Worksheet Solutions: The Three Orders | History Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The division of society in medieval Europe was known as ______________.
Ans: Feudalism
Feudalism refers to the system of social, economic, and political relationships that defined medieval European society.
Q2: The three social categories in medieval Europe were ______________, ______________, and ______________.
Ans: Christian priests, landowning nobles, and peasants
These three categories represented the clergy, nobility, and common people, which were the primary divisions in medieval European society.
Q3: Feudalism was a system of economic, legal, political, and social relationships that existed in ______________.
Ans: Europe in the medieval era
Feudalism was a complex system that encompassed various aspects of life in medieval Europe.
Q4: The Pope, the head of the Catholic Church, resided in ______________.
Ans: Rome
The Pope was the highest authority in the Catholic Church and had his residence in the city of Rome.
Q5: The nobility in medieval Europe had absolute control over their ______________.
Ans: property
The nobles had complete authority over the land they owned and could make decisions about it.
Q6: Peasants who cultivated land that belonged to the lord were known as ______________.
Ans: serfs
Serfs were bound to the land they worked on and were not free to leave. They were obligated to provide labor and a share of their produce to the lord.
Q7: The term 'taille' referred to a direct tax paid by ______________ in medieval Europe.
Ans: peasants
The taille was a direct tax imposed on the common people, primarily peasants, to support the monarch or local lords.
Q8: The development of large churches known as ______________ led to the growth of small towns around them.
Ans: Cathedral-Towns
Cathedrals became central to the communities around them, attracting people and fostering the growth of towns.
Match the Column
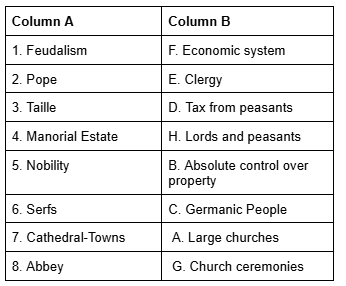
Q1: Match the items in Column A with the corresponding items in Column B. Ans:
Ans:
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: Feudalism developed in medieval France, England, and Italy.
Reason: Feudalism was a system of agricultural production.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Ans: (a)
Feudalism developed in medieval France, England, and Italy, and it was indeed a system of agricultural production, among other things.
Q2: Assertion: The nobility in medieval Europe raised troops called 'Feudal Levies.'
Reason: The nobility had absolute control over their land.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Ans: (a)
The nobility in medieval Europe did raise troops called 'Feudal Levies,' and they had absolute control over their land.
Q3: Assertion: The development of cathedrals in medieval Europe led to the growth of small towns.
Reason: Cathedrals were used for agricultural production.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Ans: (b)
The development of cathedrals did lead to the growth of small towns, but the reason given is not accurate. Cathedrals were places of worship and not related to agricultural production.
Q4: Assertion: The Black Death had a significant impact on trade in medieval Europe.
Reason: It led to a shortage of metal money due to reduced silver mine output.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Ans: (a)
The Black Death did have a significant impact on trade in medieval Europe due to reduced silver mine output leading to a shortage of metal money.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Describe the three social categories of medieval Europe.
Ans: The three social categories of medieval Europe were the clergy, nobility, and peasants. The clergy consisted of Christian priests, the nobility were landowning elites, and the peasants were common people who often worked the land.
Q2: What was the role of the Catholic Church in medieval European society?
Ans: The Catholic Church played a significant role in medieval European society, with the Pope as its head. The Church collected taxes from peasants, conducted ceremonies that mimicked feudal customs, and had considerable influence over people's lives.
Q3: Explain the term 'vassals' in relation to the nobility.
Ans: Vassals were individuals who served nobles or kings and were bound by a feudal relationship. They pledged loyalty and military service in exchange for land or protection.
Q4: Who were the knights, and what was their role in medieval Europe?
Ans: Knights were cavalry and peasant soldiers in medieval Europe. Their role was to protect the lands of the nobility, maintain order, and serve in times of conflict.
Q5: What were the two types of cultivators in medieval Europe?
Ans: Peasants and serfs were two types of cultivators in medieval Europe. Free peasants worked the lord's fields in exchange for labor rent, while serfs were bound to the land and cultivated it for their lord.
Q6: What was the significance of cathedrals in medieval Europe?
Ans: Cathedrals were large churches built in medieval Europe, often made of stone. They became centers of pilgrimage, attracting populations, and played a significant role in the development of small towns.
