Worksheet Solutions: Language of Chemistry | Chemistry Class 7 ICSE PDF Download
Section A: Multiple Choice Questions (1 mark each)
Q1. The substances formed after a chemical reaction are called:
a) Reactants
b) Products
c) Catalysts
d) Elements
Answer: (b) Products
Reasoning: New substances formed after a reaction are products.
Q2. Which type of reaction occurs when two or more substances combine to form one product?
a) Combination reaction
b) Decomposition reaction
c) Displacement reaction
d) Neutralisation
Answer: (a) Combination reaction
Reasoning: Example – H₂ + O₂ → H₂O.
Q3. Which form of energy is needed to split water into hydrogen and oxygen?
a) Light
b) Heat
c) Electricity
d) Sound
Answer: (c) Electricity
Reasoning: Electrolysis of water requires electric current.
Q4. What type of change is the rusting of iron?
a) Physical change
b) Chemical change
c) Temporary change
d) Both physical and chemical
Answer: (b) Chemical change
Reasoning: Rusting forms a new substance (hydrated iron oxide).
Q5. Which of the following is an exothermic reaction?
a) Photosynthesis
b) Decomposition of CaCO₃
c) Slaking of lime (CaO + H₂O → Ca(OH)₂)
d) Electrolysis of water
Answer: (c) Slaking of lime
Reasoning: Heat is released during the reaction.
Section B: Short Answer Questions (2–3 marks each)
Q6. Define chemical reaction. Write one example.
Answer:
A chemical reaction is a process in which reactants change into new products with different properties.
Example: Burning of magnesium ribbon → Mg + O₂ → MgO.
Q7. Differentiate between physical change and chemical change (any two points).
Answer: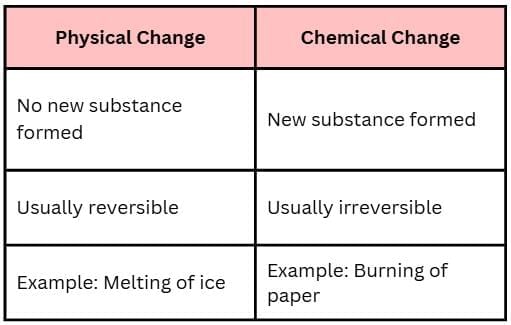
Q8. State two conditions required for chemical reactions to occur.
Answer:
Heat energy – CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂ (on heating).
Light energy – Photosynthesis (CO₂ + H₂O → Glucose + O₂ in sunlight).
Q9. What is a catalyst? Give one example.
Answer:
A catalyst is a substance that alters the rate of a reaction without undergoing permanent change.
Example: MnO₂ catalyses the decomposition of KClO₃ into KCl and O₂.
Q10. Write two observations that indicate a chemical reaction has taken place.
Answer:
Change of colour – e.g., iron in copper sulphate solution.
Evolution of gas – e.g., baking soda with vinegar gives CO₂.
Section C: Long Answer Questions (4–5 marks each)
Q11. Explain the role of heat, light, and electricity in chemical reactions with one example each.
Answer:
Heat: CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂ (decomposition).
Light: Photosynthesis (CO₂ + H₂O → Glucose + O₂).
Electricity: H₂O → H₂ + O₂ (electrolysis).
Q12. Write the main characteristics of chemical reactions with examples.
Answer:
Change of colour – Fe + CuSO₄ → green solution, copper forms.
Change of state – H₂ + O₂ → H₂O (gas to liquid).
Evolution of gas – Na₂CO₃ + acid → CO₂.
Change of smell – H₂ + S → H₂S (rotten egg smell).
Formation of precipitate – AgNO₃ + NaCl → white AgCl.
Heat change – CaO + H₂O → Ca(OH)₂ + heat.
Q13. Distinguish between:
(a) Combination and Decomposition reactions
(b) Exothermic and Endothermic reactions
Answer:
(a) Combination vs Decomposition
Combination: Two or more reactants form one product. Example: H₂ + O₂ → H₂O.
Decomposition: One reactant breaks into two or more products. Example: CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂.
(b) Exothermic vs Endothermic
Exothermic: Heat is released. Example: CaO + H₂O → Ca(OH)₂ + heat.
Endothermic: Heat is absorbed. Example: Photosynthesis (requires sunlight).
|
33 videos|58 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Language of Chemistry - Chemistry Class 7 ICSE
| 1. What is the importance of chemical symbols in the language of chemistry? |  |
| 2. How do chemical formulas represent compounds? |  |
| 3. What role do equations play in chemical reactions? |  |
| 4. Why is it necessary to balance chemical equations? |  |
| 5. What are some common examples of chemical reactions? |  |





















