Human Geography Nature And Scope Class 12 Geography
Introduction
Geography is a fascinating field that explores every event on Earth through both systematic and regional lenses. Human geography deals with how human societies interact with the physical environment, shaping our landscapes. Scholars like Ratzel, Ellen C. Semple, and Paul Vidal de la Blache have highlighted its dynamic and interconnected nature.
What is Geography?
Geography is a field of study that is integrative, empirical, and practical. It studies each and every event on the Earth over space and time.
In simpler words, geography is a field of study that brings together different subjects, relies on real-life facts and observations, and can be applied in everyday situations.
The Earth is made up of two major components: nature, which is the physical environment, and life forms, which includes human beings.
- Physical geography: studies the physical environment of the planet
- Human geography: studies the relationship between man and nature

Geography is subject to various forms of dualisms about which scholars have been debating about. Here are three forms of dualism in geography:
- Nomothetic vs. Idiographic: The debate over whether geography should focus on creating general laws and theories (nomothetic) or on describing specific places and events in detail (idiographic).
- Regional vs. Systematic: The discussion about whether geographic studies should be organized by specific regions (regional) or by themes or systems, such as climate or population (systematic).
- Theoretical vs. Historical-Institutional: The choice between interpreting geographical phenomena using abstract theoretical frameworks or through the context of historical and institutional developments.
- It follows that even though scholars debate about a number of dualisms, most agree about the relationship between physical and human geography.
- The divisions between physical and human geography is not very valid because nature and human activities are closely interconnected and should be viewed holistically or as a whole.
Definitions of Human Geography
- Ratzel: “Human geography is the synthetic study of the relationship between human societies and the earth‟s surface”.
- Ellen C: “Human geography is the study of “the changing relationship between the un-resting man and the unstable earth.” .
- Paul Vidal de la Blache: “Conception resulting from a more synthetic knowledge of the physical laws governing our earth and of the relations between the living beings which inhabit it”.

