Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Important Questions - Nutrition in Plants
Fill in the blanks:
(i) All organisms take ______ and utilize it to get energy for growth and the maintenance of their bodies.
(ii) Green plants synthesize their food themselves by the process of ______ and are called ______.
(iii) ______ energy is stored by the leaves with the help of chlorophyll.
(iv) ______derive nutrition from dead, decaying matter.
(v) Plants like cuscuta take food from ______ plant.
(vi) All animals are categorized as ______.
(vii) ______ is produced and ______ is utilized during photosynthesis.
Ans:
(i) All organisms take food and utilize it to get energy for growth and the maintenance of their bodies.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Food provides essential nutrients and energy that organisms need for growth, repair, and maintenance of their bodily functions. Both plants and animals require food, though plants produce their own food through photosynthesis, while animals consume other organisms.
(ii) Green plants synthesize their food themselves by the process of photosynthesis and are called autotrophs
 View Answer
View Answer 
Green plants, also known as autotrophs, create their own food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide through a process called photosynthesis. The word "autotroph" refers to organisms that produce their own food.
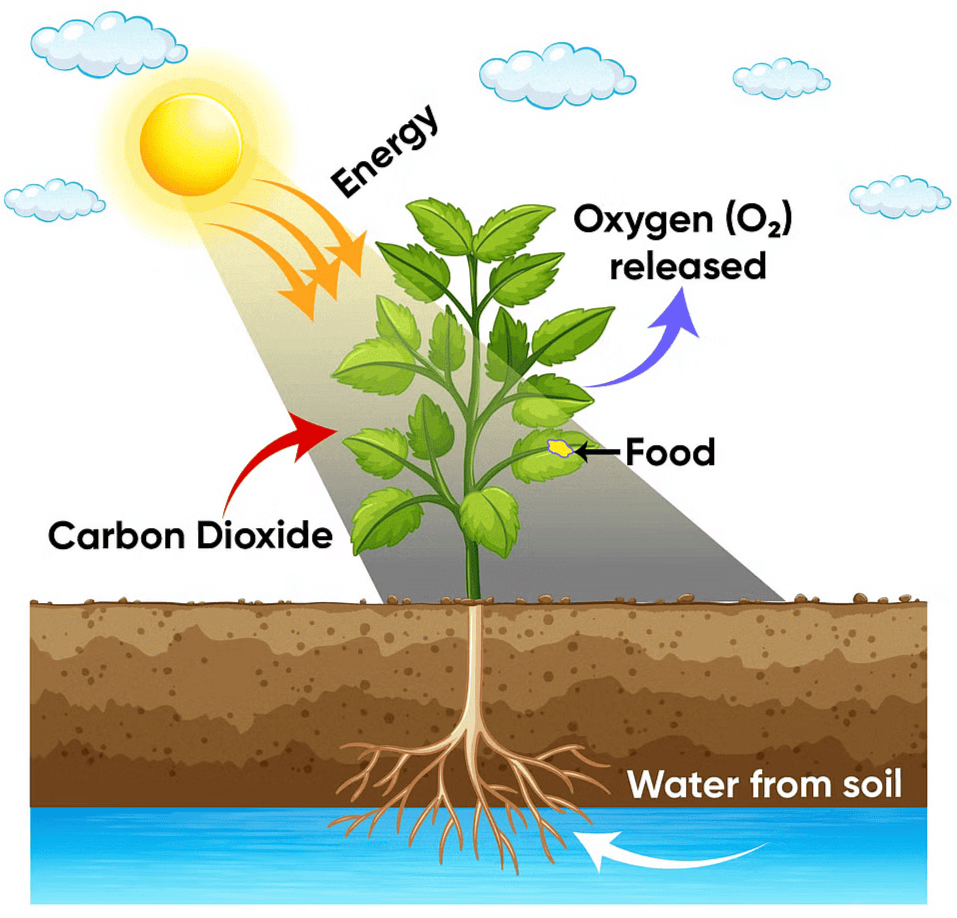 Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
(iii) Solar energy is stored by the leaves with the help of chlorophyll.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Chlorophyll, the green pigment in plant leaves, captures solar energy and uses it to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose during photosynthesis. This process stores solar energy in chemical bonds in the form of glucose.
