Worksheet Solutions: The End of Bipolarity | Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The USSR came into being after the socialist revolution in _______.
Ans: 1917
The socialist revolution in Russia in 1917 led to the establishment of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR).
Q2: The Soviet political system was centered around the _______ party.
Ans: Communist
The Communist Party was the sole political party in the Soviet Union, and all political power was concentrated within the party.
Q3: The group of countries under Soviet control was known as the _______ bloc.
Ans: socialist
The Communist Party was the sole political party in the Soviet Union, and all political power was concentrated within the party.
Q4: Mikhail Gorbachev became General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union in _______.
Ans: 1985
Mikhail Gorbachev assumed the leadership of the Communist Party in 1985 and initiated significant reforms in the USSR.
Q5: The Soviet Union collapsed in the year _______.
Ans: 1991
The Soviet Union officially dissolved on December 25, 1991, leading to the independence of several former Soviet republics.
Q6: The economic system in the USSR was characterized by _______ planning and control.
Ans: centralized
The Soviet economy was centrally planned and controlled by the state, with minimal market mechanisms.
Q7: The rise of _______ and desire for sovereignty led to the disintegration of the Soviet Union.
Ans: nationalism
Ethnic nationalism and the desire for independence among various Soviet republics contributed to the dissolution of the USSR.
Q8: The model of transition from an authoritarian socialist system to a democratic capitalist system was known as _______ therapy.
Ans: shock
Shock therapy referred to the rapid transition from a socialist to a capitalist economy, involving drastic economic reforms.
Q9: India maintained good relations with post-communist countries due to its shared vision of a _______ world order.
Ans: multipolar
India and post-communist countries shared a vision of a multipolar world, promoting cooperation among multiple global powers.
Q10: The end of the Soviet bloc led to the emergence of new countries wanting to join organizations like _______ and _______.
Ans: European Union and NATO.
Newly independent countries, especially in Eastern Europe, sought to join international organizations like the European Union for economic integration and NATO for security alliances.
Match the Column
Q1:
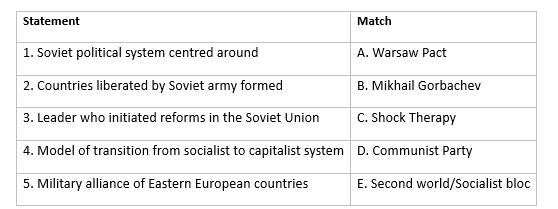
Ans: 1. Soviet political system centered around - D. Communist Party
In the Soviet political system, the Communist Party held absolute power and control. No other political party or opposition was allowed. The Communist Party was the central authority in the political structure of the USSR.
2. Countries liberated by Soviet army formed - E. Second World / socialist bloc
The countries in Eastern Europe that were liberated by the Soviet army from fascist forces after World War II formed the Second World or the socialist bloc. These countries were under Soviet influence and were part of the larger communist ideology sphere.
3. Leader who initiated reforms in the Soviet Union - B. Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Gorbachev, who became the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union in 1985, initiated significant reforms in the Soviet Union. His reforms aimed to democratize and reform the Soviet system. He played a crucial role in the eventual disintegration of the USSR.
4. Model of transition from socialist to capitalist system - C. Shock Therapy
Shock Therapy refers to the rapid transition from a socialist to a capitalist economy. It involved drastic economic reforms, including privatization and liberalization. This approach was implemented in many post-communist countries, including Russia, Central Asia, and Eastern Europe.
5. Military alliance of Eastern European countries - A. Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact was a military alliance of communist countries, led by the Soviet Union. It included Eastern European countries under the influence of the USSR. The Warsaw Pact was established as a response to NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) and was dissolved around the same time as the disintegration of the USSR.
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: The Soviet political system was centered around the communist party.
Reason: The Soviet citizens had the freedom to form multiple political parties.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Ans: (a)
The assertion is true as the Soviet political system indeed revolved around the Communist Party, which held a monopoly on political power. The reason is the correct explanation, as Soviet citizens did not have the freedom to form multiple political parties due to the one-party rule, making the Communist Party the central authority.
Q2: Assertion: Shock therapy brought ruin to the economies and disaster upon the people of the former Soviet bloc.
Reason: Shock therapy was a gradual and carefully planned economic reform process.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Ans: (b)
The assertion is true as shock therapy, involving rapid transition from socialist to capitalist economies, indeed had detrimental effects on the economies and people of the former Soviet bloc, leading to economic instability and social hardships. The reason is partially true; shock therapy was rapid but not necessarily carefully planned, contributing to its negative consequences.
Q3: Assertion: The end of the Soviet bloc led to the emergence of new countries with independent aspirations.
Reason: These countries desired to maintain close ties with Russia only.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Ans: (c)
The assertion is true; the end of the Soviet bloc resulted in the emergence of new countries seeking independent paths and sovereignty. The reason is false; while some countries desired ties with Russia, they also pursued relationships with other nations and international organizations, aiming for diverse alliances and collaborations.
