NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Number System | Maths Olympiad Class 6 PDF Download
Exercise Page: 5
In questions 1 to 38, out of the four options, only one is correct. Write the correct answer.
Q1: The product of the place values of two 2’s in 428721 is
(a) 4
(b) 40000
(c) 400000
(d) 40000000
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
The product of the place values of two 2’s in 428721 is
There are two 2’s in the given number.
So, the first 2 is in the tenth place,
Then, the product is = 2 × 10
= 20
The other 2 is in place value of ten thousand.
Then, = 2 × 10000
= 20000
Therefore, the product of place values = 20 × 20000
= 400000
Q2: 3 × 10000 + 7 × 1000 + 9 × 100 + 0 ×10 + 4 is the same as
(a) 3794
(b) 37940
(c) 37904
(d) 379409
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
3 × 10000 = 30000
The place value is 30000
7 × 1000 = 7000
The place value is 7000
9 × 100 = 900
The place value is 900
0 × 10 = 0
4 = 4
Therefore, the sum of all place value is = 30000 + 7000 + 900 + 0 + 4
= 37904
Q3: If 1 is added to the greatest 7- digit number, it will be equal to
(a) 10 thousand
(b) 1 lakh
(c) 10 lakh
(d) 1 crore
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
We know that, the greatest number is 99,99,999
Then, 1 is added to 99,99,999 = 99,99,999 + 1
= 1,00,00,000
= 1 crore
Q4: The expanded form of the number 9578 is
(a) 9 × 10000 + 5 × 1000 + 7 × 10 + 8 × 1
(b) 9 × 1000 + 5 × 100 + 7 × 10 + 8 × 1
(c) 9 × 1000 + 57 × 10 + 8 × 1
(d) 9 × 100 + 5 × 100 + 7 × 10 + 8 × 1
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Consider the given number 9578,
The place value of 8 is ones = 8 × 1
The place value of 7 is tens = 7 × 10
The place value of 5 is thousand = 5 × 100
The place value of 9 is ten thousand = 9 × 1000
Q5: When rounded off to nearest thousands, the number 85642 is
(a) 85600
(b) 85700
(c) 85000
(d) 86000
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
When rounded off to nearest thousands, the number 85642 is = 86000
Q6: The largest 4-digit number, using any one digit twice, from digits 5, 9, 2 and 6 is
(a) 9652
(b) 9562
(c) 9659
(d) 9965
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Using 9 as twice from 5, 9, 2 and 6, then then number is 9965.
Q7: In Indian System of Numeration, the number 58695376 is written as
(a) 58,69, 53, 76
(b) 58,695,376
(c) 5,86,95,376
(d) 586,95,376
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
In Indian System of Numeration, the number 58695376 is written as 5 crore, eighty six lakh, ninety five thousand, three hundred and seventy six = 5,86,95,376
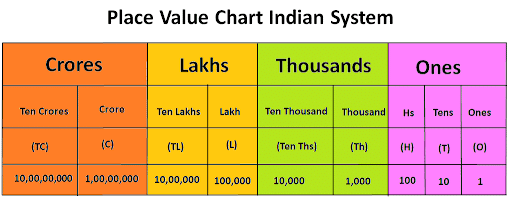 India Place Value Chart
India Place Value Chart
Q8: One million is equal to
(a) 1 lakh
(b) 10 lakh
(c) 1 crore
(d) 10 crore
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
One million is equal to ten lakh.
1,000,000 = 10,00,000
Q9: The greatest number which on rounding off to nearest thousands gives 5000, is
(a) 5001
(b) 5559
(c) 5999
(d) 5499
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The greatest number which on rounding off to nearest thousands gives 5000, is 5499.
Q10: Keeping the place of 6 in the number 6350947 same, the smallest number obtained by rearranging other digits is
(a) 6975430
(b) 6043579
(c) 6034579
(d) 6034759
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Keeping the place of 6 in the number 6350947 same, the smallest number obtained by rearranging other digits is 6034579.
Q11: Which of the following numbers in Roman numerals is incorrect?
(a) LXXX
(b) LXX
(c) LX
(d) LLX
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
As we know that, the symbol L can never be repeated.
Therefore, LLX is incorrect.
Q12: The largest 5-digit number having three different digits is
(a) 98978
(b) 99897
(c) 99987
(d) 98799
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
In the given, options there are three numbers used 9, 8 and 7
To get the largest of 5- digit we have to arrange the numbers in descending order.
Then, from the given options 99987 is the largest of 5 – digit number.
Q13: The smallest 4-digit number having three different digits is
(a) 1102
(b) 1012
(c) 1020
(d) 1002
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
In the given, options there are three numbers used 0, 1 and 2
To get the largest of 4- digit we have to arrange the numbers in ascending order.
Then, from the given options 1002 is the smallest of 4 – digit number.
Q14: Number of whole numbers between 38 and 68 is
(a) 31
(b) 30
(c) 29
(d) 28
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Number of whole numbers between 38 and 68 is 29.
Q15: The product of successor and predecessor of 999 is
(a) 999000
(b) 998000
(c) 989000
(d) 1998
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
The number which comes immediately before a particular number is called its predecessor.
The successor of a whole number is the number obtained by adding 1 to it.
So, Successor of 999 = 999 + 1 = 1000
Predecessor = 999 – 1 = 998
Then, product of successor and predecessor of 999 is = 1000 × 998
= 998000
Q16: The product of a non-zero whole number and its successor is always
(a) an even number
(b) an odd number
(c) a prime number
(d) divisible by 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
The product of a non-zero whole number and its successor is always an even number.
For example: – 4 × 5 = 20, 7 × 8 = 56
Q17: A whole number is added to 25 and the same number is subtracted from 25. The sum of the resulting numbers is
(a) 0
(b) 25
(c) 50
(d) 75
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Let us assume the number be x.
From the question it is given that, number is added to 25 = x + 25
The same number is subtracted to from 25 = 25 – x
Then, the sum of the resulting numbers is = (x + 25) + (25 – x)
= x + 25 + 25 – x
= 50 + x – x
= 50 + 0
= 50
Q18: Which of the following is not true?
(a) (7 + 8) + 9 = 7 + (8 + 9)
(b) (7 × 8) × 9 = 7 × (8 × 9)
(c) 7 + 8 × 9 = (7 + 8) × (7 + 9)
(d) 7 × (8 + 9) = (7 × 8) + (7 × 9)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Consider the left hand side = 7 + 8 × 9
= 7 + (8 × 9)
= 7 + 72
= 79
Now, consider the right hand side = (7 + 8) × (7 + 9)
= 15 × 16
= 240
By comparing LHS and RHS
LHS ≠ RHS
79 ≠ 240
Q19: By using dot (.) patterns, which of the following numbers can be arranged in all the three ways namely a line, a triangle and a rectangle?
