Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Question Answers - Is Matter Around Us Pure?
Short Ans Type:
Ques 1. Suggest separation technique(s) one would need to employ to separate the following mixtures.
(a) Mercury and water
Ans: Use a separating funnel.
Explanation: Mercury and water are immiscible liquids with different densities (mercury is denser, ~13.6 g/cm³, compared to water, ~1 g/cm³). A separating funnel allows the denser mercury to settle at the bottom, and the water can be drained off from the top, effectively separating the two liquids.
(b) Potassium chloride and ammonium chloride
Ans: Sublimation.
- Ammonium chloride sublimes (turns directly from solid to gas) when heated, while potassium chloride does not sublime and remains as a solid. By heating the mixture, ammonium chloride will vaporize and can be collected separately upon cooling, leaving potassium chloride behind.
 Fig: Sublimation(c) Common salt, water and sand
Fig: Sublimation(c) Common salt, water and sand
Ans: Sedimentation, decantation, filtration and evaporation
Sedimentation is the process where solid particles settle at the bottom of a liquid. This is followed by decantation, which involves carefully pouring off the liquid, leaving the solid behind. Next, filtration is used to separate solids from liquids using a filter paper. Finally, evaporation removes the liquid, leaving behind any dissolved solids.
- Sedimentation: Particles settle at the bottom.
- Decantation: Pouring off the liquid.
- Filtration: Using filter paper to separate solids.
- Evaporation: Removing liquid to leave solids.
(d) Kerosene oil, water and salt
Ans: Use a separating funnel followed by evaporation. Kerosene oil and water are immiscible liquids, so a separating funnel can separate them, with kerosene forming the upper layer (density ~0.8 g/cm³) and water (with dissolved salt) the lower layer (density ~1 g/cm³). After separating kerosene, the salt water solution is heated to evaporate the water, leaving the salt behind.
Ques 2. Which of the tubes in figure (a) and (b) will be more effective as a condenser in the distillation apparatus?
Ans: Condenser (a) will be more effective because it provides more surface area for cooling of the vapours passing through it.
Ques 3. Salt can be recovered from its solution by evaporation. Suggest some other technique for the same?
Ans: Salt can be recovered from its solution by crystallisation. This method is often preferred over evaporation because:
- It effectively removes soluble impurities.
- It produces pure salt crystals.
In contrast, evaporation may leave behind some impurities, making crystallisation a more efficient technique.
Ques 4. The 'sea-water' can be classified as a homogeneous as well as a heterogeneous mixture. Comment.
Ans: Sea-water can be classified as both a homogeneous and a heterogeneous mixture due to the following reasons:
- It is considered homogeneous because it contains dissolved salts, creating a uniform solution.
- It is also seen as heterogeneous because it includes various insoluble components, such as sand, microbes, and shells.
Ques 5. While diluting a solution of salt in water, a student by mistake added acetone (boiling point 56°C). What technique can be employed to get back the acetone? Justify your choice.
Ans: Acetone is soluble in water, creating a homogeneous mixture. Therefore, separation using a separating funnel is not effective. The best method to recover acetone is through simple distillation due to the significant difference in boiling points:
- Boiling point of acetone: 56°C
- Boiling point of water: 100°C
In a distillation flask:
- Acetone will boil at 56°C and convert into vapour.
- The vapour can then be condensed and collected in a separate flask.
Ques 6. What would you observe when
(a) a saturated solution of potassium chloride prepared at 60°C is allowed to cool to room temperature.
Ans: When a saturated solution of potassium chloride is prepared at 60°C and then allowed to cool to room temperature, the following observations can be made:
- The solution remains saturated at the higher temperature.
- As the temperature decreases, the solubility of potassium chloride also decreases.
- Consequently, some of the potassium chloride will settle at the bottom of the container.
- This occurs because the solution can no longer hold all the dissolved solute at the lower temperature.
(b) an aqueous sugar solution is heated to dryness.
Ans: When an aqueous solution of sugar is heated to dryness:
- The water evaporates, leaving sugar behind in the container.
- If heated further, the sugar may become charred.
(c) a mixture of iron filings and sulphur powder is heated strongly.
Ans: When a mixture of iron filings and sulphur powder is heated strongly, a chemical reaction occurs, resulting in the formation of ferrous sulphide.
