Class 7 Social Science Chapter 10 Worksheet Solutions - The Constitution of India — An Introduction
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
| Match the Following |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1: What is the primary role of the Constitution of India?
a) To make laws
b) To protect citizens' rights and outline the rules of government
c) To ensure religious harmony
d) To create a system of elections
Ans: b) To protect citizens' rights and outline the rules of government
The Constitution of India serves as a rulebook that outlines how the government works, protects citizens' rights, and defines duties.
 Republic Day Parade
Republic Day Parade
Q2: When did the Constitution of India come into effect?
a) 15th August 1947
b) 26th January 1950
c) 15th August 1948
d) 26th November 1949
Ans: b) 26th January 1950
The Constitution of India came into effect on 26th January 1950, which is celebrated as Republic Day.
Q3: What does the term "Sovereign" in the Preamble of the Constitution refer to?
a) India is governed by religious leaders
b) India has the authority to make its own decisions without external interference
c) India is a monarchy
d) India’s leaders are elected
Ans: b) India has the authority to make its own decisions without external interference
"Sovereign" means India has full control over its own decisions without being controlled by other countries.
Q4: Which document lists the rules and laws for governing India?
a) The Preamble
b) The Constitution
c) The Bill of Rights
d) The Declaration of Independence
Ans: b) The Constitution
The Constitution of India is the primary document that lists the rules, laws, and rights for governing India.
Q5: Who was the Chairman of the Constituent Assembly?
a) Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
b) Dr. Rajendra Prasad
c) Jawaharlal Nehru
d) Dr. Sachidananda Sinha
Ans: b) Dr. Rajendra Prasad
Dr. Rajendra Prasad was the Chairman of the Constituent Assembly and played a significant role in the formation of the Constitution.
Q6: Which of the following is NOT a source of influence for the Indian Constitution?
a) The Indian Freedom Movement
b) France's Constitution
c) USA's Constitution
d) Russia's Revolution
Ans: d) Russia's Revolution
The Indian Constitution was influenced by various sources, including the Indian Freedom Movement, the USA's Constitution, and France's Constitution, but not Russia's Revolution.
Q7: What does the "separation of powers" in the Constitution mean?
a) The executive controls the legislative and judicial powers
b) The legislature, executive, and judiciary function independently without interfering with each other
c) The legislature is more powerful than the executive
d) The judiciary makes laws
Ans: b) The legislature, executive, and judiciary function independently without interfering with each other
The separation of powers ensures that the three branches of government—legislature, executive, and judiciary—work independently and fairly.
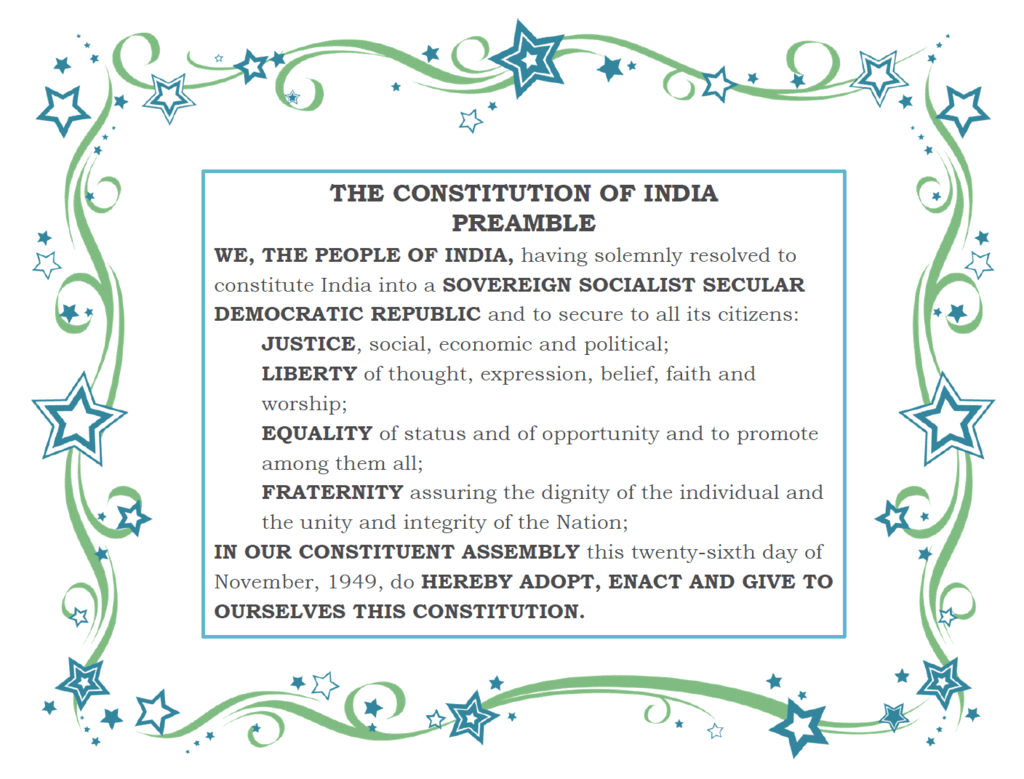
Q8: What is the Preamble of the Indian Constitution?
a) A list of laws
b) A summary of the Constitution's main values
c) The introduction to the Parliament
d) A legal document for voting
Ans: b) A summary of the Constitution's main values
The Preamble is the introduction to the Constitution that summarizes its core values, including justice, liberty, and equality.