(a) 9
(b) 10
(c) 11
(d) 12
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)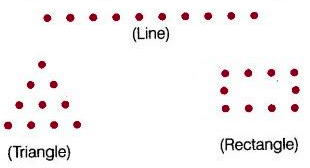
Q20: Which of the following statements is not true?
(a) Both addition and multiplication are associative for whole numbers.
(b) Zero is the identity for multiplication of whole numbers.
(c) Addition and multiplication both are commutative for whole numbers.
(d) Multiplication is distributive over addition for whole numbers.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Q21: Which of the following statements is not true?
(a) 0 + 0 = 0
(b) 0 – 0 = 0
(c) 0 × 0 = 0
(d) 0 ÷ 0 = 0
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Zero divided by zero is not defined.
Q22: The predecessor of 1 lakh is
(a) 99000
(b) 99999
(c) 999999
(d) 100001
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
The number which comes immediately before a particular number is called its predecessor.
The predecessor of 1 lakh is = 1,00,000 – 1
= 99,999
Q23: The successor of 1 million is
(a) 2 millions
(b) 1000001
(c) 100001
(d) 10001
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
The successor of a whole number is the number obtained by adding 1 to it.
We know that, 1 million = 10,00,000
Then, successor = 10,00,000 + 1
= 10,00,001
Q24: Number of even numbers between 58 and 80 is
(a) 10
(b) 11
(c) 12
(d) 13
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Even numbers between 58 and 80 are 60, 62, 64, 66, 68, 70, 72, 74, 76, 78.
Q25: Sum of the number of primes between 16 to 80 and 90 to 100 is
(a) 20
(b) 18
(c) 17
(d) 16
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Prime numbers between 16 to 80 = 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73 and 79.
Then, number of primes between 16 to 80 = 16
Prime numbers between 90 to 100 = 97
Then, number of primes between 90 to 100 = 1
Therefore, Sum of the number of primes between 16 to 80 and 90 to 100 is,
= 16 + 1
= 17
Q26: Which of the following statements is not true?
(a) The HCF of two distinct prime numbers is 1
(b) The HCF of two co prime numbers is 1
(c) The HCF of two consecutive even numbers is 2
(d) The HCF of an even and an odd number is even.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The HCF of an even and an odd number is odd number.
Q27: The number of distinct prime factors of the largest 4-digit number is
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 5
(d) 11
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
The largest 4 – digit number = 9999
Prime factors of 9999 = 3 × 3 × 11 × 101
So, 9999 = 32 × 11 × 101
Therefore, distinct prime factors are = 3, 11 and 101
Number of distinct prime factors of the largest 4-digit number is = 3
Q28: The number of distinct prime factors of the smallest 5-digit number is
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 8
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
The smallest 5 – digit number = 10000
Prime factors of 10000 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 5 × 5 × 5 × 5
So, 10000 = 24 × 54
Therefore, distinct prime factors are = 2 and 5
Number of distinct prime factors of the smallest 5-digit number is = 2
Q29: If the number 7254*98 is divisible by 22, the digit at * is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 6
(d) 0
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Take the alternating sum of the digits in the number, read from left to right. If that is divisible by 11, then the original number.
7 – 2 + 5 – 4 + * – 9 + 8 = (5 + *)
For the given number 7254 * 98 to be divisible by 11,
(5 + *) must also be divisible by 11
So, 5 + * = 11
Therefore * = 11 – 5
= 6
Q30: The largest number which always divides the sum of any pair of consecutive odd numbers is
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 8
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
1 + 3 = 4 = 4/4 = 1
3 + 5 = 8 = 8/4 = 2
The largest number which always divides the sum of any pair of consecutive odd numbers is 4.
Q31: A number is divisible by 5 and 6. It may not be divisible by
(a) 10
(b) 15
(c) 30
(d) 60
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The LCM of 6 and 5 is 30.
So, 30 is divisible by 10, 15 and 30 in the given options.
But, 30 is not divisible by 60.
Q32: The sum of the prime factors of 1729 is
(a) 13
(b) 19
(c) 32
(d) 39
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The prime factors of 1729 = 7 × 13 × 19
Therefore, the sum of prime numbers = 7 + 13 + 19
= 39
Q33: The greatest number which always divides the product of the predecessor and successor of an odd natural number other than 1, is
(a) 6
(b) 4
(c) 16
(d) 8
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Let us assume an odd natural number be 5.
Then, predecessor of 5 = 5 -1 = 4
Successor of 5 = 5 + 1 = 6
Then, the product of predecessor and successor = 4 × 6
= 24
24 is divided by 4 = 24/4 = 6
Therefore, the greatest number which always divides the product of the predecessor and successor of an odd natural number other than 1, is 4.
Q34: The number of common prime factors of 75, 60, 105 is
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Prime factors of,
75 = 3 × 5 × 5
60 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 5
105 = 3 × 5 × 7
So, common prime factors in the given three numbers are 3 and 5.
Therefore, the number of common prime factors of 75, 60, 105 is 2.
Q35: Which of the following pairs is not coprime?
(a) 8, 10
(b) 11, 12
(c) 1, 3
(d) 31, 33
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
First of all, both the numbers are even.
Then, common factor of both numbers is 2 other than 1.
Therefore, 8 and 10 are not coprime.
Q36: Which of the following numbers is divisible by 11?
(a) 1011011
(b) 1111111
(c) 22222222
(d) 3333333
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
To check the divisibility of a number by 11, the rule is, find the difference between the sum of the digits at odd places (from the right) and the sum of the digits at even places (from the right) of the number. If the difference is either 0 or divisible by 11, then the number is divisible by 11.
So, 2 – 2 + 2 – 2 + 2 – 2 + 2 – 2 = 0
Therefore, 22222222 is divisible by 11.
Q37: LCM of 10, 15 and 20 is
(a) 30
(b) 60
(c) 90
(d) 180
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Factors of 10, 15 and 30 is,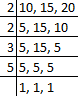
Then, LCM of 10, 15 and 30 is 2 × 2 × 3 × 5 × 1 = 60
Q38: LCM of two numbers is 180. Then which of the following is not the HCF of the numbers?
(a) 45
(b) 60
(c) 75
(d) 90
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Factors of 180.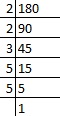
Then, factors of 180 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 5
180 is not divided by 180.
Therefore, 75 is not the HCF of the number 180.
In questions 39 to 98 state whether the given statements are true (T) or false (F).
Q39: In Roman numeration, a symbol is not repeated more than three times.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
As per the rule of the Roman numerals, a symbol is not repeated more than three times.
Q40: In Roman numeration, if a symbol is repeated, its value is multiplied as many times as it occurs.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
If a symbol is repeated, its value is added as many times as it occurs: i.e. II is equal 2, XX is 20 and XXX is 30.