Ques 7. Explain why particles of a colloidal solution do not settle down when left undisturbed, while in the case of a suspension they do?
Ans: The particles in a colloidal solution do not settle down when left undisturbed due to several reasons:
- Size and Weight: Colloidal particles are smaller and lighter compared to those in a suspension.
- Brownian Movement: These particles are in constant zig-zag motion, known as Brownian movement, which counteracts the force of gravity.
- Charge and Repulsion: Colloidal particles carry a charge that causes them to repel each other, preventing them from clumping together and settling.
In contrast, particles in a suspension are larger and heavier, resulting in less movement. This allows them to settle under the influence of gravity.
Ques 8. Smoke and fog both are aerosols. In what way are they different?
Ans: Smoke and fog are both types of aerosols, but they differ in their composition:
- The dispersion medium for both is air.
- In smoke, solid carbon particles are dispersed in the air.
- In fog, liquid water droplets are dispersed in the air.
Ques 9. Classify the following as physical or chemical properties
(a) The composition of a sample of steel is: 98% iron, 1.5% carbon and 0.5% other elements.
Ans: The composition of steel (98% iron, 1.5% carbon, 0.5% other elements) reflects the chemical identity and proportion of elements in the alloy, which is a chemical property, as it involves the substance's chemical makeup rather than a physical characteristic like colour or density.
(b) Zinc dissolves in hydrochloric acid with the evolution of hydrogen gas.
Ans: The reaction of zinc with hydrochloric acid produces hydrogen gas, indicating a chemical change. This demonstrates a key chemical property of zinc.
Fig: Reaction of zinc with hydrochloric acid
(c) Metallic sodium is soft enough to be cut with a knife.
Ans: Metallic sodium is soft enough to be cut with a knife. This characteristic demonstrates the softness of sodium, which is a physical property.
(d) Most metal oxides form alkalis on interacting with water.
Ans: Most metal oxides form alkalis on interacting with water. This characteristic demonstrates the reaction between metal oxides and water, which is a chemical property.
Ques 10. The teacher instructed three students ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ respectively to prepare a 50% (mass by volume) solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH). ‘A’ dissolved 50 g of NaOH in 100 mL of water, ‘B’ dissolved 50 g of NaOH in 100g of water while ‘C’ dissolved 50g of NaOH in water to make 100 mL of solution. Which one of them has made the desired solution and why?
Ans: Concentration is the relative percentage of solute compared to the total volume of the solution and it is calculated by dividing mass by volume.
In the case of A, since 50g of NaOH has been dissolved in 100 mL of water, the total volume of solution became about 150 mL, thus concentration of NaOH would be less than 50%.
In the case of B, since 50g of NaOH has been dissolved in 100g of water, therefore, total volume of the solution would become 150 mL, consequently concentration of NaOH would again less than 50%.
In the case of C, 50g of NaOH has been dissolved in water and then volume of the solution made to 100mL, thus concentration of NaOH would become 50%.Thus, C made the solution of NaOH having concentration equal to 50%.
Ques 11. Name the process associated with the following
(a) Dry ice is kept at room temperature and at one atmospheric pressure.
Ans: Sublimation is the process that occurs when dry ice is left at room temperature and one atmospheric pressure. During this process:
- Dry ice, which is solid carbon dioxide, turns into gas.
- This transition happens without passing through a liquid state.
- Sublimation is common in substances that can easily change from solid to gas.
 Fig: Subliming dry ice
Fig: Subliming dry ice
(b) A drop of ink placed on the surface of water contained in a glass spreads throughout the water.
Ans: When a drop of ink is placed on the surface of water, it spreads out and eventually mixes with the water. This occurs due to the motion of particles, which is known as diffusion.
(c) A potassium permanganate crystal is in a beaker and water is poured into the beaker with stirring.
Ans: When potassium permanganate crystals are placed in a beaker and water is added while stirring:
- The potassium permanganate particles mix with the water.
- Stirring increases the motion of the particles, which helps them to mix more quickly.
- This process is known as diffusion.
(d) Milk is churned to separate cream from it.
Ans: When milk is churned, the process separates the cream from the milk. This separation occurs due to the action of centrifugal force, which is the principle behind centrifugation.