Q4: Assertion: India maintained good relations with post-communist countries due to shared interests and benefits.
Reason: Post-communist countries were primarily interested in military alliances with India.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Ans: (a)
The assertion is true; India maintained positive relations with post-communist countries due to shared interests such as promoting multipolarity and mutual economic cooperation. The reason is also true, as military alliances and defense cooperation were indeed components of India's relations with these countries, strengthening their ties.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What inspired the socialist revolution in Russia in 1917?
Ans: The socialist revolution in Russia in 1917 was inspired by the ideals of socialism, aiming for social equality and an egalitarian society.
Q2: What was the role of the communist party in the Soviet political system?
Ans: The communist party was the central political authority in the Soviet Union, holding a monopoly on power and making all significant political decisions.
Q3: Which military alliance held together the socialist bloc?
Ans: The socialist bloc was held together by the Warsaw Pact, a military alliance among Soviet-controlled states.
Q4: Who initiated the series of reforms in the Soviet Union?
Ans: Mikhail Gorbachev initiated the series of reforms in the Soviet Union after becoming General Secretary of the Communist Party in 1985.
Q5: Which major republics declared the disbandment of the Soviet Union in 1991?
Ans: Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus declared the disbandment of the Soviet Union in 1991.
Q6: What was the impact of shock therapy on the Russian currency?
Ans: Shock therapy led to a dramatic decline in the value of the Russian currency (ruble) and soaring inflation, causing people to lose their savings.
Q7: Name one former Soviet republic that had a violent secessionist movement.
Ans: Chechnya, within Russia, had a violent secessionist movement, seeking independence from the Russian Federation.
Q8: What did the disintegration of the Soviet Union mean for Cold War confrontations?
Ans: The disintegration of the Soviet Union marked the end of Cold War confrontations, shifting global power dynamics and ideological disputes.
Q9: What organizations became powerful advisors to post-communist countries?
Ans: Institutions like the World Bank and International Monetary Fund (IMF) became powerful advisors to post-communist countries, guiding economic and political transitions.
Q10: Why did India benefit from its relationship with post-communist countries?
Ans: India benefited from its relationship with post-communist countries due to shared interests, diplomatic cooperation, balancing relations with other global powers, and economic collaborations, especially in defense and energy sectors.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the key features of the Soviet political system.
Ans:
- The Soviet political system was characterized by a single-party rule, with the Communist Party as the central authority.
- There was no political pluralism; all political power was concentrated within the Communist Party.
- The government controlled the economy and most aspects of public and private life, emphasizing state ownership and central planning.
Q2: Describe the factors that led to the disintegration of the Soviet Union.
Ans:
- Economic stagnation and inefficiency due to centralized planning and lack of innovation.
- Rising nationalism and desire for independence among various Soviet republics.
- Political and bureaucratic corruption, leading to public disillusionment.
- Gorbachev's reforms, like glasnost (openness) and perestroika (restructuring), inadvertently weakened the centralized Soviet control, allowing regional aspirations to surface.
Q3: What were the consequences of shock therapy on the economies and people of the former Soviet bloc?
Ans:
- Rapid privatization led to economic chaos, with many state-owned enterprises collapsing.
- Hyperinflation eroded people's savings and purchasing power.
- Dismantling of social welfare systems increased poverty and unemployment rates.
- Economic inequality widened as a small elite gained control over privatized assets.
Q4: How did the end of the Soviet bloc impact the global power dynamics?
Ans:
- The end of the Soviet bloc marked the rise of the United States as the sole superpower, altering global political dynamics.
- It led to the dominance of capitalism as the prevailing economic system internationally.
- Institutions like the World Bank and IMF gained influence, shaping economic policies of newly independent nations.
Q5: Discuss the relations between India and post-communist countries.
Ans:
- India maintained positive relations due to shared interests in a multipolar world order.
- Bilateral agreements were signed, promoting economic cooperation, technology exchange, and cultural ties.
- India's balanced foreign policy helped strengthen ties with both Russia and other post-communist countries.
Q6: Explain the role of Mikhail Gorbachev in the reforms of the Soviet Union.
Ans:
- Gorbachev initiated reforms like glasnost (openness) and perestroika (restructuring) to modernize the Soviet economy and political system.
- His policies inadvertently loosened the central control, allowing dissent and nationalist movements to gain momentum, ultimately contributing to the USSR's dissolution.
Q7: Why did some former Soviet republics experience conflicts and civil wars after the dissolution of the USSR?
Ans:
- Ethnic and nationalist tensions escalated, leading to separatist movements in regions like Chechnya (in Russia) and Nagorno-Karabakh (in Azerbaijan).
- Political power struggles emerged, intensifying ethnic and regional conflicts in newly independent states like Armenia, Georgia, and Tajikistan.