(iv) Saprotrophs derive nutrition from dead, decaying matter.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Saprotrophs are organisms that obtain nutrients by decomposing dead and decaying organic matter. They secrete enzymes that break down complex organic substances into simpler, soluble forms, which they then absorb. Examples include fungi and certain bacteria. This process is essential for nutrient recycling in ecosystems.
(v) Plants like Cuscuta take food from the host plant.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Cuscuta, a parasitic plant, lacks chlorophyll and cannot produce its own food. Instead, it attaches itself to a host plant and absorbs nutrients and water from the host, depending on it for survival.
(vi) All animals are categorized as Heterotrophs.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Animals are heterotrophs, meaning they cannot produce their own food and must consume other organisms (plants or animals) to obtain energy and nutrients. Heterotrophs rely on autotrophs or other heterotrophs for their food.
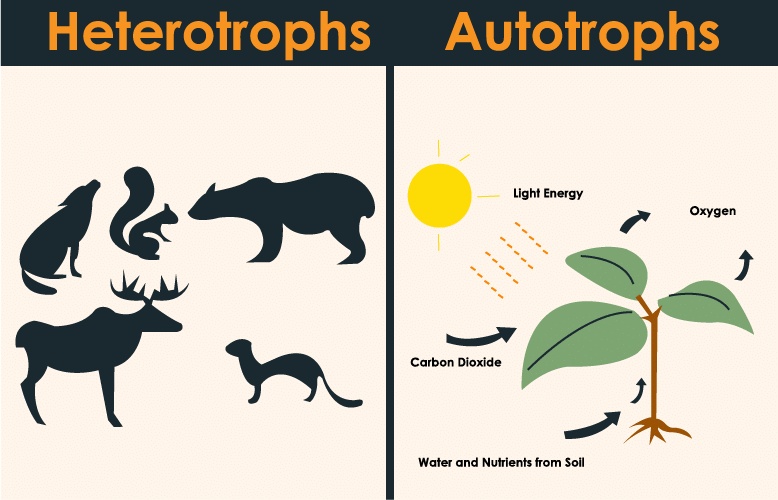 Heterotrophs & Autotrophs
Heterotrophs & Autotrophs
(vii) Oxygen is produced, and carbon dioxide is utilized during photosynthesis.
 View Answer
View Answer 
During photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and use it to produce glucose, releasing oxygen as a byproduct. This oxygen is vital for the respiration of most living organisms, while the plants use glucose as a source of energy.
Choose the true (T) and false (F) statements:
(i) Food is essential for all living beings.
(ii) Leaves are the food factories of plants.
(iii) Water comes into leaves through stomata in the form of vapours.
(iv) Plants utilize the carbon dioxide dissolved in the water absorbed by the roots for photosynthesis.
(v) The sun is the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms.
(vi) Algae are saprotrophs.
(vii) Cuscuta is a parasite.
(viii) Saprotrophs take their food in solution form from dead and decaying matter.
(ix) Insectivorous plants are partial Heterotrophs.
(x) Plants take atmospheric nitrogen through stomata and utilize a nutrient.
(xi) The Pitcher plant is an insectivorous plant.
(xii) Many fungi are saprotrophs.
(xiii) The leaves of a plant are called its food factory.
(xiv) Insectivorous plants eat insects to fulfill their needs for energy.
Ans:
(i) Food is essential for all living beings.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer 
All living organisms require food to obtain energy, grow, and maintain their bodily functions. Food provides essential nutrients needed for survival, such as carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals.
(ii) Leaves are the food factories of plants.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer 
Leaves are known as the food factories of plants because they are the primary sites of photosynthesis. Through this process, plants convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose (a form of sugar) and oxygen, providing energy for growth and development.
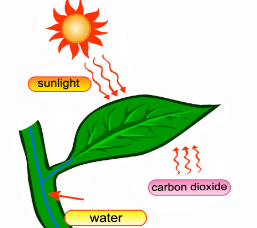 Leaves are food factories of Plants
Leaves are food factories of Plants
(iii) Water comes into leaves through stomata in the form of vapours.
