The Making of a Global World - 4 Class 10 Worksheet History Chapter 2
Q.1. “Trade flourished and markets expanded in the 19th century, but there was a darker side to process.” Justify the statement. Marks 3
Ans. (i) In many parts of the world, these developments meant the loss of freedom and livelihoods.
(ii) Late 19th century, Europeans conquest brought about many destructive economic, social and ecological changes in the colonies.
(iii) In Africa, in the 1890s, a fast spreading disease of cattle plague or rinderpest had a terrifying impact on people’s livelihoods and the local economy.
(iv) The example of indentured labour migration from India illustrates that it was a world of faster economic growth for some and great misery and poverty for others; technological advances in Europe and new forms of coercion in Asia and Africa. (Any three)
Q.2. Describe the effects of abolishing the ‘Corn Laws’. Marks3
OR
Explain three far reaching effects of the abolition of the Corn Laws.
Ans. (i) Britain began to import food grains from the rest of the world. British agriculture was unable to compete with imports.
 The Corn Laws
The Corn Laws
(ii) Vast areas of land were now left uncultivated.
(iii) Thousands of men and women were thrown out of work. They started migrating to cities.
(iv) Food prices fell and consumption in Britain rose.
(v) Other countries: Russia, America and Australia sent food grains to meet British demand.
(vi) They required railways to link the ports. (Any three)
Q.3. Describe in brief the economic conditions of the post First World War period. Marks 5
Ans. Post First World War period economic conditions:
(i) Britain, which was the world's leading economy in the pre-war period faced a prolonged crisis.
(ii) Indian and Japanese industries were developed as Britain was occupied with war.
(iii) After the war, it was difficult for Britain to recapture its earlier position in the Indian market.
(iv) Britain was burdened with huge external debts from the US.
(v) Government reduced bloated war expenditure. This led to huge job losses and unemployment.
(vi) Grain prices witnessed a steep fall as wheat supply was disrupted during the First World War. (Any five)
Q.4. Give three examples to show that the pre-modern world changed with the discovery of new sea routes to America. Marks 3
Ans. Three examples are as follows:
(i) Many common foods, e.g., potatoes, soya, tomatoes, maize, etc., were introduced to Europe from America. These crops made a difference between life and death. The poor began to eat better and live longer in England with the introduction of potatoes.
(ii) Religious dissenters from Europe fled due to the fear of persecution in Europe and migrated to America.
(iii) Slave trade was started. European traders captured slaves in Africa and took them to America where they worked on plantations. Europe became the centre of the world trade.
(iv) Precious metals, e.g., Silver from mines located in present day Peru and Mexico also enhanced Europe’s wealth and financed its trade. (Any three)
Q.5. Explain the effect of the death of men of working age in Europe because of the First World War? Marks 3
OR
Write a note to explain "The death of men of working age in Europe because of the World War''.
Ans. (i) Majority of the people killed in the First World War were men of working age. It reduced the able bodied workforce in Europe.
(ii) With fewer earning members within the family, household incomes declined.
(iii) Women stepped in to undertake jobs that earlier only men were expected to do.
Q.6. What was Rinderpest? How did it adversely affect the lives and fortunes of the Africans? Marks 5
OR
What was Rinderpest? How did Rinderpest change the economy of the African Society?
OR
Describe briefly the effects of Rinderpest in Africa in the 1890s.
Ans. Rinderpest was the fast spreading disease of cattle plague that arrived in Africa in the late 1880s. It was carried by infected cattle imported from British Asia to feed the Italian soldiers Invading Eritrea in East Africa. Within two years, it spread throughout the whole continent. It affected the Africans in the following ways:
(i) Rinderpest moved like forest fire in Africa.
(ii) 90% of cattle were killed.
(iii) The loss of cattle destroyed African livelihoods. Earlier people rarely worked for a wage. They possessed land and livestock. Due to Rinderpest, they were forced to work for wages and so it affected the economy.
(iv) Colonial government forced the Africans into the labour market.
Q.7. Describe any five factors that led to the end of the Bretton Woods System and the beginning of globalisation. Marks 5
OR
Discuss the factors that led to the end of Bretton Woods System and the beginning of globalization.
Ans. The important reasons behind the end of Bretton Woods system are:
(i) Decline in economic power of the USA.
(ii) Change in the international financial system.
(iii) Unemployment in industrialised countries.
(iv) Shifting of production enterprises.
(v) Changes in China.
Detailed Answer:
(i) Decline in economic power of the USA:
(a) The US dollar no longer commanded confidence in the world’s principal currency.
(b) The US dollar could not maintain its value in relation to gold.
(c) Collapse of fixed exchange rates and introduction of floating exchange rates.
(ii) Change in the international financial system:
(a) The International Monetary Fund and the World Bank were created to meet the financial needs of the industrial countries.
(b) International financial system changed, and developing countries were forced to borrow from western commercial banks.
(c) This led to periodic debt crises in the developing world, increased poverty in Africa and Latin America.
(iii) Unemployment in industrialised countries:
(a) Industrial world was hit by unemployment.
(b) The number of unemployed started rising and people trudged long distances looking for any work they could find.
(iv) Shifting of production enterprises: MNCs shifted their production units to Asian countries because of cheap labour and low wages.
(v) Changes in China:
(a) China became an attraction destination for investment by foreign MNCs.
(b) China which had been cut off from the post-war world economy, since its revolution in 1949, has now come back into the fold of the world economy.
(c) Its new economic policies and the collapse of the Soviet Union has led to it. Low cost structure of the Chinese economy, its low wages, has flooded the world market with Chinese goods.
Correct the following statement and rewrite:
Q.8. The laws allowing the British government to impose restrictions on the export of corn are called the Corn Laws.