Q41: 5555 = 5 × 1000 + 5 × 100 + 5 × 10 + 5 × 1
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
Left Hand Side = 5555
Right Hand Side = 5 × 1000 + 5 × 100 + 5 × 10 + 5 × 1
= 5000 + 500 + 50 + 5
= 5555
Left Hand Side = Right Hand Side
Q42: 39746 = 3 × 10000 + 9 × 1000 + 7 × 100 + 4 × 10 + 6
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
Left Hand Side = 39746
Right Hand Side = 3 × 10000 + 9 × 1000 + 7 × 100 + 4 × 10 + 6
= 30000 + 9000 + 700 + 40 + 6
= 39746
Left Hand Side = Right Hand Side
Q43: 82546 = 8 × 1000 + 2 × 1000 + 5 × 100 + 4 × 10 + 6
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Left Hand Side = 82546
Right Hand Side = 8 × 1000 + 2 × 1000 + 5 × 100 + 4 × 10 + 6
= 8000 + 2000 + 500 + 40 + 6
= 10,546
Left Hand Side ≠ Right Hand Side
Q44: 532235 = 5 × 100000 + 3 × 10000 + 2 × 1000 + 2 × 100 + 3 × 10 + 5
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
Left Hand Side = 532235
Right Hand Side = 5 × 100000 + 3 × 10000 + 2 × 1000 + 2 × 100 + 3 × 10 + 5
= 5,00,000 + 30,000 + 2000 + 200 + 30 + 5
= 5,32,235
Left Hand Side = Right Hand Side
Q45: XXIX = 31
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Where, X = 10
IX = 9
So, XXIX = 10 + 10 + 9
= 29
Q46: LXXIV = 74
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
Where, L = 50
X = 10
IV = 4
So, LXXIV = 50 + 10 + 10 + 4
= 74
Q47: The number LIV is greater than LVI.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Where, L = 50
IV = 4
VI = 6
So, LIV = 50 + 4 = 54
LVI = 50 + 6
Therefore, 54 < 56
Hence, LIV < LVI
Q48: The numbers 4578, 4587, 5478, 5487 are in descending order.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
In the question, the arrangement of the numbers in ascending order.
Descending order of the given number = 5487, 5478, 4587, 4578.
Q49: The number 85764 rounded off to nearest hundreds is written as 85700.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
The number 85764 rounded off to nearest hundreds is written as 85800.
Q50: Estimated sum of 7826 and 12469 rounded off to hundreds is 20,000.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
The number 7826 rounded off to nearest hundreds is written as 7800.
The number 12469 rounded off to nearest hundreds is written as 12500
So, sum of numbers after rounded off to hundreds = 7800 + 12500 = 20,300
Therefore, 20,300 is nearest to 20,000.
Q51: The largest six digit telephone number that can be formed by using digits 5, 3, 4, 7, 0, 8 only once is 875403.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
The largest six digit telephone number that can be formed by using digits 5, 3, 4, 7, 0, 8 only once is 875430.
Q52: The number 81652318 will be read as eighty one crore six lakh fifty two thousand three hundred eighteen.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
The given number 8,16,52,318 will be read as eight crore sixteen lakh fifty two thousand three hundred and eighteen.
Q53: The largest 4-digit number formed by the digits 6, 7, 0, 9 using each digit only once is 9760.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
Q54: Among kilo, milli and centi, the smallest is centi.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Among kilo, milli and centi, the smallest is milli.
Q55: Successor of a one-digit number is always a one-digit number.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
The successor of a whole number is the number obtained by adding 1 to it.
Example: – consider the number 9 it is a one digit, then its successor = 9 + 1 = 10.
Q56: Successor of a 3-digit number is always a 3-digit number.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
The successor of a whole number is the number obtained by adding 1 to it.
Example: – consider 3-digit number 999 it is a one digit, then its successor = 999 + 1 = 1000.
Q57: Predecessor of a two-digit number is always a two-digit number.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
The number which comes immediately before a particular number is called its predecessor.
Example: – consider 2-digit number 10, then its predecessor = 10 – 1 = 9.
Q58: Every whole number has its successor.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
Q59: Every whole number has its predecessor.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Consider the whole number 0,
Then, its predecessor = 0 – 1 = -1
– 1 is an integer.
Q60: Between any two natural numbers, there is one natural number.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Consider the two natural numbers 4 and 8.
Then, natural numbers between 4 and 8 are 5, 6, 7.
Q61: The smallest 4-digit number is the successor of the largest 3-digit number.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
The successor of a whole number is the number obtained by adding 1 to it.
The largest 3-digit number = 999
Then, its successor = 999 + 1
= 1000
Q62: Of the given two natural numbers, the one having more digits is greater.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
As per the rule, Of the given two natural numbers, the one having more digits is greater.
Q63: Natural numbers are closed under addition.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
We know that, sum of two natural numbers is always natural number.
Therefore, natural numbers are closed under addition.
Q64: Natural numbers are not closed under multiplication.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
We know that, multiplication of two natural numbers is always natural number.
Therefore, natural numbers are closed under multiplication.
Q65: Natural numbers are closed under subtraction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Difference of two natural numbers are not always a natural number.
Therefore, natural numbers are not closed under subtraction.
Q66: Addition is commutative for natural numbers.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
Let us assume ‘a’ and ‘b’ are the two natural numbers.
Then commutative for natural numbers is a + b = b + a.
Consider the two natural numbers 2 and 4.
Where, a = 2, b = 4
a + b = b + a
2 + 4 = 4 + 2
6 = 6
Q67: is the identity for addition of whole numbers.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Zero (0) is the identity for addition of whole numbers.
Consider any whole number i.e. 8.
Then, 8 + 0 = 8
Q68: is the identity for multiplication of whole numbers.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
Consider any whole number i.e. 6.
6 × 1 = 6
Q69: There is a whole number which when added to a whole number, gives the number itself.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
Zero (0) is a whole number which when added to a whole number, gives the number itself.
Q70: There is a natural number which when added to a natural number, gives the number itself.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
We know that, ‘0’ is not a natural number.
Therefore, there is no any natural number which when added to a natural number, gives the number itself.
Q71: If a whole number is divided by another whole number, which is greater than the first one, the quotient is not equal to zero.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
As per the standard rule, if a whole number is divided by another whole number, which is greater than the first one, the quotient is not equal to zero.
Q72: Any non-zero whole number divided by itself gives the quotient 1.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
Consider any non-zero whole number i.e. 5
5 is divided by itself = 5/5 = 1
Q73: The product of two whole numbers need not be a whole number.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
The product of two whole number is always a whole number.
Because, we know that, whole numbers are closed under multiplication.
Q74: A whole number divided by another whole number greater than 1 never gives the quotient equal to the former.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
As per the standard rule, a whole number divided by another whole number greater than 1 never gives the quotient equal to the former.
Q75: Every multiple of a number is greater than or equal to the number.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
As per the standard rule, every multiple of a number is greater than or equal to the number.