Ans: False
 View Answer
View Answer 
Water is absorbed by the roots from the soil and transported to the leaves through the plant's vascular system (xylem). While stomata allow water vapor to exit the leaves during transpiration, water does not enter leaves through stomata; it enters through the xylem in liquid form.
(iv) Plants utilize the carbon dioxide dissolved in the water absorbed by the roots for photosynthesis.
Ans: False
 View Answer
View Answer 
Plants primarily take in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through the stomata in their leaves, not from water. While some carbon dioxide can dissolve in soil water, the majority comes from the air during the process of photosynthesis.
(v) The sun is the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer 
The sun provides energy that drives the process of photosynthesis in plants. This energy is then passed along the food chain to herbivores and carnivores, making sunlight the ultimate source of energy for all life on Earth.
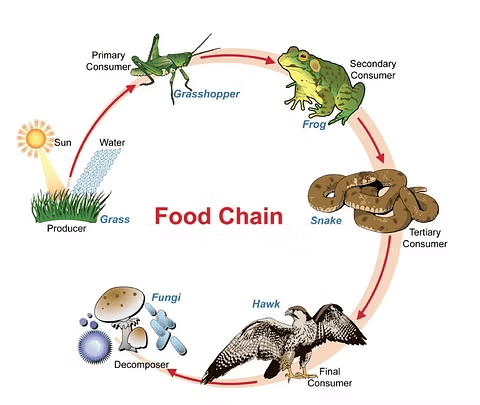 Food Chain
Food Chain
(vi) Algae are saprotrophs.
Ans: False
 View Answer
View Answer 
Explanation: Algae are not saprotrophs; they are primarily photosynthetic organisms that produce their own food using sunlight. Saprotrophs, such as fungi and certain bacteria, feed on dead and decaying organic matter.
(vii) Cuscuta is a parasite.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer 
Cuscuta, commonly known as dodder, is a parasitic plant that lacks chlorophyll and cannot photosynthesize. It attaches itself to host plants and derives nutrients and water from them, making it a true parasite.
(viii) Saprotrophs take their food in solution form from dead and decaying matter.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer 
Saprotrophs, like fungi and some bacteria, decompose dead organic matter. They secrete enzymes that break down complex organic substances into simpler soluble forms, which they then absorb as nutrients.
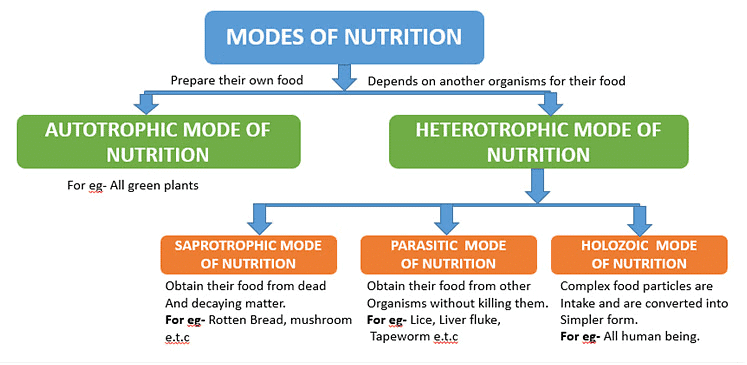 Modes of Nutrition(ix) Insectivorous plants are partial heterotrophs.
Modes of Nutrition(ix) Insectivorous plants are partial heterotrophs.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer 
Insectivorous plants, such as pitcher plants and Venus flytraps, are primarily autotrophic, producing their own food through photosynthesis using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. However, they supplement their nutrient requirements, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus, by trapping and digesting insects. This reliance on external sources for some nutrients makes them partial heterotrophs, as they exhibit both autotrophic and heterotrophic modes of nutrition.
(x) Plants take atmospheric nitrogen through stomata and utilize a nutrient.
Ans: False
 View Answer
View Answer 
Plants do not absorb atmospheric nitrogen (N₂) through stomata. Instead, they take up nitrogen in the form of nitrates or ammonium from the soil through their roots. Some plants, such as legumes, form symbiotic relationships with nitrogen-fixing bacteria (e.g., Rhizobium) in their roots, which convert atmospheric nitrogen into compounds that plants can use.