Nature of Human Geography
- Human geography studies the inter-relationship between the physical environment and socio-cultural environment created by human beings through mutual interaction with each other.
- The elements like houses, villages, cities, road-rail networks, industries, etc, and all other elements of material culture have been created by human beings using the resources provided by the physical environment.
- While the physical environment has been greatly modified by human beings, it has also, in turn, impacted human lives.
Naturalization Of Humans and Humanisation of Nature
Naturalization Of Human
Human beings engage with their physical environment through technology, which reflects the level of cultural development in society.
- Human beings were able to create technology after gaining a deeper understanding of natural laws. For instance, knowledge of friction and heat led to the discovery of fire. In the same way, discovering the secrets of DNA and genetics allowed us to overcome many diseases.
- In the early stages humans adapted to the dictates of Nature because the level of technology was very low and the stage of human social development was also primitive.
- The type of interaction between primitive human society and strong forces of nature was termed environmental determinism.
- In the period of very low technological development, we can imagine a naturalised human who was closely connected to nature, listened to its signs, feared its power, and worshipped it.
Humanisation of Nature
- Occurs as humans develop better and more efficient technology, creating possibilities with the resources obtained from the environment.
- This leads to the creation of a cultural landscapes, as humans move from a state of necessity to a state of freedom.
- Earlier scholars termed this as possibilism, where nature provides opportunities, and humans create possibilities within environmental limits.
- Human activities leave imprints on nature, examples of which include health resorts on highlands, huge urban sprawls, fields, orchards, pastures in plains, ports on coasts, oceanic routes, and satellites in space.
- Humanisation of nature, therefore, involves modern societies overcoming environmental constraints through technology.
Neodeterminism
- Neodeterminism, introduced by Griffith Taylor, represents a middle path between environmental determinism and possibilism, suggesting that human actions are regulated by nature in a manner similar to traffic lights, where signals dictate when to stop, get set, and go. It is also known as stop and go determinism.
- The concept emphasizes that development and progress are achievable by respecting and following the environmental cues and limits, avoiding the extremes of absolute necessity (environmental determinism) and absolute freedom (possibilism).
- Neodeterminism indicates that human possibilities for development exist within environmental limits, and exceeding these limits leads to environmental degradation, as seen in issues like the greenhouse effect, ozone layer depletion, global warming, receding glaciers, and degrading lands.
- The unrestricted exploitation of nature by developed economies has resulted in severe environmental consequences, highlighting the need for a balanced approach that respects environmental constraints while pursuing development.
- Neodeterminism aims to harmonize human progress with environmental sustainability, ensuring that development is pursued responsibly to prevent irreversible damage to the natural world, thereby ending the dichotomy of 'either' 'or'.
 Schools of Thought in Human Geography
Schools of Thought in Human Geography
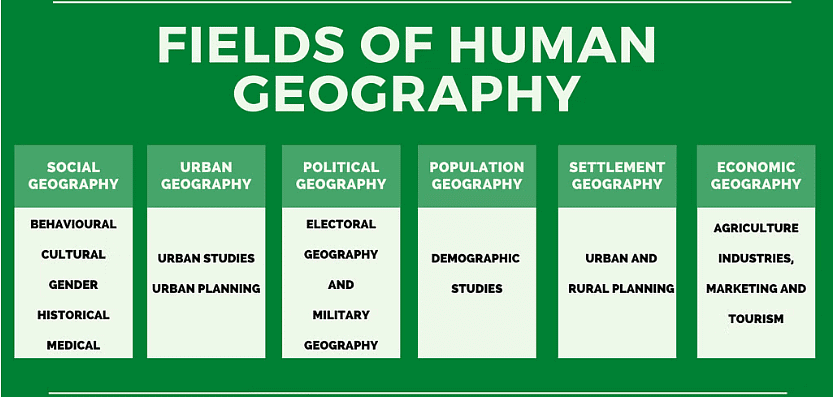
Fields and Sub fields of Human Geography
- Human geography attempts to explain the relationship between all elements of human life and the space they occur over.
- It assumes a highly inter-disciplinary nature, developing close interfaces with other sister disciplines in social sciences. This inter-disciplinary approach helps in understanding and explaining human elements on the surface of the earth.
- With the expansion of knowledge, new sub-fields have emerged within human geography. These fields and sub-fields provide a comprehensive examination of various aspects of human geography.
Broad Stages and Thrust of Human Geography
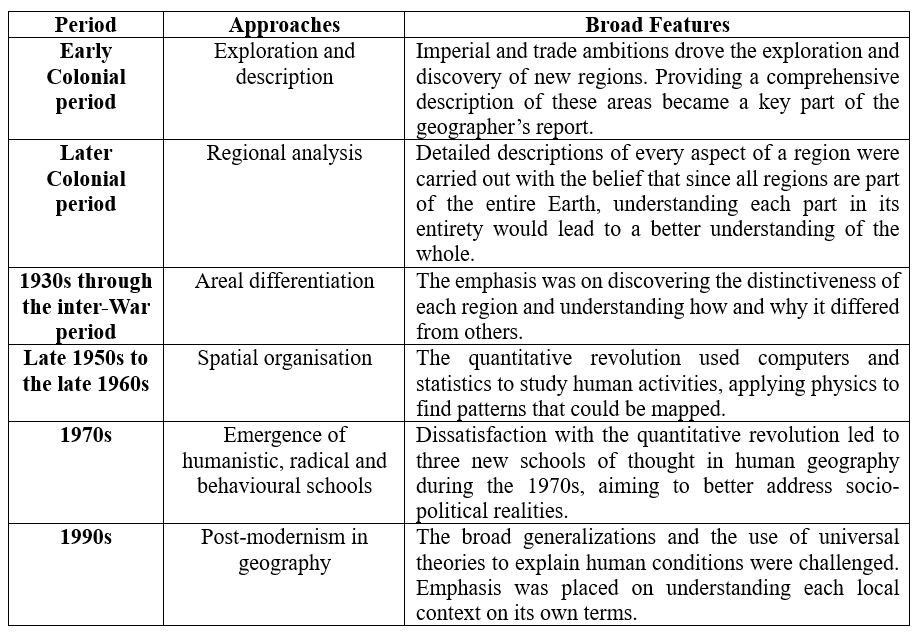 Broad Stages and Thrust of Human Geography
Broad Stages and Thrust of Human Geography
Human Geography and Sister Disciplines of Social Sciences
Conclusion
Human geography unravels the complex interplay between humans and their environment, showing how culture and technology drive this relationship. Concepts like the naturalization of humans and the humanization of nature reflect our evolving dynamics. Griffith Taylor's neodeterminism offers a balanced approach, advocating for sustainable development within environmental limits. The interdisciplinary nature of human geography broadens our understanding of the diverse and intricate interactions shaping our world.
|
50 videos|249 docs|43 tests
|
FAQs on Human Geography Nature And Scope Class 12 Geography
| 1. What is the definition of Human Geography? |  |
| 2. What is the nature of Human Geography? |  |
| 3. How do humans naturalize their surroundings and how does nature humanize humans according to Human Geography? |  |
| 4. What are some of the fields and subfields of Human Geography? |  |
| 5. Why is Human Geography important in understanding the world we live in? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Humanities/Arts exam
|

|


















