NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science - Sources of Energy
| Table of contents |

|
| Page No. 243 |

|
| Page No. 248 |

|
| Page No. 253 |

|
| Page No. 254 |

|
| Page No. 254 - 255 |

|
Page No. 243
Q1. What is a good source of energy?
Ans: A good source of energy fulfils the following criteria:
 Good Source of Energy
Good Source of Energy
- It produces a lot of heat per unit mass.
- It does a huge amount of work per unit mass.
- It is easily accessible.
- It is easy to store and transport.
- It is economical.
- It produces less amount of smoke.
Q2. What is a good fuel?
Ans: A good fuel should have the following characteristics:
- A good fuel should be easily available and release a good amount of heat on burning.
- It should not produce smoke or any other harmful gases.
It should be safe to handle, store and transport. - It should be inexpensive.
- Left no residue after burning.
 Good Fuel
Good Fuel
Q3. If you could use any source of energy for heating your food, which one would you use and why?
Ans: Natural gas can be used for heating and cooking food because it is a clean source of energy. It does not produce a huge amount of smoke on burning. Although it is highly inflammable, it is easy to use, transport, and it produces a huge amount of heat on burning.
Page No. 248
Q1. What are the disadvantages of fossil fuels?
Ans:
The disadvantages of fossil fuels are as follows:
- Burning of coal and petroleum produces a lot of pollutants causing air pollution.
- Fossil fuels release oxides of carbon, nitrogen, sulphur, etc. that cause acid rain, which affects soil fertility and potable water.
- Burning of fossil fuels produce gases such as carbon dioxide that causes global warming.
Q2. Why are we looking at alternate sources of energy?
Ans: Fossil fuels, which have been traditionally used by human beings as an energy source, are non-renewable sources of energy. These sources of energy are limited and cannot replenish on their own.
 Alternative Source of Energy
Alternative Source of Energy
They are being consumed at a large rate. If this rate of consumption continues, then fossil fuels would be exhausted from the Earth. Therefore, we have to conserve energy sources. Hence, we should look for alternative sources of energy.
Q3. How has the traditional use of wind and water energy been modified for our convenience?
Ans: Traditionally, waterfalls were used as a source of potential energy which was converted to electricity with the help of turbines. Since waterfalls are few in number, water dams have been constructed in large numbers. Nowadays, hydro-dams are used in order to harness the potential energy of stored water. In water dams, waterfalls from a height on the turbine, which produces electricity.
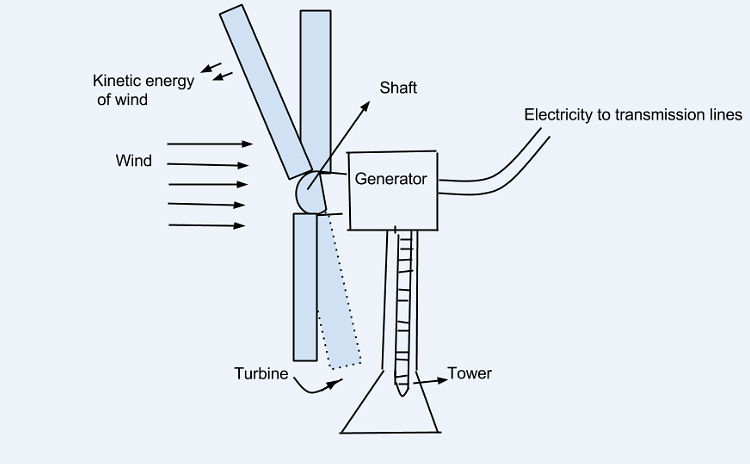 Wind and Water EnergyEarlier, the windmills were used to harness wind energy to do mechanical work such as lifting/drawing water from a well. Today, windmills are used to generate electricity. In windmills, the kinetic energy of wind is harnessed and converted into electricity. The rotatory motion of the blades turns the turbine of the electric generator to generate electricity.
Wind and Water EnergyEarlier, the windmills were used to harness wind energy to do mechanical work such as lifting/drawing water from a well. Today, windmills are used to generate electricity. In windmills, the kinetic energy of wind is harnessed and converted into electricity. The rotatory motion of the blades turns the turbine of the electric generator to generate electricity.
Page No. 253
Q1. What kind of mirror − concave, convex or plain − would be best suited for use in a solar cooker? Why?
Ans: A solar cooker uses the heat of the sunlight to cook and heat food. A mirror is used in order to reflect and focus sunlight at a point.