(e) Settling of sand when a mixture of sand and water is left undisturbed for some time.
Ans: When mixture of sand and water is left undisturbed, the sand settle at the bottom of water, thus this is the process of sedimentation.
 Fig: Mixture of sand and water
Fig: Mixture of sand and water
(f) Fine beam of light entering through a small hole in a dark room, illuminates the particles in its paths.
Ans: When a fine beam of light enters a dark room through a small hole, it illuminates particles in its path. This occurs due to:
- The collision of air and dirt particles.
- The scattering of light, which makes the dust particles appear to dance.
- This phenomenon is known as the Tyndall effect.
Ques 12. You are given two samples of water labelled as ‘A’ and ‘B’. Sample ‘A’ boils at 100°C and sample ‘B’ boils at 102°C. Which sample of water will not freeze at 0°C? Comment.
Ans: Since impurities in water raise its boiling point, thus water in sample B is impure. Hence it will not freeze at 00C because of impurities since impAns: Since impurities in water raise its boiling point, thus water in sample B is impure. Hence it will not freeze at 00C because of impurities since impurities decreases the freezing point below the 00C, this is the cause that’s why sea water remain liquid below the 00C.
Ques 13. An element is sonorous and highly ductile. Under which category would you classify this element? What other characteristics do you expect the element to possess?
Ans: Since the element is sonorous and ductile, it can be classified as a metal. Other expected characteristics of metals include:
- Good conductivity of heat and electricity
- Lustrous appearance
- Malleability (can be shaped into thin sheets)
Ques 14. Give an example each for the mixture having the following characteristics. Suggest a suitable method to separate the components of these mixtures.
(a) A volatile and a non-volatile component.
Ans: The mixture of acetone and water. In this acetone is volatile and water is non-volatile. The mixture of water and acetone can be separated by the process of distillation.
(b) Two volatile components with appreciable difference in boiling points.
Ans: Mixture of acetone and ethanol. The boiling point of acetone is 560C and that of ethyl alcohol is 78.40C.
The mixture of acetone and ethanol can Ans: Mixture of acetone and ethanol. The boiling point of acetone is 560C and that of ethyl alcohol is 78.40C.
The mixture of acetone and ethanol can be separated using fractional distillation. Since they are two immiscible liquids, thus their mixture can be separated using separating funnel.Fig: Fractional distillation(c) One of the components changes directly from solid to gaseous state.
Ans: The mixture of salt and ammonium chloride. In this mixture ammonium chloride changes from solid to gaseous state directly.The mixture of salt and ammonium chloride can be separated by the process of sublimation.
(d) Two or more coloured constituents soluble in some solvent.
Ans: The ink is the mixture of dyes of many colours. The different dyes of ink can be separated using chromatography.
Ques 15. Fill in the blanks
(a) A colloid is a __________ mixture and its components can be separated by the technique known as _________.
Ans: heterogeneous, centrifugation
(b) Ice, water and water vapour look different and display different _________ properties but they are ___________ the same.
Ans: Physical, chemically
(c) A mixture of chloroform and water taken in a separating funnel is mixed and left undisturbed for some time. The upper layer in the separating funnel will be of________ and the lower layer will be that of ___________.
Ans: Upper layer: Water
Lower layer: Chloroform
(d) A mixture of two or more miscible liquids, for which the difference in the boiling points is less than 25 K can be separated by the process called____________.
Ans: Fractional distillation
(e) When light is passed through water containing a few drops of milk, it shows a bluish tinge. This is due to the _________ of light by milk and the phenomenon is called _________ . This indicates that milk is a ________ solution.
Ans: scattering, Tyndall Effect, colloidal
Ques 16. Sucrose (sugar) crystals obtained from sugarcane and beetroot are mixed together. Will it be a pure substance or a mixture? Give reasons for the same.
Ans: Pure substance, since it contains a single component, i.e. sucrose.
Fig: Structure of sucrose
Ques 17. Give some examples of Tyndall effect observed in your surroundings?
Ans: Examples of Tyndall Effect:
- When a sunbeam shines through a window, dust particles in the air make the beam visible.
- Milk appears faint blue in a glass due to its colloidal nature, which scatters light.