2 × 1 = 2
2 × 3 = 6
Q76: The number of multiples of a given number is finite.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
The number of multiples of a given number is infinite.
Because, we know that numbers are infinite.
Q77: Every number is a multiple of itself.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
We know that, 1 is the identity for multiplication of whole numbers
Therefore, any number is multiplied by 1 we get the number itself.
Hence, every number is a multiple of itself.
Q78: Sum of two consecutive odd numbers is always divisible by 4.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
For example, 1 + 3 = 4 = 4/4 = 1
11 + 13 = 24 = 24/4 = 6
Q79: If a number divides three numbers exactly, it must divide their sum exactly.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
As per the standard rule, if a number divides three numbers exactly, it must divide their sum exactly.
Let us consider one number i.e. 2, it divides 4, 6 and 8.
Then, sum of three numbers = 4 + 6 + 8
= 18 is exactly divisible by 2
Q80: If a number exactly divides the sum of three numbers, it must exactly divide the numbers separately.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Q81: If a number is divisible both by 2 and 3, then it is divisible by 12.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Let us consider the number 6, it is actually divisible by 2 and 3, But 6 is not divisible by 12.
Q82: A number with three or more digits is divisible by 6, if the number formed by its last two digits (i.e., ones and tens) is divisible by 6.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Q83: A number with 4 or more digits is divisible by 8, if the number formed by the last three digits is divisible by 8.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
As per the rule of divisibility test, a number with 4 or more digits is divisible by 8, if the number formed by the last three digits is divisible by 8.
Q84: If the sum of the digits of a number is divisible by 3, then the number itself is divisible by 9.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
As per the rule of divisibility test, the sum of the digits of a number is divisible by 9, then the number itself is divisible by 9.
Q85: All numbers which are divisible by 4 may not be divisible by 8.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
Consider the number 20, it is divisible by 4 but not divisible by 8.
Q86: The Highest Common Factor of two or more numbers is greater than their Lowest Common Multiple.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
The Highest Common Factor of two or more numbers is lower than their Lowest Common Multiple.
Q87: LCM of two or more numbers is divisible by their HCF.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
As per the rule, LCM of two or more numbers is divisible by their HCF.
Q88: LCM of two numbers is 28 and their HCF is 8.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
From the question it is given that, LCM of two numbers is 28 and their HCF is 8.
But, 28 is not exactly divide by 8.
Q89: LCM of two or more numbers may be one of the numbers.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
Consider the two numbers 2 and 4.
Then, LCM of 2 and 4 is 4.
Q90: HCF of two or more numbers may be one of the numbers.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
Q91: Every whole number is the successor of another whole number.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
We know that, 0 is the whole number.
0 is no the successor of another whole number.
Q92: Sum of two whole numbers is always less than their product.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
For example:-
2 + 3 = 5
2 × 3 = 6
From the above example, we can say that sum of two whole numbers is not always less than their product.
Q93: If the sum of two distinct whole numbers is odd, then their difference also must be odd.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
Consider the two odd numbers 2 and 5.
Then, sum = 2 + 5 = 7 it is an odd number.
Now, difference = 2 – 5 = 3 it also an odd number.
Q94: Any two consecutive numbers are coprime.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
Co-prime number is a set of numbers or integers which have only 1 as their common factor i.e. their highest common factor (HCF) will be 1. Co-prime numbers are also known as relatively prime or mutually prime numbers. It is important that there should be two numbers in order to form co-primes.
Q95: If the HCF of two numbers is one of the numbers, then their LCM is the other number.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
Q96: The HCF of two numbers is smaller than the smaller of the numbers.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
The HCF of two numbers is either greater than or equal to the smaller of the numbers.
Q97: The LCM of two numbers is greater than the larger of the numbers.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
The LCM of two numbers may be equal to or greater than the larger of the numbers.
Q98: The LCM of two coprime numbers is equal to the product of the numbers.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
In questions 99 to 100, fill in the blanks to make the statements true.
Q99: (a) 10 million = _____ crore.
 View Answer
View Answer 
10 million = 1 crore
We know that, 1 million = 10 lakh
Then, 10 million = 10 × 10 = 100 lakh = 1,00,00,000
Therefore, 10 million = 1 crore.
(b) 10 lakh = _____ million.
 View Answer
View Answer 
10 lakh = 1 million.
Q100: (a) 1 metre = _____ millimetres.
 View Answer
View Answer 
1 metre = 1000millimetres
We know that, 1 metre = 100 centimetre
1 centimetre = 10 millimeter
Then, 100 cm = 10 × 100 = 1000 millimetres
(b) 1 centimetre = _____ millimetres.
 View Answer
View Answer 
1 centimetre = 10 millimetres.
(c) 1 kilometre = _____ millimetres.
 View Answer
View Answer 
1 kilometre = 10,00,000 millimetres.
We know that, 1 km = 1000 meters.
1 metre = 100 centimetre
1000 metre = 1000 × 100
= 1,00,000 centimetre
1 cm = 10 millimetres
Then, 1,00,000 centimetre = 10 × 1,00,000 = 10,00,000 millimetres
Q101: (a) 1 gram = _____ milligrams.
(b) 1 litre = _____ millilitres.
(c) 1 kilogram = _____ miligrams.
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) 1000,
(b) 1000,
(c) 10,00,000
Q102: 100 thousands = _____ lakh.
Q103: Height of a person is 1m 65cm. His height in millimetres is_______.
 View Answer
View Answer 
1650 : 1 m 65 cm = (1000 + 650) mm = 1650 mm
Q104: Length of river ‘Narmada’ is about 1290km. Its length in metres is_______.
 View Answer
View Answer 
1290000 : 1290 km = (1290 × 1000) m = 1290000 m
Q105: The distance between Sringar and Leh is 422km. The same distance in metres is_____.
 View Answer
View Answer 
422000 : 422 km= (422 × 1000) m = 422000 m
Q106: Writing of numbers from the greatest to the smallest is called an arrangement in _____ order.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Descending
Q107: By reversing the order of digits of the greatest number made by five different non-zero digits, the new number is the _____ number of five digits.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Smallest
By reversing the order of digits of the greatest number made by five different non-zero digits, the new number is the smallest number of these digits.
Q108: By adding 1 to the greatest_____ digit number, we get ten lakh.
 View Answer
View Answer 
6 : Greatest 6-digit number = 999999
By adding 1 to 999999, we get 1000000.
Q109: The number five crore twenty three lakh seventy eight thousand four hundred one can be written, using commas, in the Indian System of Numeration as _____.
 View Answer
View Answer 
5, 23, 78, 401
Q110: In Roman Numeration, the symbol X can be subtracted from_____, M and C only.
Q111: The number 66 in Roman numerals is_____.
