Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Question Answers - Resources and Development
Q1. Distinguish between Potential Resource and Stock with the help of examples.
 Example of Potential Resources
Example of Potential Resources
Ans: Potential Resource: A potential resource refers to resources that exist in a region but are not currently utilised. They may be:
- Not easily accessible
- Not fully developed for present use
Examples of Potential Resources:
- The states of Rajasthan and Gujarat have significant potential for wind and solar energy, yet these resources remain underdeveloped.
- The hot springs in the Himalayan region could provide geothermal energy, but development is lacking. Additionally, mineral deposits are buried in mountains and oceans, awaiting exploitation.
Stocks: Stocks are materials in the environment that can satisfy human needs, but we currently lack the technology to access them.
Examples of Stocks:
- Water is made up of hydrogen and oxygen, which could be a rich energy source. However, we do not yet have the technical knowledge to utilise these gases effectively.
- With advancements in desalination technology, ocean water could become drinkable. Yet, we currently lack the expertise and funding for such projects.
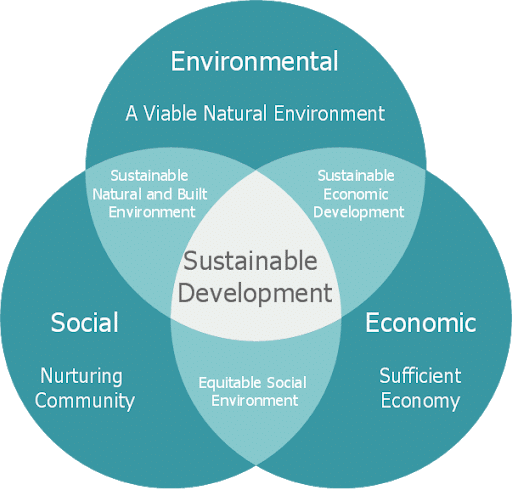
Q2. What does the term ‘sustainable economic development’ mean? How can we eradicate irrational consumption and over-utilization of resources?
Ans: Sustainable economic development refers to growth that meets the needs of the present without harming the environment or compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
To eliminate irrational consumption and the overuse of resources, we can:
- Focus on the conservation of resources.
- Recognise that irrational consumption leads to various socio-economic and environmental issues.
- Implement proper management strategies to ensure resources are preserved for future generations.
Q3. List the problems caused due to the indiscriminate use of resources by human beings.
Ans: Indiscriminate use of resources by humans has resulted in several significant problems:
- Depletion of resources to satisfy the greed of a few individuals.
- Wealth accumulation in the hands of a few, leading to a divide in society between the rich and the poor.
- Uncontrolled exploitation of resources has caused serious ecological issues, including global warming, ozone layer depletion, environmental pollution, and land degradation.
Q4. Why does the pattern of the net sown area vary from one state to another?
Ans: The pattern of the net sown area varies significantly across different states in India:
- In Punjab and Haryana, over 80% of the total area is cultivated, benefiting from favourable geographical conditions such as climate and soil.
- The Green Revolution has also contributed to increased cultivation in these regions.
- Conversely, states like Manipur, Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands have less than 10% of their area under cultivation.
- The low net sown area in these states is due to:
- Topographical constraints
- Unfavourable climate
- Socio-economic factors
Q5. Analyze the four main factors which help in the formation of soil.
Ans: Relief, nature of parent rock, climate, vegetation, and time are key factors in the formation of soil.
These factors contribute to the weathering of parent rocks through:
- Climatic factors: Changes in temperature, wind, frost action, and rainfall.
- Natural forces: Actions of running water, wind, and glaciers.
The four main factors of soil formation are:
- Relief: Influences weathering and erosion.
- Climate: Affects the rate of rock denudation and influences weathering.
- Nature of parent rock: Determines soil colour, texture, and mineral content.
- Time: Influences soil maturity, often taking millions of years to form just a few centimetres.
Q6. What is the main cause of land degradation in Gujarat, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh? How can it be checked?

Ans: The main cause of land degradation in Gujarat, Rajasthan, and Madhya Pradesh is primarily due to overgrazing by a large population of cattle. This practice has led to significant damage to the grasslands in these regions.
To address this issue, several measures can be implemented:
- Planting trees and managing grazing areas effectively.
- Implementing controls on grazing by designating specific areas for this purpose.
Q7. Where was Agenda 21 signed? What were the main provisions of Agenda 21?
Ans: Agenda 21 was signed in 1992 at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The main provisions of Agenda 21 include:
- Elimination of poverty and hunger worldwide.
- Improvement of health and education, particularly in literacy.
- Protection and restoration of ecosystems that support life.
Q8. Do you think the future generation may not have sufficient resources as compared to the present generations? Why?
Ans: Yes, the future generation may not have sufficient resources compared to the present generations.
- This is largely due to human activities such as deforestation and increased agriculture and mining.
- These activities lead to the degradation of land and the environment.
- The rapid consumption of fossil fuels may result in their depletion, as they are non-renewable.
- If we continue at this pace, there may not be enough resources left for future generations.
|
66 videos|798 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Question Answers - Resources and Development
| 1. What are the different types of resources in development? |  |
| 2. How can sustainable development be achieved? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of human resources in development? |  |
| 4. What role do natural resources play in a country's development? |  |
| 5. How do capital resources contribute to economic development? |  |

















