Worksheets With Solutions: Light Class 7 Worksheet Science Chapter 13
| Table of contents |

|
| Section A: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Section B: Short Questions |

|
| Section C: Fill in the blanks |

|
| Section D: Match the column |

|
| Section E: True/False |

|
Section A: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q.1. Which of the following is not a property of light?
(a) It travels in a straight line
(b) It can be reflected
(c) It can be refracted
(d) It can be compressed
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Light cannot be compressed as it does not have a physical substance. It is a form of energy that travels in waves and can be described as having both particle-like and wave-like properties.
Q.2. What type of mirror is used in cars to provide a wider field of view?
(a) Concave mirror
(b) Convex mirror
(c) Plane mirror
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Convex mirrors are used in cars to provide a wider field of view as they produce a smaller, virtual image that appears farther away than it actually is. This allows drivers to see more of their surroundings without having to turn their heads as much.
Q.3. Which of the following lenses is also known as a converging lens?
(a) Concave lens
(b) Convex lens
(c) Both a and b
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (b)
A convex lens is also known as a converging lens because it causes parallel light rays to converge or come together at a focal point. This type of lens is thicker in the middle than at the edges and can be used to magnify objects.
Q.4. Sir Isaac Newton proved that white light is made up of _______.
(a) 5 colours
(b) 6 colours
(c) 7 colours
(d) 8 colours
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Sir Isaac Newton proved that white light is made up of seven colours by passing a beam of light through a prism, which separates the colours into a spectrum (red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet).
Q.5. What is the name of the point where light rays converge after passing through a convex lens?
(a) Focal point
(b) Centre of curvature
(c) Principal axis
(d) Vertex
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The point where light rays converge after passing through a convex lens is called the focal point. This point is located on the principal axis and is the point where an object placed in front of the lens will form a sharp, focused image.
Section B: Short Questions
Q.1. What is rectilinear propagation of light?
Rectilinear propagation of light refers to the straight-line movement of light in a homogeneous and transparent medium.
Q.2. Explain the difference between a real image and a virtual image.
A real image is formed when light rays converge at a point after passing through a lens or mirror, whereas a virtual image is formed when light rays appear to diverge from a point but do not actually pass through that point.
Q.3. How does a concave mirror differ from a convex mirror?
A concave mirror is curved inwards and can produce real and virtual images, whereas a convex mirror is curved outwards and can only produce virtual images.
Q.4. What are the primary colours of light?
The primary colours of light are red, blue, and green. These colours can be combined in different ways to create all other colours.
Q.5. How does a Newton's disc help in understanding the concept of colours.
Newton's disc is a device that consists of a spinning disc with different colours arranged in a specific order. When the disc is spun, the colours blend together to produce white light. This helps to explain the concept of colours because it shows that white light is made up of different colours and that these colours can be separated and combined in different ways.
Section C: Fill in the blanks
Q.1. Light travels in a ___________ line.
Straight
Light travels in a straight line, also known as rectilinear propagation.
Q.2. The shadow of an object is formed when light is ___________ by it.
Blocked
When an object blocks the path of light, it creates a shadow.
Q.3. The angle of incidence is ___________ to the angle of reflection.
Equal
The angle of incidence (incoming angle of light) is equal to the angle of reflection (outgoing angle of light).
Q.4. A mirror that curves inward is called a ___________ mirror.
Concave
A concave mirror curves inward, causing light to converge at a point.
Q.5. A lens that curves inward is called a ___________ lens.
Concave
A concave lens curves inward, causing light to diverge.
Section D: Match the column
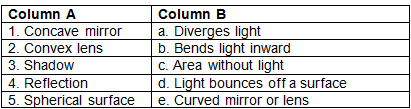

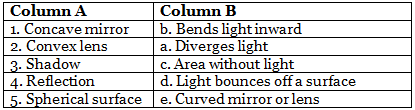
1. Concave mirror - b. Bends light inward
A concave mirror is a spherical surface that curves inward. When light rays hit a concave mirror, they are reflected towards the center of curvature. This causes the light rays to converge, or come together, at a focal point. This property of a concave mirror makes it useful for reflecting light in telescopes, headlights, and makeup mirrors.
2. Convex lens - a. Diverges light
A convex lens is a spherical surface that curves outward. When light rays pass through a convex lens, they are refracted, or bent outwards. This causes the light rays to diverge, or spread apart, rather than converge. This property of a convex lens makes it useful for correcting nearsightedness, farsightedness, and other vision problems.
3. Shadow - c. Area without light
A shadow is a dark area that results from an object blocking light. When light rays hit an object, some are absorbed, some are reflected, and some pass through the object. The area behind the object where the light is blocked is called a shadow. The size and shape of a shadow depend on the size and shape of the object, as well as the direction and intensity of the light source.
4. Reflection - d. Light bounces off a surface
Reflection is the process by which light waves bounce off a surface and change direction. When light rays hit a smooth surface, such as a mirror or a calm body of water, they reflect at the same angle as they hit the surface. This property of reflection makes it possible to see images in mirrors and to use reflective surfaces in optical devices.
5. Spherical surface - e. Curved mirror or lens
A spherical surface is a curved surface that has the same radius of curvature at every point. Spherical surfaces can be either mirrors or lenses, depending on their shape and the material they are made of. Mirrors reflect light, while lenses refract light. Both mirrors and lenses can be either convex or concave, depending on their curvature.
Section E: True/False
Q.1. Light always travels in a straight line. (True/False)
True
Light travels in a straight line until it interacts with an object or medium that causes it to bend or scatter.
Q.2. Shadows are always the same size as the object. (True/False)
False
The size of a shadow depends on the angle and direction of the light source, as well as the distance between the object and the surface on which the shadow is cast.
Q.3. A convex mirror is used as a side-view mirror in a car. (True/False)
True
Convex mirrors are used as side-view mirrors in cars because they provide a wider field of view than flat mirrors, making it easier to see objects in the driver's blind spot.
Q.4. A concave lens is used to correct nearsightedness. (True/False)
False
A concave lens is used to correct farsightedness by diverging light rays before they enter the eye. Nearsightedness is corrected with a concave lens, which converges light rays before they enter the eye.
Q.5. The colors of the spectrum are red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and purple. (True/False)
True
The colors of the visible spectrum in order are red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet.
|
139 videos|151 docs|18 tests
|