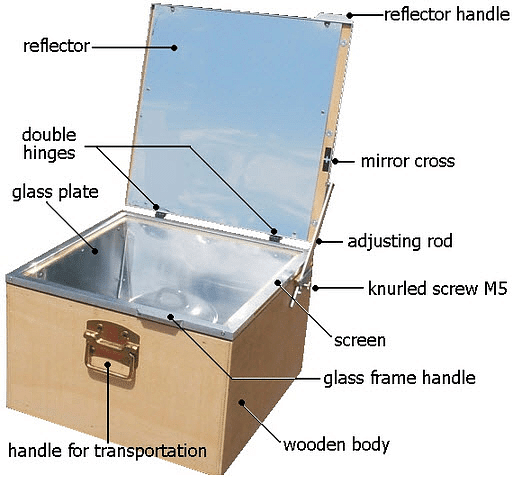 Solar Cooker: Concave MirrorA concave mirror is used in a solar cooker for this purpose. The mirror focuses all the incident sunlight at a point. The temperature at that point increases, thereby cooking and heating the food placed at that point.
Solar Cooker: Concave MirrorA concave mirror is used in a solar cooker for this purpose. The mirror focuses all the incident sunlight at a point. The temperature at that point increases, thereby cooking and heating the food placed at that point.
Q2. What are the limitations of the energy that can be obtained from the oceans?
Ans: The forms of energy that can be obtained from the ocean are tidal energy, wave energy, and ocean thermal energy. There are several limitations in order to harness these energies.
 Limitations of the Ocean Energy
Limitations of the Ocean Energy
- Tidal energy depends on the relative positioning of the Earth, the moon, and the Sun.
- High dams are required to be built to convert tidal energy into electricity.
Very strong waves are required to obtain electricity from wave energy. - To harness ocean thermal energy efficiently, the difference in the temperature of surface water (hot) and the water at depth (cold) must be 20ºC or more.
Q3. What is geothermal energy?
Ans: Geothermal power plants use the heat of the Earth to generate electricity. This heat energy of the Earth is known as geothermal energy.
When there are geological changes, the molten rocks present in the core of the earth are pushed to the earth’s crust.
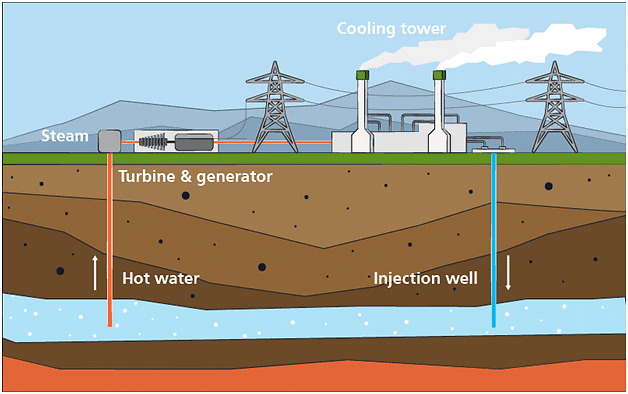 Geo-thermal Energy
Geo-thermal Energy
This forms regions of a hot spot. Steam is generated when the underground water comes in contact with these hot spots forming hot springs. This trapped steam is used to generate electricity in the geothermal power plants.
Q4. What are the advantages of nuclear energy?
Ans: The advantages of nuclear energy are as follows:
- Large amount of energy is produced per unit mass.
- It does not produce smoke. It is clean energy.
- Fission of one atom of uranium produces 10 million times the energy released by the burning of one atom of carbon.
- Fusion of four hydrogen atoms produces a huge amount of energy approximately equal to 27 MeV.
Q5. Can any source of energy be pollution-free? Why or why not?
Ans: No source of energy can be pollution-free. It is considered that solar cells are pollution-free. However, even their making causes environmental damage indirectly.
Also, in the case of nuclear energy, there is no waste produced after the fusion reactions. However, it is not totally pollution-free. To start the fusion reactions, approximately 107 K temperature is required, which is provided by fission reactions. The wastes released from fission reactions are very hazardous. Hence, no source of energy is pollution-free.
Q6. Hydrogen has been used as rocket fuel. Would you consider it a cleaner fuel than CNG? Why or why not?
Ans: Hydrogen gas is cleaner than CNG. CNG contains hydrocarbons. Therefore, it has carbon contents.
 Hydrogen Used as Rocket Fuel
Hydrogen Used as Rocket Fuel
Carbon is a form of pollutant present in CNG. On the other hand, hydrogen is waste-free. The fusion of hydrogen does not produce any waste. Hence, hydrogen is cleaner than CNG.
Page No. 254
Q1. Name two energy sources that you would consider to be renewable. Give reasons for your choices.
Ans: Two renewable sources of energy are as follows:
(a) Sun: The energy derived from the Sun is known as solar energy. Solar energy is produced by the fusion of hydrogen into helium, fusion of helium into other heavy elements, and so on. A large amount of hydrogen and helium is present in the Sun. Therefore, solar energy can replenish on its own. The Sun has 5 billion years more to burn. Hence, solar energy is a renewable source of energy.