 View Answer
View Answer 
LXVI : 66 = LXVI
Q112: The population of Pune was 2,538,473 in 2001. Rounded off to nearest thousands, the population was __________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
2,538,000
Q113: The smallest whole number is_____.
 View Answer
View Answer 
0 : 0 is the smallest whole number.
Q114: Successor of 106159 is _____.
 View Answer
View Answer 
106160 : Successor of 106159 is 106159 + 1, i.e., 106160
Q115: Predecessor of 100000 is_____.
 View Answer
View Answer 
99999 : Predecessor of 100000 is 100000-1, i.e., 99999
Q116: 400 is the predecessor of _____.
 View Answer
View Answer 
401 : 400 is the predecessor of 400 + 1, i.e., 401
Q117: _____ is the successor of the largest 3 digit number.
 View Answer
View Answer 
1000 : Largest 3 digit number = 999
Successor of 999 is 999 + 1, i.e., 1000
Q118: If 0 is subtracted from a whole number, then the result is the _____ itself .
 View Answer
View Answer 
Number
Q119: The smallest 6 digit natural number ending in 5 is _____.
 View Answer
View Answer 
100005
Q120: Whole numbers are closed under _____ and under_____.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Addition, multiplication
Q121: Natural numbers are closed under _____ and under_____.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Addition, multiplication
Q122: Division of a whole number by _____ is not defined.
Q123: Multiplication is distributive over _____ for whole numbers.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Addition
Q124: 2395 × _____ = 6195 × 2395
 View Answer
View Answer 
6195 : Since, multiplication is commutative for whole numbers.
Q125: 1001 × 2002 = 1001 × (1001+_____ )
 View Answer
View Answer 
1001
Q126: 10001 × 0 = _____
Q127: 2916 × _____ = 0
Q128: 9128 × _____ = 9128
 View Answer
View Answer 
1 : Since, 1 is the multiplicative identity for whole numbers.
Q129: 125 + (68+17) = (125 + _____ ) + 17
 View Answer
View Answer 
68 : Since, addition is associative for whole numbers.
Q130: 8925 ×1 = _____
 View Answer
View Answer 
8925
Q131: 19 × 12 + 19 = 19 × (12 + _____)
 View Answer
View Answer 
1 : Since, multiplication is distributive over addition for whole numbers.
Q132: 24 × 35 = 24 × 18 + 24 × _____
 View Answer
View Answer 
17
Q133: 32 × (27 × 19) = (32 × _____ ) × 19
 View Answer
View Answer 
27 : Since, multiplication is associative for whole numbers.
Q134: 786 × 3 + 786 × 7 = _____
 View Answer
View Answer 
7860 : 786 × 3 + 786 × 7 = 786 × (3 + 7)
= 786 × 10 = 7860
Q135: 24 × 25 = 24 × 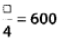
 View Answer
View Answer 
100
Q136: A number is a _____ of each of its factor.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Multiple
Q137: _____ is a factor of every number.
Q138: The number of factors of a prime number is_____.
Q139: A number for which the sum of all its factors is equal to twice the number is called a _____ number.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Perfect
Q140: The numbers having more than two factors are called _____ numbers.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Composite
Q141: 2 is the only _____ number which is even.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Prime
Q142: Two numbers having only 1 as a common factor are called _____ numbers.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Co-prime
Q143: Number of primes between 1 to 100 is _____.
 View Answer
View Answer 
25 : Prime numbers between 1 to 100 are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97.
So, there are 25 primes between 1 to 100.
Q144: If a number has _____ in ones place, then it is divisible by 10.
Q145: A number is divisible by 5, if it has _____ or _____ in its ones place.
 View Answer
View Answer 
0, 5
Q146: A number is divisible by _____ if it has any of the digits 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8 in its ones place.
Q147: If the sum of the digits in a number is a _____ of 3, then the number is divisible by 3.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Multiple
Q148: If the difference between the sum of digits at odd places (from the right) and the sum of digits at even places (from the right) of a number is either 0 or divisible by _____, then the number is divisible by 11.
 View Answer
View Answer 
11
Q149: The LCM of two or more given numbers is the lowest of their common_____.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Multiple
Q150: The HCF of two or more given numbers is the highest of their common _____.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Factors
Q151:Given below are two columns – Column I and Column II. Match each item of Column I with the corresponding item of Column II.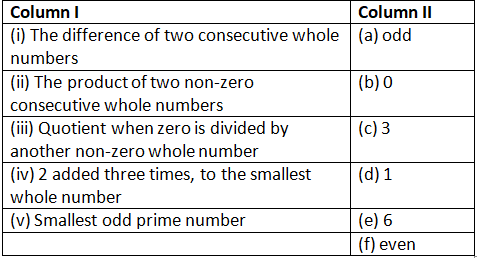
 View Answer
View Answer 
(i) ➝ (d) ; (ii) ➝ (f) ; (iii) ➝ (b) ; (iv) ➝ (e) ; (v) ➝ (c)
Q152: Arrange the followng numbers in descending order:
8435, 4835, 13584, 5348, 25843
 View Answer
View Answer 
Descending order of given numbers is,
25843, 13584, 8435, 5348, 4835
Q153: Of the following numbers which is the greatest? Which is the smallest
38051425, 30040700, 67205602
 View Answer
View Answer 
The greatest number is 67205602 and the smallest number is 30040700.
Q154: Write in expanded form :
(a) 74836
(b) 574021
(c) 8907010
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) 74836 = 7 × 10000 + 4 × 1000 + 8 × 100 + 3 × 10 + 6 × 1
(b) 574021 = 5 × 100000 + 7 × 10000 + 4 x 1000 + 0 × 100 + 2 × 10 + 1 × 1
(c) 8907010 = 8 × 1000000 + 9 × 100000 + 0 × 10000 + 7 × 1000 + 0 × 100 + 1 × 10 + 0 × 1
Q155: As per the census of 2001, the population of four states are given below. Arrange the states in ascending and descending order of their population.
(a) Maharashtra 96878627
(b) Andhra Pradesh 76210007
(c) Bihar 82998509
(d) Uttar Pradesh 166197921
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ascending order ➝ (b), (c), (a), (d)
Descending order ➝ (d), (a), (c), (b)
Q156: The diameter of Jupiter is 142800000 metres. Insert commas suitably and write the diameter according to International System of Numeration.
 View Answer
View Answer 
The diameter of Jupiter is 142,800,000 metres.
Q157: India’s population has been steadily increasing from 439 millions in 1961 to 1028 millions in 2001. Find the total increase in population from 1961 to 2001. Write the increase in population in Indian System of Numeration, using commas suitably.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Total increase in population from 1961 to 2001 = 1028 millions – 439 millions = 589 millions
According to Indian System of Numeration, the increase in population = 58,90,00,000
Q158: Radius of the Earth is 6400km and that of Mars is 4300000m. Whose radius is bigger and by how much?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Radius of the Earth = 6400 km = 6400 × 1000 m = 6400000 m
And radius of the Mars = 4300000 m
∴ Radius of the Earth is greater than the radius of the Mars by (6400000 – 4300000) m = 2100000 m.