Q7: What factors contributed to the economic slowdown in Europe during the fourteenth century?
Ans: The economic slowdown in Europe during the fourteenth century was influenced by factors such as climate changes, reduced output of silver mines, and the arrival of the Black Death. These factors disrupted agriculture, trade, and the economy.
Q8: Who were the new monarchs, and what did they do to strengthen their power?
Ans: New monarchs in the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries, such as Louis XI, Maximilian, Henry VII, Isabelle, and Ferdinand, strengthened their power by organizing standing armies and centralizing authority.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the factors affecting social and economic relations in medieval Europe, including the role of the environment and new agricultural technology.
Ans: Factors Affecting Social and Economic Relations:
- The Environment: Climate changes, including colder summers, reduced the growing seasons for crops.
- Land Use: The nobility's absolute control over land limited peasants' ability to own and cultivate their land.
- New Agricultural Technology: Innovations in agriculture improved productivity and allowed for population growth.
- Urbanization: The growth of towns provided opportunities for paid work and greater freedom for peasants.
Q2: Describe the development of large churches known as cathedrals and their impact on medieval European towns.
Ans: Development of Cathedrals and Impact: Large stone cathedrals were built, primarily in France, and became centers of pilgrimage. They attracted populations and led to the growth of small towns around them. Stained glass in cathedrals conveyed biblical stories through pictures.
Q3: Discuss the political changes in Europe during the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries, and how they led to the decline of feudalism.
Ans: Political Changes in the Fifteenth and Sixteenth Centuries: New monarchs like Louis XI, Maximilian, Henry VII, Isabelle, and Ferdinand centralized power, organized standing armies, and reduced the influence of the nobility. This marked the decline of feudalism and the rise of nation-states in Europe.
Q4: How did the rise of new towns and townspeople contribute to the transformation of medieval European society?
Ans: Transformation of Medieval European Society: The growth in agriculture led to population, trade, and town expansion. Towns offered paid work and greater freedom, attracting young people from peasant families. The guild system organized economic activities and regulated product quality and sales.
Q5: Define the term 'guild' and explain its role in medieval European economic organization.
Ans: Guilds in Medieval European Economic Organization: Guilds were associations that controlled the quality, price, and sale of products in various crafts or industries. They had guild halls for ceremonial functions and meetings of guild leaders. This system ensured quality standards and regulated economic activities.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Describe the key features of the three social orders in medieval Europe, including the roles and privileges of each order. Discuss the economic and social relationships within these orders.
Ans: Key Features of the Three Social Orders in Medieval Europe:
- Clergy: The clergy, consisting of Christian priests, had a powerful role in the Catholic Church. The Pope resided in Rome, and bishops played a significant role. They collected taxes from peasants, conducted ceremonies mimicking feudal customs, and influenced society.
- Nobility: Nobles were landowners who had absolute control over their land. They could raise troops, including knights, and lived in manor houses. The nobility was central to the feudal system.
- Peasants: Peasants included both free peasants who labored for lords in exchange for land and serfs who were bound to the land they worked. They paid taxes like the 'taille' to support monarchs or local lords. Economic and social relationships within these orders were hierarchical, with the nobility having significant power over peasants. Peasants provided labor and produce in exchange for protection.
Q2: Analyze the causes and consequences of the economic slowdown in Europe during the fourteenth century, including the impact of climate changes, the shortage of metal money, and the Black Death. Explain how these factors influenced trade, agriculture, and society.
Ans: Causes and Consequences of the Economic Slowdown in Europe During the Fourteenth Century:
- Causes:
- Climate Changes: Europe experienced colder summers, reducing the time available for crop cultivation.
- Shortage of Metal Money: Silver mines in Austria and Serbia produced less silver, causing a scarcity of metal money and leading to currency devaluation.
- Black Death: Ships carrying rats carrying the bubonic plague arrived in Europe, causing a devastating pandemic and reducing population and labor force.
- Consequences:
- Economic Slowdown: Trade and economic activities were severely affected by the shortage of money, labor force, and population.
- Social Upheaval: The Black Death led to social unrest, and economic changes paved the way for the decline of feudalism.
- Political Changes: The crisis prompted political changes and the rise of new monarchs who organized standing armies, centralizing power and contributing to the decline of feudalism.
|
27 videos|125 docs|20 tests
|




