Q9: Which of these was included in the Indian Constitution after it was adopted?
a) Universal adult franchise
b) Democracy
c) Separation of powers
d) All of the above
Ans: d) All of the above
The Indian Constitution includes principles like universal adult franchise, democracy, and separation of powers.
Q10: Who was the Chairman of the Drafting Committee that prepared the Constitution?
a) Jawaharlal Nehru
b) Dr. Rajendra Prasad
c) Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
d) Mahatma Gandhi
Ans: c) Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
Dr. B.R. Ambedkar was the Chairman of the Drafting Committee and played a key role in shaping the Constitution of India.
 Preamble
Preamble
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The Constitution of India was adopted on ________ and came into effect on ________.
Ans: 26th November 1949; 26th January 1950
The Constitution was adopted on 26th November 1949 and came into effect on 26th January 1950, which is celebrated as Republic Day.
Q2: The Constitution of India is stored in a ________-filled glass case in Parliament.
Ans: Helium
The Constitution is kept in a helium-filled glass case in Parliament to preserve its integrity.
Q3: The Constitution’s main features include fundamental rights, fundamental duties, and ________.
Ans: Directive Principles of State Policy
The Directive Principles of State Policy guide the government’s actions but are not enforceable in court.
Q4: India’s Constitution is shaped by the ________ struggle, which inspired the values of equality, freedom, and justice.
Ans: Freedom
The Indian Freedom Movement contributed significantly to the values included in the Constitution.
Q5: Dr. ________ was the first Law and Justice Minister of India and is called the Architect of the Indian Constitution.
Ans: B.R. Ambedkar
Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, as the Law and Justice Minister, played a key role in drafting the Indian Constitution.
Q6: The ________ of India includes values like justice, liberty, and equality.
Ans: Preamble
The Preamble summarizes the core values that guide the Constitution and government.
Q7: The Constitution provides for the ________ system, dividing power among the central, state, and local governments.
Ans: Three-tier
The three-tier system refers to the division of government powers into Central, State, and Local levels.
Q8: ________ is the part of the government that makes laws.
Ans: Legislature
The legislature is responsible for creating and passing laws.
Q9: ________ are basic rights that protect citizens against discrimination and exploitation.
Ans: Fundamental Rights
Fundamental Rights are guaranteed to all citizens and ensure equality, freedom, and protection.
Q10: ________ refers to the principle of shared values and mutual respect among different communities.
Ans: Secularism
Secularism in the Indian Constitution ensures that all religions are treated equally.
 Secularism
Secularism
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1: When was the Indian Constitution adopted?
Ans: The Indian Constitution was adopted on 26th November 1949.
Q2: What is the Preamble to the Indian Constitution?
Ans: The Preamble is the introduction to the Constitution, outlining its core values and goals.
Q3: Who was the first President of the Constituent Assembly?
Ans: Dr. Sachidananda Sinha was the first President of the Constituent Assembly.
Q4: Who played a key role in drafting the Indian Constitution?
Ans: Dr. B.R. Ambedkar played a key role in drafting the Indian Constitution.
Q5: What does the term "sovereign" in the Constitution mean?
Ans: "Sovereign" means India has the right to make its own decisions without outside control.
Short Answer Questions
Q1: What are the main parts of the government as outlined in the Constitution?
Ans: The three main parts of the government are the legislature, executive, and judiciary. They each have separate functions to ensure fairness and accountability.
Q2: How is the Constitution of India a "living document"?
Ans: The Constitution is a living document because it can be amended to meet the changing needs of society, as seen in the addition of Fundamental Duties and other changes over time.
Q3: Why is the Constitution important for the citizens of India?
Ans: The Constitution protects citizens' rights, outlines their duties, and ensures fairness by setting rules for governance, making it essential for maintaining justice and equality.
Q4: What role did the freedom struggle play in shaping the Indian Constitution?
Ans: The freedom struggle influenced the Constitution by promoting values like equality, justice, freedom, and fraternity, which were key principles in the document.
Q5: How did the Indian Constitution borrow ideas from other countries?
Ans: The Indian Constitution incorporated ideas from various countries, like the USA’s independent judiciary, France’s liberty, equality, and fraternity, and Ireland’s Directive Principles.
Match the Following
(Match Column A with the correct option in Column B)
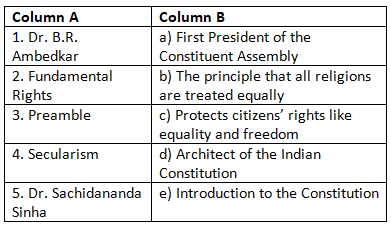
Ans: Matched Pairs and Explanations:
- 1 → d: Dr. B.R. Ambedkar was the Architect of the Indian Constitution.
- 2 → c: Fundamental Rights protect citizens' rights such as equality and freedom.
- 3 → e: The Preamble introduces the Constitution and outlines its values.
- 4 → b: Secularism means that all religions are treated equally.
- 5 → a: Dr. Sachidananda Sinha was the first President of the Constituent Assembly.
|
1 videos|107 docs
|
FAQs on Class 7 Social Science Chapter 10 Worksheet Solutions - The Constitution of India — An Introduction
| 1. What is the significance of the Constitution of India in shaping the country's governance? |  |
| 2. How does the Constitution of India promote fundamental rights for citizens? |  |
| 3. What are the main features of the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 4. How does the Constitution of India ensure the separation of powers among different branches of government? |  |
| 5. What role does the Preamble of the Constitution of India play? |  |




