Q159: In 2001, the poplulations of Tripura and Meghalaya were 3,199,203 and 2,318,822, respectively. Write the populations of these two states in words.
 View Answer
View Answer 
The population of Tripura = 3,199,203 i.e., Three million one hundred ninety-nine thousand two hundred three.
And the population of Meghalaya = 2,318,822, i.e., Two million three hundred eighteen thousand eight hundred twenty two.
Q160: In a city, polio drops were given to 2,12,583 children on Sunday in March 2008 and to 2,16,813 children in the next month. Find the difference of the number of children getting polio drops in the two months.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Number of children getting polio drops in March 2008 = 2,12,583
Number of children getting polio drops in April 2008 = 2,16,813
∴ The required difference of the number of children getting polio drops in the two months = 2,16,813 – 2,12,583 = 4,230
Q161: A person had Rs 1000000 with him. He purchased a colour T.V. for Rs 16580, a motor cycle for Rs 45890 and a flat for Rs 870000. How much money was left with him?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Total amount a person had = ₹ 1000000
The amount he spent on a colour T.V. = ₹ 16580
The amount he spent on a motorcycle = ₹ 45890
The amount he spent on a flat = ₹ 870000
∴ Total amount he spent = ₹ (16580 + 45890 + 870000) = ₹ 932470
Thus, the amount left with him = ₹ 1000000 – ₹ 932470 = ₹ 67530
Q162: Out of 180000 tablets of Vitamin A, 18734 are distributed among the students in a district. Find the number of the remaining vitamin tablets.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Total tablets of Vitamin A = 180000
Number of tablets distributed among the students in a district = 18734
∴ The number of remaining vitamin tablets = 180000 – 18734 = 161266
Q163: Chinmay had Rs 610000. He gave Rs 87500 to Jyoti, Rs 126380 to Javed and Rs 350000 to John. How much money was left with him?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Chinmay had total amount = ₹ 610000
The amount he gave to Jyoti = ₹ 87500
The amount he gave to Javed = ₹ 126380
The amount he gave to John = ₹ 350009
Total amount given by Chinmay = ₹ (87500 + 126380 + 350000) = ₹ 563880
Thus, the amount left with him
= ₹ 610000 – ₹ 563880 = ₹ 46120
Q164: Find the difference between the largest number of seven digits and the smallest number of eight digits.
 View Answer
View Answer 
The smallest number of eight digits = 10000000
The largest number of seven digits = 9999999
The required difference = 10000000 – 9999999 = 1
Q165: A mobile number consists of ten digits. The first four digits of the number are 9, 9, 8 and 7. The last three digits are 3, 5 and 5. The remaining digits are distinct and make the mobile number, the greatest possible number. What are these digits?
 View Answer
View Answer 
A mobile number consists of 10 digits.
If the first four digits of the number are 9, 9, 8 and 7 and the last three digits of the number are 3, 5 and 5.
Thus, for the greatest possible number, the remaining distinct digits are 6, 4 and 2.
Q166: A mobile number consists of ten digits. First four digits are 9,9,7 and 9. Make the smallest mobile number by using only one digit twice from 8, 3, 5, 6, 0.
 View Answer
View Answer 
A mobile number consists of 10 digits.
If the first four digits are 9, 9, 7 and 9.
Thus, the smallest mobile number by using only one digit twice from 8, 3, 5, 6, 0 is 9979003568.
Q167: In a five digit number, digit at ten’s place is 4, digit at unit’s place is one fourth of ten’s place digit, digit at hunderd’s place is 0, digit at thousand’s place is 5 times of the digit at unit’s place and ten thousand’s place digit is double the digit at ten’s place. Write the number.
 View Answer
View Answer 
A number consists of 5 digits.
Now, the digit at ten’s place = 4,
the digit at unit’s place
= (1/4) x 4 = 1,
the digit at hundred’s place = 0,
the digit at thousand’s place = 5 × 1 = 5
the digit at ten thousand’s place = 2 × 4 = 8
Therefore, the number is 85041.
Q168: Find the sum of the greatest and the least six digit numbers formed by the digits 2, 0, 4, 7, 6, 5 using each digit only once.
 View Answer
View Answer 
By using the digits 2, 0, 4, 7, 6, 5
The greatest number formed = 765420,
and the least number formed = 204567
∴ The required sum = 765420 + 204567 = 969987
Q169: A factory has a container filled with 35874 litres of cold drink. In how many bottles of 200 ml capacity each can it be filled?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Quantity of cold drink in a container = 35874 litres = 35874 × 1000 ml = 35874000 ml
The capacity of one bottle = 200 ml
∴ The required number of bottles = 35874000 ÷ 200 = 179370
Therefore, 179370 bottles can be filled by cold drink.
Q170: The population of a town is 450772. In a survey, it was reported that one out of every 14 persons is illiterate. In all how many illiterate persons are there in the town?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Total population of a town = 450772
Since, one out of every 14 persons is illiterate.
∴ The number of illiterate persons in the town = 450772 ÷ 14 = 32198 Therefore, 32198 persons are illiterate in the town
Therefore, 32198 persons are illiterate in the town
Q171: Find the LCM of 80, 96, 125, 160.
 View Answer
View Answer 
we have, The LCM of 80, 96, 125 and 160 is
The LCM of 80, 96, 125 and 160 is
= 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 5 × 5 × 5 = 12000
Q172: Make the greatest and the smallest 5-digit numbers using different digits in which 5 appears at ten’s place.
 View Answer
View Answer 
By using the digit 5 at ten’s place, the greatest 5-digit number is 98756, and the smallest 5-digit number is 10253
Q173: How many grams should be added to 2kg 300g to make it 5kg 68g?
 View Answer
View Answer 
5 kg 68 g = (5 × 1000 + 68) g = 5068 g and 2 kg 300 g = (2 × 1000 + 300) g = 2300 g
∴ The required number of grams should be added = 5068 g – 2300 g = 2768 g or 2 kg 768 g
Q174: A box contains 50 packets of biscuits each weighing 120g. How many such boxes can be loaded in a van which cannot carry beyond 900kg?
 View Answer
View Answer 
The total weight of a box containing 50 packets of biscuits each weighing 120 g
= 50 × 120 g = 6000 g
The capacity of a van = 900 kg = 900 × 1000 g = 900000 g
∴ The required number of boxes = 900000 + 6000 = 150
Therefore, 150 boxes can be loaded in the van.
Q175: How many lakhs make five billions?
 View Answer
View Answer 
50000 lakhs make 5 billions.
Q176: How many millions make 3 crores?
 View Answer
View Answer 
30 millions make 3 crores.
