NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics - Presentation of Data
Q1: Bar diagram is a
(i) one-dimensional diagram
(ii) two-dimensional diagram
(iii) diagram with no dimension
(iv) none of the above
Ans: Bar diagrams are One-dimensional diagrams. These are represented on a plane of two axis and depicts the relationship between the two variables (plotted on the either axis) in form of rectangular bars.
Q2: Data represented through a histogram can help in finding graphically the
(i) mean
(ii) mode
(iii) median
(iv) all the above
Ans: Graphically mode can be determined by presenting the data in the form of Histogram. The highest Histogram indicates the modal class. The intersection point of the lines diagonally joining the two top corners of the modal rectangles to the corners of the adjacent Histograms indicates the Modal Value.
Q3: Ogives can be helpful in locating graphically the
(i) mode
(ii) mean
(iii) median
(iv) none of the above
Ans: Graphically, Median can be determined by the intersection point of Less than Ogive and More than Ogive. The value of x-axis corresponding to the intersection point indicates the median.
Q4: Data represented through arithmetic line graph help in understanding
(i) long-term trend
(ii) cyclicity in data
(iii) seasonality in data
(iv) all the above
Ans: Data represented through arithmetic line graph (or time series graph) helps in understanding the long-term trend and periodicity.
Q5: Width of bars in a bar diagram need not be equal (True/False).
Ans: The above statement is false as all bars in a bar diagram need to be of equal width. Moreover, all bars are at equal distance from each other.
Q6: Width of rectangles in a histogram should essentially be equal (True/False).
Ans: The above statement is false, as the width of all rectangles in a histogram may or may not be equal. The width of a rectangle depends on the width of its corresponding class interval.
Q7: Histogram can only be formed with continuous classification of data (True/False).
Ans: Yes, a Histogram can only be formed with the continuous classification of data. The frequency distribution of a continuous series is graphically presented in form of a Histogram. If the given data is not continuous, then it is to be converted into exclusive series before presenting the data in the form of Histogram. Histograms can never be prepared for discrete series.
Q8: Histogram and column diagram are the same method of presentation of data (True/False).
Ans: The above statement is false. This is because Histogram and column diagram are different method of presentation. While the Histogram is a Two-dimensional diagram, the bar diagram is a One-dimensional diagram. Histograms are prepared for the continuous series, whereas the bar diagrams are prepared for the discrete series. Further, Histograms are drawn continuously without any space between two consecutive Histograms, whereas the space is must between two bars in a bar diagram.
Q9: Mode of a frequency distribution can be known graphically with the help of histogram (True/False).
Ans: The above statement is true. Graphically, mode can be determined by presenting the data in the form of Histogram. The highest Histogram indicates the modal class. The intersection point of the lines diagonally joining the two top corners of the modal rectangles to the corners of the adjacent Histograms indicates the Modal Value.
Q10: Median of a frequency distribution cannot be known from the ogives (True/False).
Ans: The statement is false. Graphically Ogives can be determined by the intersection point of the less than Ogive and more than Ogive. The value of x-axis corresponding to the intersection point indicates the median.
Q11: What kinds of diagrams are more effective in representing the following?
(i) Monthly rainfall in a year
(ii) Composition of the population of Delhi by religion
(iii) Components of cost in a factory
Ans: (i) The monthly rainfall in a year can be best represented by a bar diagram as only one variable i.e. monthly rainfall is to be compared visually. The highest bar diagram indicates the highest rainfall in the corresponding month that is plotted on the x-axis.
(ii) Composition of the population of Delhi by religion can be represented by a simple bar diagram. Plotting different religion on the x-axis and the number of people on the y-axis, one can easily compare the number of the population religion-wise..
(iii) In order to represent different components of cost in a factory, a pie chart is more effective. The entire circle represents the total cost and various components of costsare shown by different portions of the circle.
Q12: Suppose you want to emphasise the increase in the share of urban non-workers and lower level of urbanisation in India as shown in Example 4.2. How would you do it in the tabular form?
Ans: Share of Rural and Urban Non-workers in India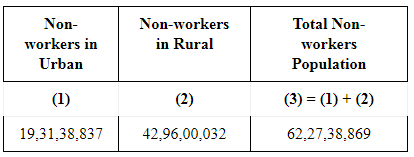 We can infer from the above table that the absolute number of the rural non-workers is greater than the absolute number of the urban non-workers. The higher ( lower) share of the rural non-workers (urban non-workers) reveals lower degree of urbanisation in India.