Q8: What were the main goals of shock therapy in post-communist regimes?
Ans:
- Rapid transition from state-controlled economies to market-driven capitalism.
- Dismantling of socialist economic structures, privatization of state-owned assets.
- Integration into the global economy through trade liberalization and attracting foreign investments.
- Implementing austerity measures to control inflation and stabilize national currencies.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the internal weaknesses of Soviet political and economic institutions that led to the disintegration of the Soviet Union.
Ans: Economic Stagnation and Resource Allocation: The Soviet economy allocated a substantial portion of its resources to maintain a vast nuclear and military arsenal. This emphasis on military strength, along with the financial burden of supporting satellite states in Eastern Europe and the five Central Asian Republics, led to economic stagnation. The allocation of resources for defense and foreign aid left little for domestic development, resulting in consumer shortages and economic hardship.
- Lack of Accountability and Centralization of Authority: The Communist Party, which ruled the Soviet Union for over 70 years, lacked accountability to the people. Bureaucratic inefficiencies and corruption were pervasive, causing public dissatisfaction. The lack of transparency and responsiveness in the system further alienated ordinary citizens. Additionally, the centralization of authority in a vast land with diverse cultures and ethnicities hindered effective governance and contributed to discontent.
- Rise of Nationalism and Desire for Sovereignty: As the Cold War waned, nationalist sentiments and the desire for sovereignty grew among various Soviet republics. Many republics sought greater autonomy and independence from the central Soviet government. This rise in nationalism and regional aspirations became a powerful force for disintegration, especially evident in the Baltic states, Ukraine, and Russia itself.
Q2: Examine the consequences of shock therapy on the economies and societies of the former Soviet bloc.
Ans:
- Currency Devaluation and Hyperinflation: Shock therapy, which aimed to rapidly transition to capitalism, led to a sharp decline in the value of national currencies. This resulted in hyperinflation, eroding the savings of ordinary citizens and causing economic uncertainty. People experienced difficulty affording basic necessities.
- Dismantling of Social Welfare: As state-owned enterprises were privatized, governments reduced or eliminated subsidies for basic goods and services, including healthcare and education. This change led to a loss of social safety nets, pushing a large section of the population into poverty and insecurity.
- Impact on Democratic Institutions: The focus of shock therapy was primarily on economic transition, often at the expense of building democratic institutions. This resulted in a lack of strong political parties and civil society organizations that are essential for the proper functioning of democratic systems. In some cases, the rushed privatization of state assets led to the concentration of wealth and power in the hands of a few, exacerbating economic inequality.
Q3: Explore how the end of the Soviet bloc impacted global power dynamics.
Ans:
- Emergence of the US as the Sole Superpower: The end of the Soviet bloc left the United States as the only remaining superpower in the world. This shift in the global balance of power significantly altered international relations and allowed the U.S. to assert its influence in global affairs without the constraints of the Cold War rivalry.
- Influence of Liberal Democracy: With the collapse of the socialist system and the spread of democratic ideals, the notion of liberal democracy gained prominence as the preferred system for organizing political life. Many newly independent states adopted democratic principles and institutions, shaping their domestic governance and foreign policies.
- Role of International Institutions: The end of the Soviet bloc led to the increased importance of international institutions like the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) in advising and guiding economic policies for newly independent nations. These institutions played a crucial role in shaping economic reforms and financial stability in the post-communist world.
Q4: Evaluate India's strategic relations with post-communist countries and the significance of these relationships in the global context.
Ans:
- Shared Vision of a Multipolar World Order: India's relations with post-communist countries were founded on a shared vision of a multipolar world order. Both India and these nations sought to diversify global power centers and reduce dependence on a single superpower, contributing to a more balanced and equitable international system.
- Bilateral Agreements and Mutual Benefits: India's relations with post-communist countries were reinforced through the signing of numerous bilateral agreements covering a wide range of areas, including trade, technology transfer, and cultural exchanges. These agreements not only promoted economic growth but also fostered cooperation in various sectors.
- India's Position as a Major Arms Market: India emerged as one of the major markets for Russian arms and military technology. This mutually beneficial relationship allowed India to modernize its defense capabilities while providing Russia with a vital source of revenue in the arms industry.
India's balanced approach in building and maintaining relationships with both Russia and other post-communist countries solidified its position in the international arena, playing a significant role in shaping the global geopolitical landscape.
|
34 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: The End of Bipolarity - Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What were the major events that led to the end of bipolarity in international relations? |  |
| 2. How did the Cold War contribute to the concept of bipolarity? |  |
| 3. What were the implications of the end of bipolarity for global politics? |  |
| 4. In what ways did the end of bipolarity affect international organizations? |  |
| 5. What are some of the current challenges in a multipolar world following the end of bipolarity? |  |