(xi) The Pitcher plant is an insectivorous plant.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer 
The Pitcher plant is indeed an insectivorous plant. It has modified leaves that form a "pitcher" shape, which traps insects. The plant secretes digestive enzymes to break down the trapped insects and absorb the nutrients, aiding in its growth.
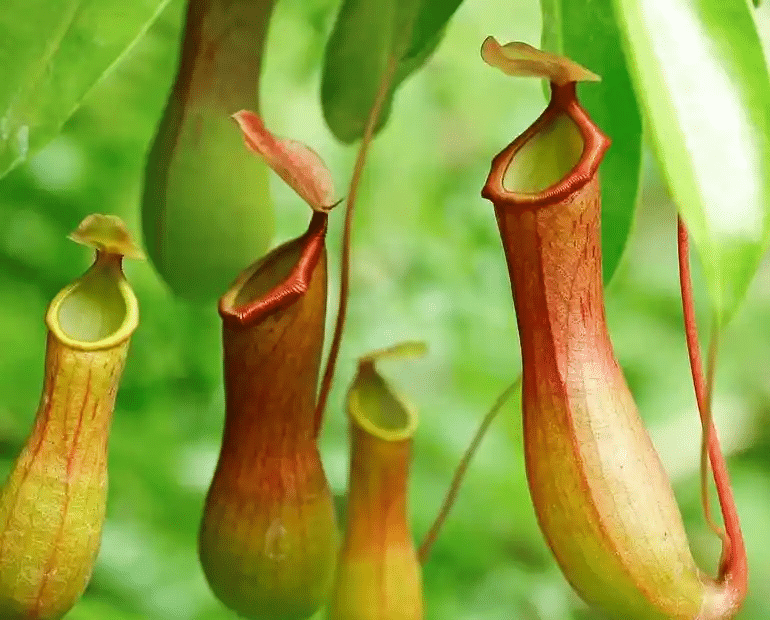 Pitcher Plant
Pitcher Plant
(xii) Many fungi are saprotrophs.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer 
Many fungi are saprotrophic, meaning they obtain their nutrients by decomposing dead organic matter. They play a vital role in nutrient cycling in ecosystems by breaking down complex organic substances into simpler forms.
(xiii) The leaves of a plant are called its food factory.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer 
Leaves are often referred to as the food factory of the plant because they are the main site of photosynthesis, where sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water are converted into glucose and oxygen.
(xiv) Insectivorous plants eat insects to fulfill their needs for energy.
Ans: False
Insectivorous plants, such as pitcher plants and Venus flytraps, primarily derive energy from photosynthesis. They consume insects to obtain nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, which are limited in their environments, not to fulfill their energy needs.
Short & Long Answer Type Questions
Q.1. Define
(a) Parasites
Ans: Parasites are organisms that live on or in a host organism and derive nutrients, often including food and shelter, at the host’s expense, causing harm— examples: Cuscuta (dodder), tapeworm, liver fluke. Parasites are classified as total or partial parasites based on their dependency.
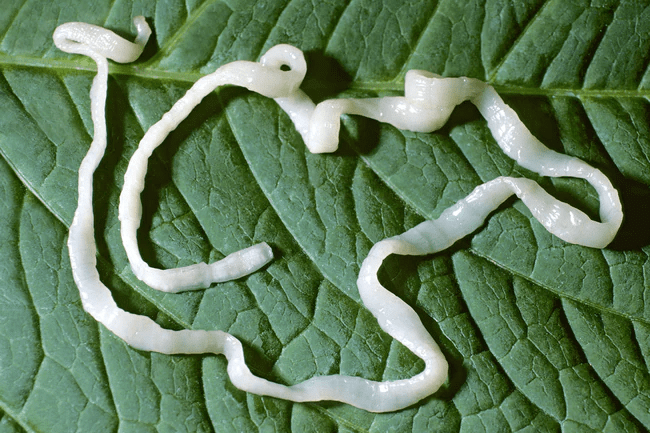 Example of Parasite: Tapeworm
Example of Parasite: Tapeworm
(b) Total Parasites
Ans: The parasites that depend on the host for food and shelter are called total parasites. For example, liver fluke and tapeworm.
