entire surface, making the pan hot. Metals are used for cooking because they are good conductors of heat.
Q.12. What is convection and how does it affect coastal areas?
Convection is heat transfer in liquids and gases where warm particles rise and cool ones sink. In coastal areas, during the day, land heats up faster than sea, causing a sea breeze. At night, land cools faster, creating a land breeze. These breezes are examples of convection currents and provide comfort in coastal climates.
Q.13. Describe radiation and give two real-life applications.
Radiation is the transfer of heat through invisible waves, without needing a medium. For example, the Sun heats the Earth through radiation. Another example is the warmth felt near a fire. Light-colored clothes reflect radiation, keeping us cool, while dark-colored clothes absorb heat, keeping us warm in winter.
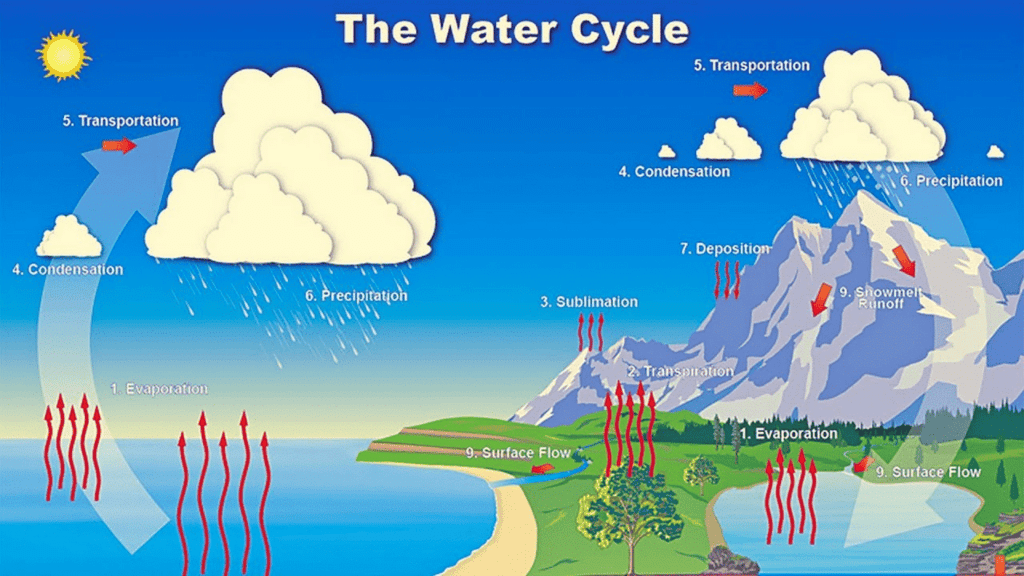
Q.14. How does the water cycle help in redistributing water on Earth?
The Sun's heat drives the water cycle through evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and seepage. Water evaporates from oceans and lakes, forms clouds, and falls back as rain or snow. Some of this water seeps underground to become groundwater. This cycle keeps water circulating and available across regions.
Q.15. What are ice stupas and how do they help conserve water in Ladakh?
Ice stupas are cone-shaped ice structures built in Ladakh to store water in winter. Stream water is frozen in these shapes and melts slowly in spring, providing water for farming. They help solve water scarcity in dry, mountainous areas and are an example of traditional knowledge used for modern conservation.
|
1 videos|107 docs
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Worksheet Solutions - Heat Transfer in Nature
| 1. What are the three main methods of heat transfer in nature? |  |
| 2. How does heat transfer affect weather patterns? |  |
| 3. Can you explain the process of conduction with an example? |  |
| 4. What role does convection play in ocean currents? |  |
| 5. How does radiation from the sun impact Earth's temperature? |  |