We can infer from the above table that the absolute number of the rural non-workers is greater than the absolute number of the urban non-workers. The higher ( lower) share of the rural non-workers (urban non-workers) reveals lower degree of urbanisation in India.
Q13: How does the procedure of drawing a histogram differ when class intervals are unequal in comparison to equal class intervals in a frequency table?
Ans: A Histogram of equal class intervals has equal width of all rectangles indicating the same class intervals. In contrast, a Histogram of unequal class intervals has rectangles of varying width as per their corresponding class intervals. Before constructing a Histogram, frequencies of unequal class intervals are to be adjusted. The adjustment factor of each class is calculated with the following formula.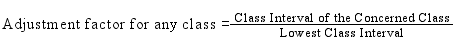 And the adjusted frequency will be calculated by dividing the original frequency by adjustment factor.
And the adjusted frequency will be calculated by dividing the original frequency by adjustment factor.
Q14: The Indian Sugar Mills Association reported that, ‘Sugar production during the first fortnight of December 2001 was about 3,87,000 tonnes, as against 3,78,000 tonnes during the same fortnight last year (2000). The off-take of sugar from factories during the first fortnight of December 2001 was 2,83,000 tonnes for internal consumption and 41,000 tonnes for exports as against 1,54,000 tonnes for internal consumption and nil for exports during the same fortnight last season.’
(i) Present the data in tabular form.
(ii) Suppose you were to present these data in diagrammatic form which
of the diagrams would you use and why?
(iii) Present these data diagrammatically.
Ans: (ii) With a view to present the data diagrammatically the multiple bar diagram can be effectively used.
(ii) With a view to present the data diagrammatically the multiple bar diagram can be effectively used.
(iii)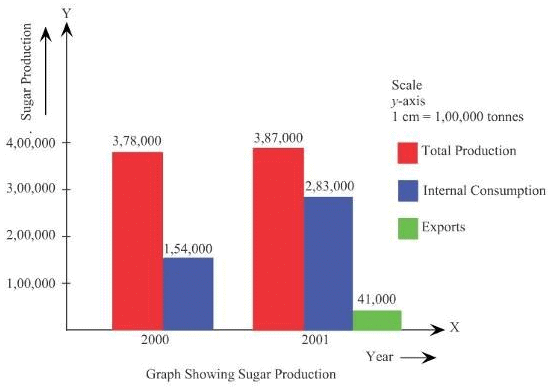
Q15: The following table shows the estimated sectoral real growth rates (percentage change over the previous year) in GDP at factor cost.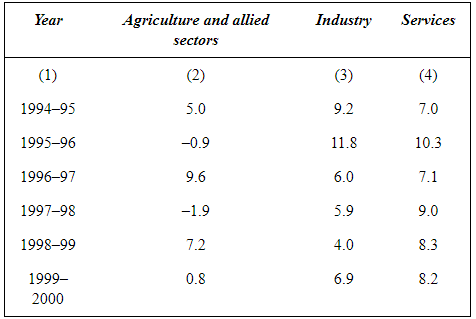 Represent the data as multiple time series graphs.
Represent the data as multiple time series graphs.
Ans: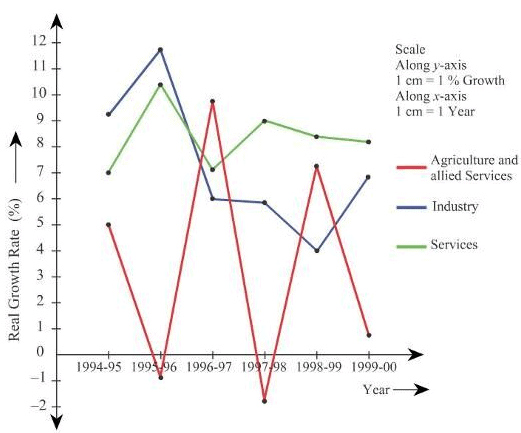
|
59 videos|290 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics - Presentation of Data
| 1. What is the importance of data presentation? |  |
| 2. What are the different methods of data presentation? |  |
| 3. How can data presentation help in data analysis? |  |
| 4. What are the factors to consider while choosing a data presentation method? |  |
| 5. How can data presentation enhance data storytelling? |  |

