(c) Partial Parasites
Ans: Partial parasites are organisms, typically plants, that can photosynthesize but depend on a host for water, nutrients, or support. For example, Mistletoe
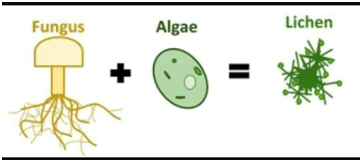
Q.2. What is Symbiosis? What is a symbiotic relationship?
Ans:
- Symbiosis is a close, long-term relationship between two different organisms where both benefit, often involving sharing of nutrients, shelter, or other resources.
- Example: In lichens, algae provide nutrients via photosynthesis, and fungi provide shelter and water.
Q.3. What are stomata? Explain their function.
Ans:
- Stomata are tiny pores on the underside of the leaf surface that are surrounded by guard cells.
- Their functions are to exchange gases by diffusion for photosynthesis and respiration and to cause transpiration by evaporation of water from the leaf surface.
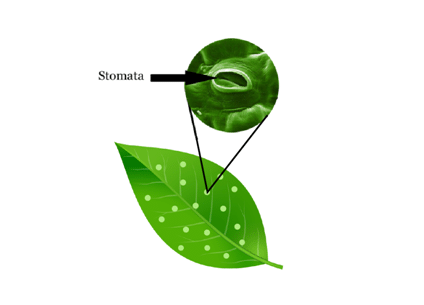 Stomata
Stomata
Q.4. How does the plant use sunlight for photosynthesis?
Ans:
- Sunlight is the energy source for photosynthesis.
- It is trapped by the green pigment chlorophyll in the leaves and all green parts of the plants.
- The chlorophyll is present in organelles called chloroplasts.
- Most of the chlorophyll is present in the leaves; therefore, leaves are the major site for trapping sunlight to convert it to chemical energy.
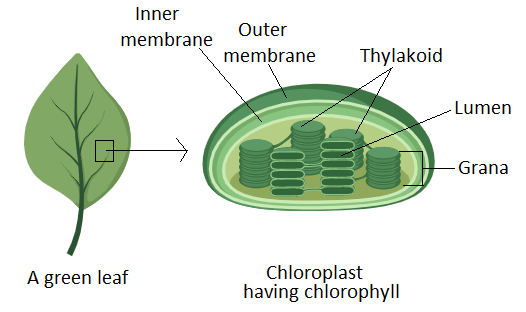 Chloroplasts contain Chlorophyll
Chloroplasts contain Chlorophyll
Q.5. Explain how photosynthesis occurs in plants.
Ans: Photosynthesis is a vital process that allows green plants to make their own food using sunlight.
Here’s how it works:
- Energy Source: Plants use solar energy (sunlight) to create food.
- Raw Materials: The two main ingredients needed for photosynthesis are:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): This gas comes from the air and is absorbed by the plant's leaves.
- Water (H₂O): Plants take up water from the soil through their roots. - Role of Chlorophyll: The leaves of plants contain a green pigment called chlorophyll, which is essential for photosynthesis. Chlorophyll captures sunlight, providing the energy needed for the process.
- Chemical Reaction: Using the energy from sunlight, plants transform carbon dioxide and water into glucose (a type of sugar) and oxygen (O₂). The overall chemical reaction for photosynthesis can be summarized as:
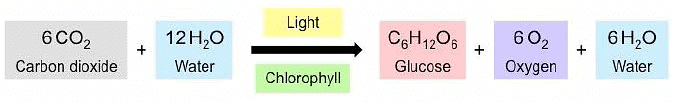 Reaction of Photosynthesis
Reaction of Photosynthesis
- Products of Photosynthesis: The main product of photosynthesis is glucose, which serves as food for the plant. Oxygen is also produced and released into the atmosphere, which is essential for all living beings to breathe.
Q.6. How can we demonstrate that chlorophyll is necessary for photosynthesis?
Ans: Here’s a simple experiment to show that chlorophyll is necessary for photosynthesis:
Materials Needed:
- A potted plant with variegated leaves (green and non-green parts)
- Boiling water
- Ethanol (alcohol)
- Iodine solution
- Light source (sunlight or lamp)
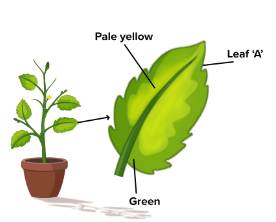 Variegated LeavesSteps:
Variegated LeavesSteps:
Prepare the Plant:
- Take a variegated leaf from the plant.