 Renewable Energy: Suna and Wind(b) Wind: Wind energy is derived from the air blowing with high speed. Wind energy is harnessed by windmills in order to generate electricity. Air blows because of uneven heating of the Earth. Since the heating of the Earth will continue forever, wind energy will also be available forever.
Renewable Energy: Suna and Wind(b) Wind: Wind energy is derived from the air blowing with high speed. Wind energy is harnessed by windmills in order to generate electricity. Air blows because of uneven heating of the Earth. Since the heating of the Earth will continue forever, wind energy will also be available forever.
Q2. Give the names of two energy sources that you would consider to be exhaustible. Give reasons for your choices.
Ans: Two exhaustible energy sources are as follows:
(a) Coal: It is produced from dead remains of plants and animals that remain buried under the earth’s crust for millions of years. It takes millions of years to produce coal. Industrialization has increased the demand of coal. However, coal cannot replenish within a short period of time. Hence, it is a non-renewable or exhaustible source of energy.
(b) Wood: It is obtained from forests. Deforestation at a faster rate has caused a reduction in the number of forests on the Earth. It takes hundreds of years to grow a forest. If deforestation is continued at this rate, then there would be no wood left on the Earth. Hence, wood is an exhaustible source of energy.
Page No. 254 - 255
Exercise
Q1. A solar water heater cannot be used to get hot water on
(a) a sunny day
(b) a cloudy day
(c) a hot day
(d) a windy day
Ans: (b) a cloudy day
A solar water heater uses solar energy to heat water. It requires bright and intense sunlight to function properly. On a cloudy day, the sunlight reflects back in the sky from the clouds and is unable to reach the ground. Therefore, solar energy is not available for the solar heater to work properly. Hence, solar water heater does not function on a cloudy day.
Q2. Which of the following is not an example of a bio-mass energy source?
(a) wood
(b) gobar gas
(c) nuclear energy
(d) coal
Ans: (c) nuclear energy
Bio-mass is a source of energy that is obtained from plant materials and animal wastes. Nuclear energy is released during nuclear fission and fusion. In nuclear fission, uranium atom is bombarded with low-energy neutrons. Hence, uranium atom splits into two relatively lighter nuclei. This reaction produces huge amount of energy. In nuclear fusion reaction, lighter nuclei are fused together to form a relatively heavier nucleus. This reaction produces a tremendous amount of energy. Hence, nuclear energy is not an example of biomass energy source.
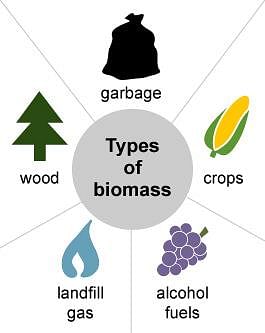 Biomass Energy
Biomass Energy
Wood is a plant material, gobar gas is formed from animal dung, and coal is a fossil fuel obtained from the buried remains of plants and animals. Hence, these are bio-mass products.
Q3. Most of the sources of energy we use represent stored solar energy. Which of the following is not ultimately derived from the Sun’s energy?
(a) Geothermal energy
(b) Wind energy
(c) Nuclear energy
(d) Bio-mass
Ans: (c) Nuclear energy
Nuclear energy is released during nuclear fission and fusion. In nuclear fission, uranium atom is bombarded with low-energy neutrons. Hence, uranium atom splits into two relatively lighter nuclei. This reaction produces huge amount of energy. In nuclear fusion reaction, lighter nuclei are fused together to form a relatively heavier nucleus. The energy required to fuse the lighter nuclei is provided by fission reactions. This reaction produces tremendous amount of energy. These reactions can be carried out in the absence or presence of sunlight. There is no effect of sunlight on these reactions. Hence, nuclear energy is not ultimately derived from Sun’s energy.
Geothermal energy, wind energy, and bio-mass are all ultimately derived from solar energy.
Geothermal energy is stored deep inside the earth’s crust in the form of heat energy. The heating is caused by the absorption of atmospheric and oceanic heat. It is the sunlight that heats the atmosphere and oceans.
wind energy is harnessed from the blowing of winds. The uneven heating of the earth’s surface by the Sun causes wind.
Bio-mass is derived from dead plants and animal wastes. Chemical changes occur in these dead plants and animal wastes in the presence of water and sunlight. Hence, bio-mass is indirectly related to sunlight.
Q4. Compare and contrast fossil fuels and the Sun as direct sources of energy
Ans: Fossil fuels are energy sources, such as coal and petroleum, obtained from underneath the Earth’s crust. They are directly available to human beings for use. Hence, fossil fuels are the direct source of energy. These are limited in amount. These are non-renewable sources of energy because they cannot be replenished in nature. Fossil fuels take millions of years for their formation. If the present fossil fuel of the Earth gets exhausted, its formation will take several years. Fossil fuels are also very costly.