Ans. The laws allowing the British government to impose restrictions on the import of corn are called the Corn Laws.
Find the incorrect option:
Q.9. (a) Rinderpest arrived in Africa in the late 1980s.
(b) Rinderpest moved like forest fire in Africa.
(c) The loss of cattle due to this destroyed African livelihoods.
(d) Colonial government forced the Africans into the labour market.
Ans. The Incorrect option is (a): Rinderpest arrived in Africa in the late 1980s.
Correct answer is: Rinderpest arrived in Africa in the late 1880s.
Answer in one word/one sentence:
Q.10. What do we call the law that allowed the British Government to restrict the import of corn?
Ans. Corn Laws
Q.11. Who are referred to as the Bretton Woods twins?
Ans. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank.
Q.12. What is referred to as EI Dorado?
Ans. An imaginary city of gold situated in South America.
Fill in the blanks:
Q.13. India was the single largest exporter of ______ in the 1820s.
Ans. Opium
Q.14. Germany, Austria-Hungary and Ottoman Turkey were the countries known as the ______ in Europe.
Ans. Central Powers
Q.15. “The relocation of industry to low-wage countries stimulated world trade and capital flows.” Justify the statement. Marks 3
OR
Why did MNCs begin to shift their production centres to Asian countries? What were its effects?
OR
Write a note to explain the effects of the decision of MNCs to relocate production to Asian countries.
Ans. (i) MNCs shifted their production units to Asian countries because of cheap labour and low wages.
(ii) Availability of raw materials and a large market.
(iii) Effects: It stimulated world trade and the flow of capital. Countries like India, China and Brazil underwent a rapid economic transformation. It generated employment opportunities and introduced competition in the domestic markets.
Q.16. Assertion and Reason Type Questions :the question given below, there are two statements. One is marked as Assertion (A) and other as Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option:
Assertion: The Silk Routes are a good example of pre-modern trade and cultural links between distant parts of the world.
Reason: The name 'Silk Routes' points to the importance of West-bound Chinese silk cargoes along this route.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
(d) (A) is wrong but (R) is correct.
Ans. a
Q.17. Analyze the information given below, considering one of the following correct options:
The silk routes are a good example of vibrant pre-modern trade and cultural links between distant parts of the world. The name ‘silk routes’ points to the importance of West-bound Chinese silk cargoes along this route. Historians have identified several silk routes, over land and by sea, knitting together vast regions of Asia, and linking Asia with Europe and northern Africa. They are known to have existed since before the Christian Era and thrived almost till the fifteenth century. But Chinese pottery also travelled the same route, as did textiles and spices from India and Southeast Asia. In return, precious metals – gold and silver – flowed from Europe to Asia. Trade cultural exchange always went hand in hand. Early Christian missionaries almost certainly travelled this route to Asia, as did early Muslim preachers a few centuries later. Much before all this, Buddhism emerged from eastern India and spread in several directions through intersecting points on the silk routes.
(a) Pre-modern trade and cultural links
(b) Trade and Cultural exchange
(c) Silk Routes link the world
(d) Chinese Silk cargoes
Ans. c
Q.18. Complete the following table related to resources on the basis of exhaustibility:
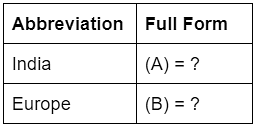
Ans. (A) - Migration of indentured labour
(B) - Selling of Manchester goods in India
Q.19. Arrange the following in the correct sequence:
(i) Indentured labour was abolished.
(ii) Rinderpest (Cattle Plague) had a terrifying impact on the livelihoods of the African people and the local economy.
(iii) The First World War was fought.
(iv) Potato Famine in Ireland
Options:
(a) (iv) - (ii) - (iii) - (i)
(b) (iii) - (i) - (ii) - (iv)
(c) (i) - (iv) - (iii) - (ii)
(d) (ii) - (iii) - (iv) - (i)
Ans. a
Q.20. Read the extract and answer the Questions that follows:
Despite years of stable and rapid growth, not all was well in this post-war world. From the 1960s the rising costs of its overseas involvements weakened the US’s finances and competitive strength. The US dollar now no longer commanded confidence as the world’s principal currency. It could not maintain its value in relation to gold. This eventually led to the collapse of the system of fixed exchange rates and the introduction of a system of floating exchange rates. from the mid-1970s the international financial system also changed in important ways. Earlier, developing countries could turn to international institutions for loans and development assistance. But now they were forced to borrow from Western commercial banks and private lending institutions. This led to periodic debt crises in the developing world, and lower incomes and increased poverty, especially in Africa and Latin America.
The industrial world was also hit by unemployment that began rising from the mid-1970s and remained high until the early 1990s. From the late 1970s MNCs also began to shift production operations to low-wage Asian countries. China had been cut off from the post-war world economy since its revolution in 1949. But new economic policies in China and the collapse of the Soviet Union and Soviet-style communism in Eastern Europe brought many countries back into the fold of the world economy. Marks 5
Questions:
(i) What was the consequence of the US Dollar not being able to maintain its position in context to gold?
(ii) Mention any two major problems which emerged due to change in the international finance system from the mid-1970s.
(iii) Which circumstances brought many countries back into the fold of the world economy?
Ans. (i) This eventually led to the collapse of the system of fixed exchange rates and the introduction of a system of floating exchange rates.
(ii) Two major problems which emerged due to change in the international finance system from the mid1970s were:
(a) Periodic debt crisis, lower income and increase in poverty.
(b) Increase in unemployment.
(iii) New economic policies in China and the collapse of the Soviet Union and Soviet-style communism in Eastern Europe brought many countries back into the fold of the world economy.
|
27 videos|79 docs|36 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|