- Keep the plant in the dark for 24 hours.
Boil the Leaf:
- Boil the leaf in water for 2-3 minutes to kill it.
Decolorize the Leaf:
- Place the boiled leaf in a beaker with ethanol and heat it in a hot water bath for 5-10 minutes. This removes chlorophyll and turns the leaf pale.
Stain with Iodine:
- Rinse the leaf in warm water, then soak it in iodine solution for a few minutes. Iodine will turn blue-black in the presence of starch.
Observe the Results: The green parts turn blue-black, indicating starch is present (photosynthesis occurred).
The non-green parts stay yellow or brown, showing no starch (no photosynthesis).
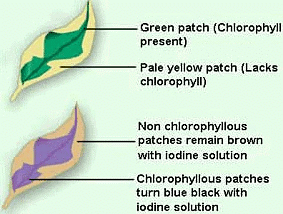
Conclusion:
- The experiment shows that only the green parts of the leaf, which contain chlorophyll, can make food (starch) through photosynthesis. Non-green parts do not have chlorophyll and cannot perform photosynthesis.
Q.7. How do plants obtain nutrients other than carbohydrates?
Ans: Plants primarily produce carbohydrates through photosynthesis, using sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into starch. However, they obtain other essential nutrients directly from the soil. Here’s how this process works:
- Nutrient Absorption: Plants absorb nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrates and ammonium.
- Role of Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria: Nitrogen compounds in the soil are created by nitrogen-fixing bacteria, such as Rhizobium. These bacteria live in a symbiotic relationship with the roots of leguminous plants, helping to convert atmospheric nitrogen into forms that plants can use.
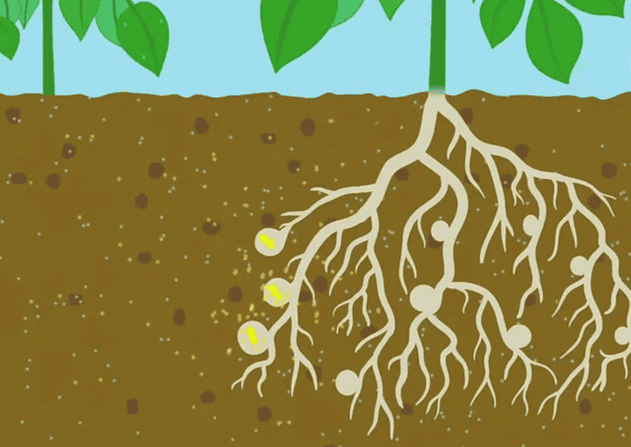 Rhizobium: Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria
Rhizobium: Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria
- Replenishing Nutrients: Farmers can replenish nitrogen compounds in the soil by adding fertilizers and manure. These additions enrich the soil, providing essential nutrients for plant growth.
- Insectivorous Plants: Some plants, like the pitcher plant and Venus flytrap, obtain nitrogen by trapping and digesting insects. This process releases nutrients from the insects, which are then absorbed by the plant.
Q.8. What is the mode of nutrition in fungi?
Ans:
- The mode of nutrition in fungi is heterotrophic.
- They cannot synthesize their food and depend on other ‘organisms’ for their carbon source.
- They perform extracellular digestion by releasing enzymes into their environment and obtaining organic and inorganic nutrients through absorption.
- There are three main ways of obtaining nutrition in Heterotrophic Mode are:
(i) Saprotrophic: Decomposition of ‘dead organic matter’.
(ii) Parasitic: Feeding from a living host.
(iii) Mutualism: Living in a mutually beneficial interaction with another organism. (Example: lichen is a mutualism between fungi and algae).
|
112 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Important Questions - Nutrition in Plants
| 1. What is the process of photosynthesis in plants? |  |
| 2. How do plants obtain nutrients from the soil? |  |
| 3. What role do fungi play in plant nutrition? |  |
| 4. Why are legumes important for soil fertility? |  |
| 5. What are the different types of nutrition in plants? |  |

