- Sunlight filtering through clouds looks bright because of light scattering by water droplets.
- In a dense forest, mist with tiny water droplets creates a visible beam of light.
Ques 18. Can we separate alcohol dissolved in water by using a separating funnel? If yes, then describe the procedure. If not, explain.
Ans: The mixture of alcohol and water cannot be separated using a separating funnel, since these are not immiscible liquids. The mixture of alcohol and water can be separated by the process of distillation.
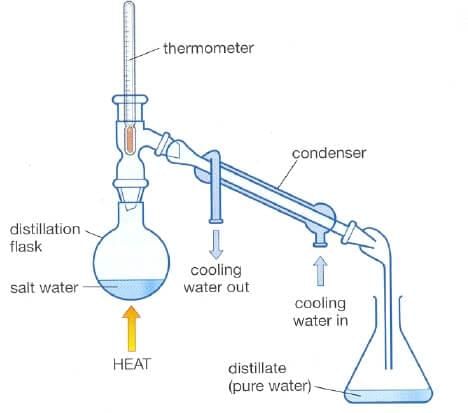 Fig: Distillation process
Fig: Distillation process
Ques 19. On heating calcium carbonate gets converted into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
(a) Is this a physical or a chemical change?
Ans: The conversion of calcium carbonate into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide is a chemical change.
(b) Can you prepare one acidic and one basic solution by using the products formed in the above process? If so, write the chemical equation involved.
Ans: Yes one acidic and one basic solution can be formed by the calcium oxide and carbon dioxide, which are product formed in the above process. Since metallic oxides are basic and non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature.Calcium oxide is a metallic oxide. Hence by dissolving it in water a basic solution is formed because of the formation of calcium hydroxide. The reaction involved Calcium oxide is a metallic oxide. Hence by dissolving it in water a basic solution is formed because of the formation of calcium hydroxide. The reaction involved in this can be written as follows:
CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
Carbon is a non metal hence carbon dioxide is acidic in nature. When it is dissolved in water an acidic solution is formed.
CO2+H2O→ H2CO3
Ques 20. Non metals are usually poor conductors of heat and electricity. They are non-lustrous, non-sonorous, non-malleable and are coloured.
(a) Name a lustrous non-metal.
Ans: Graphite.
 Fig: Graphite
Fig: Graphite
(b) Name a non-metal which exists as a liquid at room temperature.
Ans: Bromine
(c) The allotropic form of a non-metal is a good conductor of electricity. Name the allotrope.
Ans: Graphite. Graphite is a good conductor of electricity. It is an allotropic form of carbon.
(d) Name a non-metal which is known to form the largest number of compounds.
Ans: Carbon is a non-metal. It is known to form the largest number of compounds.
(e) Name a non-metal other than carbon which shows allotropy.
Ans: Sulphur is a non-metal which shows allotropy. Disulphur and trisulphur are some of the allotropes of sulphur.
(f) Name a non-metal which is required for combustion.
Ans: Oxygen
Ques 21. Classify the substances given in Figure into elements and compounds
Ans: Elements: Cu, Zn, O2, F2, Hg, Diamond
Compound: CaCO3, NaCl(aq), H2O,
Ques 22. Which of the following are not compounds?
(a) Chlorine gas
(b) Potassium chloride
(c) Iron
(d) Iron sulphide
(e) Aluminium
(f) Iodine
(g) Carbon
(h) Carbon monoxide
(i) Sulphur powder
Ans: Chlorine gas, iron, aluminium, iodine, carbon, and sulphur powder are not compounds.
- Chlorine gas is a diatomic molecule, consisting of two chlorine atoms.
- Iron and aluminium are both elements, not chemically combined with others.
- Iodine is also an elemental substance.
- Carbon can exist as a pure element, such as in graphite or diamond.
- Sulphur powder is a form of elemental sulphur.
|
84 videos|543 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Question Answers - Is Matter Around Us Pure?
| 1. What is Matter Around Us Pure? |  |
| 2. What are pure substances? |  |
| 3. What are mixtures? |  |
| 4. What are the methods of separation of mixtures? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of the Matter Around Us Pure chapter? |  |






