On the other hand, solar energy is a renewable and direct source of energy. The Sun has been shining for several years and will do so for the next five billion years. Solar energy is available free of cost to all in unlimited amount. It replenishes in the Sun itself.
Q5. Compare and contrast bio-mass and hydroelectricity as sources of energy.
Ans: Bio-mass and hydro-electricity both are renewable sources of energy. Bio-mass is derived from dead plants and animal wastes. Hence, it is naturally replenished. It is the result of natural processes. Wood, gobar gas, etc. are some of the examples of bio-mass.
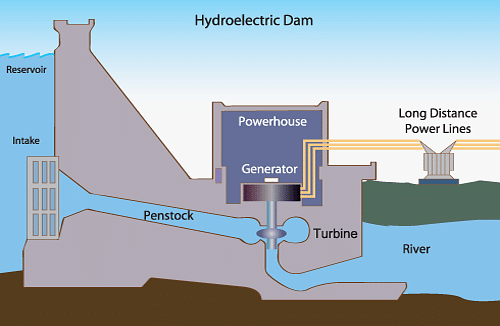 Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, on the other hand, is obtained from the potential energy stored in water at a height. Energy from it can be produced again and again. It is harnessed from water and obtained from mechanical processes.
Q6. What are the limitations of extracting energy from:
(a) the wind?
(b) waves?
(c) tides?
Ans:
(a) Wind energy is harnessed by windmills. One of the limitations of extracting energy from wind is that a windmill requires wind of speed more than 15 km/h to generate electricity. Also, a large number of windmills are required, which covers a huge area.
(b) Very strong ocean waves are required in order to extract energy from waves.
(c) Very high tides are required in order to extract energy from tides. Also, the occurrence of tides depends on the relative positions of the Sun, moon, and Earth.
Q7. On what basis would you classify energy sources as
(a) renewable and non-renewable?
(b) exhaustible and inexhaustible?
Are the options are given in (a) and (b) the same?
Ans:
(a) The source of energy that replenishes in nature is known as renewable source of energy. Sun, wind, moving water, bio-mass, etc. are some of the examples of renewable sources of energy.
The source of energy that does not replenish in nature is known as non-renewable source of energy. Coal, petroleum, natural gas, etc. are some of the examples of non-renewable sources of energy.
(b) Exhaustible sources are those sources of energy, which will deplete and exhaust after a few hundred years. Coal, petroleum, etc. are the exhaustible sources of energy.
Inexhaustible resources of energy are those sources, which will not exhaust in future. These are unlimited. Bio-mass is one of the inexhaustible sources of energy.
Yes. The options given in (a) and (b) are the same.
Q8. What are the qualities of an ideal source of energy?
Ans: An ideal source of energy must be:
- Economical
- Easily accessible
- Smoke or pollution-free
- Easy to store and transport
- Able to produce a huge amount of heat and energy on burning.
Q9. What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a solar cooker? Are there places where solar cookers would have limited utility?
Ans: The solar cooker uses Sun’s energy to heat and cook food. It is an inexhaustible and clean renewable source of energy. It is free for all and available in unlimited amount. Hence, operating a solar cooker is not expensive.
The disadvantage of a solar cooker is that it is very expensive. It does not work without sunlight. Hence, on a cloudy day, it becomes useless.
The places where the days are too short or places with cloud covers round the year have limited utility for solar cooker.
Q10. What are the environmental consequences of the increasing demand for energy? What steps would you suggest to reduce energy consumption?
Ans: Industrialization increases the demand for energy. Fossil fuels are easily accessible sources of energy that fulfil this demand. The increased use of fossil fuels has a harsh effect on the environment.
 Industrialization Demand Increases for Energy
Industrialization Demand Increases for Energy
Too much exploitation of fossil fuels increases the level of greenhouse gas content in the atmosphere, resulting in global warming and a rise in the sea level.
It is not possible to completely reduce the consumption of fossil fuels. However, some measures can be taken such as using electrical appliances wisely and not wasting electricity. Unnecessary usage of water should be avoided. Public transport system with mass transit must be adopted on a large scale. These small steps may help in reducing the consumption of natural resources and conserving them.
|
23 videos|67 docs|58 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science - Sources of Energy
| 1. What are the different sources of energy mentioned in the article? |  |
| 2. How does the article explain the concept of renewable energy? |  |
| 3. Can you provide some advantages of using solar energy? |  |
| 4. What are the environmental impacts of using fossil fuels? |  |
| 5. How does nuclear energy work? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|


















