Class 7 Science Question Answers - Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
Q1: “Minimise use of plastics for healthy environment”, comment on this advice.
Ans: Plastic is a polymer that can be recycled, coloured, reused, mould or drawn into wires or various other shapes. When it burns it releases lot of poisonous fumes, into the atmosphere causing air pollution. We should not throw polybags in the water bodies or on the road because animals like cow while eating garbage waste food items swallow the polythene bags and food wrappers, the plastic materials chokes the respiratory system of these animals and form a lining in their stomachs and may cause death of these animals.The polybags carelessly thrown here and there are responsible for clogging the drains too. Thus we say we should minimise use of plastics for healthy environment by adopting the following ways:
- Avoid use of plastics as far as possible
- Use bags made from cotton or jute while going for shopping
- Try to recycle plastic wastes by returning them back to your grocery shop for recycling, and by using them as garbage bag liners.
- We can urge plastic manufacturers to develop biodegradable plastic.
- We can urge our legislators to ban plastic in children's toys and food and beverage containers.
Q2: Increasing application of synthetic fibres is actually helping in conservation of forests. Do you agree, if yes comment how?
Ans: Synthetic fibres are made by human beings by using various chemicals, it minimises the use of natural fibres whose source is plants, thus we can say increasing use of man- made fibres are playing very important role in conservation of forests.
Q3: What are synthetic fibres and its various types?
Ans: Fibres made by human being or man- made fibres are called synthetic fibres
Following are the various types of synthetic fibres:
- Rayon: Rayon is synthesized from wood pulp. Rayon resembles silk, so it is also known as artificial silk. Rayon can be dyed in different colours and is much cheaper than silk.
- Nylon: The first fully synthetic fibre was nylon. It was prepared from coal, water and air. It is very strong, elastic and light, it is very easy to wash and used for making variety of things like socks, ropes, bags, curtains, parachutes etc. Nylon thread is very strong infact it is stronger than steel wire, because of this property of nylon it is used for making parachutes and ropes for rock climbing.
- Polyester: Polyester, one of the most popular man-made fibres. It is made of repeating unit of a chemical called ester. It is widely used to make clothes. Polyester fabrics do not get wrinkled easily and it remains crisp and can be washed easily than any other fabrics. Thus it is used to make dress, shirts etc.
Terylene and PET are two widely used polyester fabrics. - Acrylic: Acrylic fabric resembles wool, it is cheaper than wool and available is variety of colours. It is also more durable than wools.
Q4: Write short notes on various characteristics of synthetic fibres and natural fibre.
Ans: Characterstics of Synthetic fibres are:
- Less expensive than natural fibres
- Strong and long lasting
- Easily available
- Easy to maintain
- Dry up quickly
Characteristics of natural fibres:
These fibers have higher tensile strength than other fibers. Therefore, these fibers are used for durable yarn, fabric, packaging, and paper. Some examples are flax, jute, industrial hemp, soybean fiber, and even vine fibers and banana fibers.
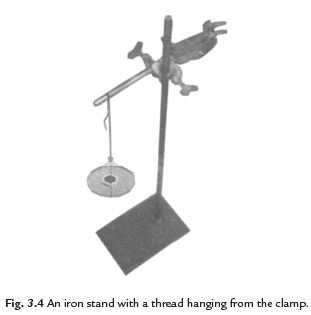
Q. 5. Explain with the help of an activity that nylon thread is stronger than cotton, wool, silk and nylon.
Ans. Take an iron stand with a clamp. Take a cotton thread of about 60 cm length. Tie it to the clamp so that it hangs freely from it as shown in figure. At the free end suspend a pan so that weight can be placed in it. Add weight one by one till the thread breaks. Note the total weight required to break the thread. Repeat the same activity with threads of wool, silk and nylon. We observe that more weight is required to break the nylon thread in comparison to other threads. So we can say that nylon is much stronger than other threads.
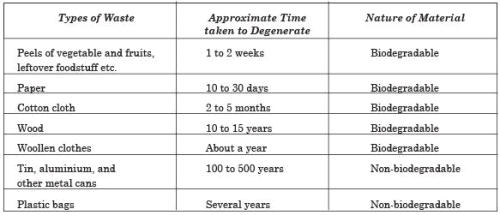
Q. 6. Make a table to show various types of wastes, time taken to degenerate and their nature.
Ans.
Q. 7. Explain thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics with examples.
Ans. There are following two type of plastics:
(i) Thermoplastics (ii) Thermosetting plastics.
(i) Thermoplastics: The plastics which get deformed easily by heating and can be bent easily are known as thermoplastics. Polythene and PVC are the examples of some thermoplastics.
(ii) Thermosetting Plastics: The plastics which when moulded once cannot be softened again by heating are called thermosetting plastics. Bakelite and Melamine are two most common examples of thermosetting plastics. Bakelite is used in making electrical switches, handles of various utensils. Melamine is used for making floor tiles, kitchenware and fabrics which resist fire.


Fig. 3.5 Some articles made of plastics.
|
18 videos|34 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Question Answers - Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
| 1. What are synthetic fibers and plastics? |  |
| 2. What are the advantages of using synthetic fibers and plastics? |  |
| 3. What are the environmental concerns associated with synthetic fibers and plastics? |  |
| 4. How are synthetic fibers and plastics recycled? |  |
| 5. What are some common uses of synthetic fibers and plastics? |  |





