Q177: Estimate each of the following by rounding off each number to nearest hundreds:
(a) 874 + 478
(b) 793 + 397
(c) 11244 + 3507
(d) 17677 + 13589
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) 874 rounded off to the nearest hundreds = 900
478 rounded off to the nearest hundreds = 500
Estimated sum = 900 + 500 = 1400
(b) 793 rounded off to the nearest hundreds = 800
397 rounded off to the nearest hundreds = 400
Estimated sum = 800 + 400 = 1200
(c) 11244 rounded off to the nearest hundreds =11200
3507 rounded off to the nearest hundreds = 3500
Estimated sum = 11200 + 3500 = 14700
(d) 17677 rounded off to the nearest hundreds =17700
13589 rounded off to the nearest hundreds =13600
Estimated sum = 17700 + 13600 = 31300
Q178: Estimate each of the follwoing by rounding off each number to nearest tens:
(a) 11963 – 9369
(b) 76877 – 7783
(c) 10732 – 4354
(d) 78203 – 16407
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) 11963 rounded off to the nearest tens = 11960
9369 rounded off to the nearest tens = 9370
Estimated difference = 11960 – 9370 = 2590
(b) 76877 rounded off to the nearest tens = 76880
7783 rounded off to the nearest tens = 7780
Estimated difference = 76880 – 7780 = 69100
(c) 10732 rounded off to the nearest tens =10730
4354 rounded off to the nearest tens = 4350
Estimated difference = 10730 – 4350 = 6380
(d) 78203 rounded off to the nearest tens = 78200
16407 rounded off to the nearest tens =16410
Estimated difference = 78200 – 16410 = 61790
Q179: Estimate each of the following products by rounding off each number to nearest tens:
(a) 87 × 32
(b) 311×113
(c) 3239 × 28
(d) 1385 × 789
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) 87 rounded off to the nearest tens = 90
32 rounded off to the nearest tens = 30
Estimated product = 90 × 30 = 2700
(b) 311 rounded off to the nearest tens = 310
113 rounded off to the nearest tens = 110
Estimated product = 310 x 110 = 34100
(c) 3239 rounded off to the nearest tens = 3240
28 rounded off to the nearest tens = 30
Estimated product = 3240 × 30 = 97200
(d) 1385 rounded off to the nearest tens = 1390
789 rounded off to the nearest tens = 790
Estimated product = 1390 × 790 = 1098100
Q180: The population of a town was 78787 in the year 1991 and 95833 in the year 2001. Estimate the increase in population by rounding off each population to nearest hundreds.
 View Answer
View Answer 
78787 rounded off to the nearest hundreds = 78800
95833 rounded off to the nearest hundreds = 95800
The estimated increase in population = 95800 – 78800 = 17000
Q181: Estimate the product 758 × 6784 using the general rule.
 View Answer
View Answer 
758 can be rounded off to 800 and 6784 can be rounded off to 7000
∴ Estimated product = 800 × 7000 = 5600000
Q182: A garment factory produced 216315 shirts, 182736 trousers and 58704 jackets in a year. What is the total production of all the three items in that year?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Number of shirts produced by the factory = 216315
Number of trousers produced by the factory =182736
Number of jackets produced by the factory = 58704
Total production of the factory = 216315 + 182736 + 58704 = 457755
Q183: Find the LCM of 160, 170 and 90.
 View Answer
View Answer 
We have,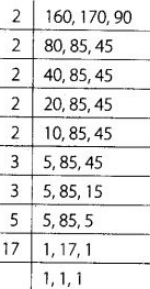 The LCM of 160,170 and 190 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 5 × 17 = 24480
The LCM of 160,170 and 190 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 5 × 17 = 24480
Q184: A vessel has 13 litres 200 mL of fruit juice. In how many glasses each of capacity 60 mL can it be filled?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Quantity of fruit juice in a vessel = 13 L 200 mL = (13 × 1000 + 200) mL = 13200 mL
Capacity of one glass = 60 mL
∴ The required number of glasses = 13200 ÷ 60 = 220
Therefore, 220 glasses can be filled by fruit juice.
Q185: Determine the sum of the four numbers as given below:
(a) successor of 32
(b) predecessor of 49
(c) predecessor of the predecessor of 56
(d) successor of the successor of 67
 View Answer
View Answer 
Since, successor of 32 is 33, predecessor of 49 is 48, predecessor of the predecessor of 56 is 54 and successor of the successor of 67 is 69.
∴ The required sum = 33 + 48 + 54 + 69 = 204
Q186: A loading tempo can carry 482 boxes of biscuits weighing 15kg each, whereas a van can carry 518 boxes each of the same weight. Find the total weight that can be carried by both the vehicles.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Total weight can be carried by a tempo = (482 × 15) kg = 7230 kg and the total weight can be carried by a van = (518 × 15) kg = 7770 kg Thus, the total weight that can be carried by both the vehicles = (7230 + 7770) kg = 15000 kg
Q187: In the marriage of her daughter, Leela spent Rs 216766 on food and decoration,Rs 122322 on jewellery, Rs 88234 on furniture and Rs 26780 on kitchen items. Find the total amount spent by her on the above items.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Amount spent by Leela on food and decoration = ₹ 216766
Amount spent by her on jewellery = ₹ 122322
Amount spent by her on furniture = ₹ 88234
Amount spent by her on kitchen items = ₹ 26780
∴ Total amount spent by her = ₹ (216766 + 122322 + 88234 + 26780)
= ₹ 454102
Q188: A box contains 5 strips having 12 capsules of 500mg medicine in each capsule. Find the total weight in grams of medicine in 32 such boxes.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Quantity of medicine in one capsule = 500 mg
∴ Quantity of medicine in 12 capsules or 1 strip = (500 × 12) mg = 6000 mg = 6 g
Quantity of medicine in 5 strips or 1 box = (6 × 5) g = 30 g
Quantity of medicine in 32 boxes = (30 × 32)g = 960 g
Q189: Determine the least number which when divided by 3, 4 and 5 leaves remainder 2 in each case.
 View Answer
View Answer 
We have,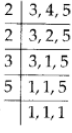 Since, the LCM of 3,4 and 5 is 2 × 2× 3 × 5 = 60.
Since, the LCM of 3,4 and 5 is 2 × 2× 3 × 5 = 60.
∴ The required number is 6is the least number which when divided by 3, 4 and 5 leaves remainder 2 in each case.
Q190: A merchant has 120 litres of oil of one kind, 180 litres of another kind and 240 litres of a third kind. He wants to sell the oil by filling the three kinds of oil in tins of equal capacity. What should be the greatest capacity of such a tin?
 View Answer
View Answer 
A merchant has 3 kinds of oil with different quantities like 120 litres, 180 litres and 240 litres.
Since, he wants to sell the oil by filling the three kinds of oil in tins of equal capacity, so the greatest capacity of such a tin is the HCF of 120,180 and 240.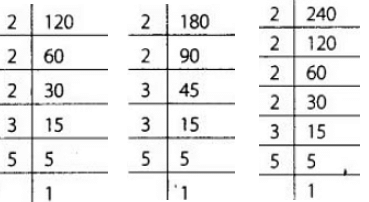
Now 120 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 5
180 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 5
240 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 4
∴ The required greatest capacity of a tin = (2 × 2 × 3 × 5) litres = 60 litres
Q191: Find a 4-digit odd number using each of the digits 1, 2, 4 and 5 only once such that when the first and the last digits are interchanged, it is divisible by 4.
 View Answer
View Answer 
By using the digits 1, 2, 4 and 5 only once, we get a 4 digit odd number 4521.
When we interchanged its first and last digits we get a new number, i.e., 1524 which is divisible by 4.
Thus, the required number is 4521.
Q192: Using each of the digits 1, 2, 3 and 4 only once, determine the smallest 4-digit number divisible by 4.
 View Answer
View Answer 
By using the digits 1, 2, 3 and 4 only once, the smallest 4-digit number which is divisible by 4 is 1324.
Q193: Fatima wants to mail three parcels to three village schools. She finds that the postal charges are Rs 20, Rs 28 and Rs 36, respectively. If she wants to buy stamps only of one denomination, what is the greatest denomination of stamps she must buy to mail the three parcels?
 View Answer
View Answer 
The postal charges to mail three parcels are ₹ 20, ₹ 28 and ₹ 36 respectively.
Also, Fatima wants to buy stamps only of one denomination.
So, to find the greatest denomination of stamps, we find the HCF of 20, 28 and 36.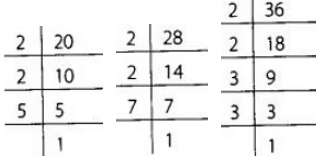 Now 20 = 2 × 2 ×5
Now 20 = 2 × 2 ×5
28 = 2 × 2 × 7
36 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 3
∴ The HCF of 20, 28 and 36 is 2 × 2 = 4
So, ₹ 4 is the greatest denomination of stamps, she must buy to mail the three parcels.
Q194: Three brands A, B and C of biscuits are available in packets of 12, 15 and 21 biscuits respectively. If a shopkeepeer wants to buy an equal number of biscuits, of each brand, what is the minimum number of packets of each brand, he should buy?
 View Answer
View Answer 
A shopkeeper has three brands A, B and C of biscuits are available in packets of 12, 15 and 21 biscuits respectively.
Also, a shopkeeper wants to buy equal number of biscuits of each brand for that we need to find the LCM of 12, 15 and 21.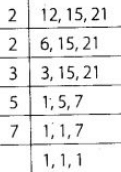 ∴ The LCM of 12,15 and 21 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 5 × 7 = 420 Thus, the required number of packets of 420.
∴ The LCM of 12,15 and 21 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 5 × 7 = 420 Thus, the required number of packets of 420.
brand A = 420/12 = 35,
brand B = 420/15 = 28 and
brand C = 420/21 = 20
Q195: The floor of a room is 8m 96cm long and 6m 72cm broad. Find the minimum number of square tiles of the same size needed to cover the entire floor.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Length of floor of a room = 8 m 96 cm = 896 cm
Breadth of floor of the room = 6 m 72 cm = 672 cm
To find the minimum number of square tiles of same size needed to cover the entire floor, we find the LCM of 896 cm and 672 cm.
∴ LCM of 672 and 896 is 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 7 = 2688
∴ Number of square tiles = 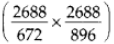
= 4 x 3 = 12
Q196: In a school library, there are 780 books of English and 364 books of Science. Ms. Yakang, the librarian of the school wants to store these books in shelves such that each shelf should have the same number of books of each subject. What should be the minimum number of books in each shelf?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Number of books of English = 780
Number of books of Science = 364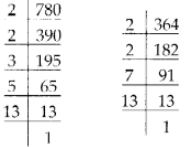
780 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 5 × 13
364 = 2 × 2 × 7 × 13
∴ The HCF of 780 and 364 = 2 × 2 × 13 = 52
Thus, the minimum number of books in each shelf = 52
Q197: In a colony of 100 blocks of flats numbering 1 to 100, a school van stops at every sixth block while a school bus stops at every tenth block. On which stops will both of them stop if they start from the entrance of the colony?
 View Answer
View Answer 
There are 100 blocks in a colony numbering 1 to 100.
A school van stops at every sixth block and a school bus stops at every tenth block.
We have to find the common stops at which they both stop if they start from a same entrance.
∴ We need to find the LCM of 6 and 10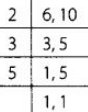 The LCM of 6 and 10 is 2 × 3 × 5 = 30. Firstly both will stop at 30th block, then aL 60th block and lastly at 90th block.
The LCM of 6 and 10 is 2 × 3 × 5 = 30. Firstly both will stop at 30th block, then aL 60th block and lastly at 90th block.
Q198: Test the divisiblity of following numbers by 11
(a) 5335
(b) 9020814
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) We have the difference between the sum of digits at odd places (from the right) and the sum of digits at even places (from the right) of a number 5335 is (5 + 3) – (3 + 5) = 8 – 8 = 0, which is divisible by 11.
∴ 5335 is divisible by 11.
(b) We have the difference between the sum of digits at odd places (from the right) and the sum of digits at even places (from the right) of the number 9020814 is
(4 + 8 + 2 + 9) – (1 + 0 + 0) = 23 – 1 = 22, which is divisible by 11.
∴ 9020814 is divisible by 11.
Q199: Using divisiblity tests, determine which of the following numbers are divisible by 4?
(a) 4096
(b) 21084
(c) 31795012
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) We have, 4096
Since, the last two digits 96 is divisible by 4.
∴ 4096 must be divisible by 4.
(b) We have, 21084
Since, the last two digits 84 is divisible by 4.
∴ 21084 must be divisible by 4.
(c) We have, 31795012
Since, the last two digits 12 is divisible by 4.
∴ 31795012 must be divisible by 4.
Q200: Using divisiblity test. determine which of the following numbers are divisible by 9?
(a) 672
(b) 5652
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) We have, 672
Since, the sum of all the digits of 672 is 15, which is not divisible by 9.
∴ 672 is not divisible by 9.
(b) We have, 5652
Since, the sum of all the digits of 5652 is 18, which is divisible by 9.
∴ 5652 must be divisible by 9.
|
34 videos|123 docs|58 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Number System - Maths Olympiad Class 6
| 1. What are the different types of numbers in the number system? |  |
| 2. How do we represent rational and irrational numbers on a number line? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the number system in mathematics? |  |
| 4. How can we convert a decimal number into a fraction? |  |
| 5. What are the properties of integers in the number system? |  |

















