Class 8 Science - Question Answers Crop Production and Management- 2
Q.21. Why do we have to eat food?
Ans. Food provides us energy. The energy provided by food is utilised by the organisms for carrying out their various body functions, such as digestion, respiration and excretion. We get our food from plants and animals.
Q.22. Explain various types of crops.
Ans. Crops are of two types:
(a) Kharif crops: The crops which are grown in the rainy season are called kharif crops (June to September). Paddy, maize, soyabean, groundnut, cotton are some of the major kharif crops.
(b) Rabi crops: The crops sown in the winter season are called rabi crops (October to March). Wheat, gram, pea, mustard and linseed are some of the major rabi crops.
Q.23. List various agricultural practices.
Ans. The agricultural practices are listed below:
(a) Preparation of soil
(b) Sowing
(c) Adding manure and fertilizers
(d) Irrigation
(e) Protecting from weeds
(f) Harvesting
(g) Storage
Q.24. What is plough?
Ans. This implement is made of wood and iron. It is drawn by a pair of bulls or other animals. It contains a strong triangular iron strip called ploughshare. The main part of the plough is a long log of wood which is called ploughshaft. The plough is used for tilling the soil, adding fertilizers to the crop, removing the weeds and scraping of soil.
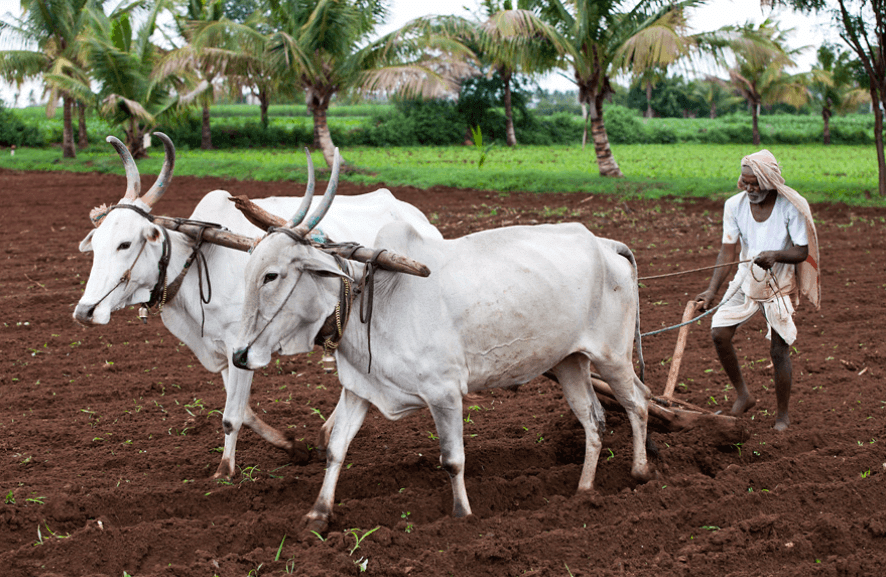

Fig: Farmer Ploughing
Q.25. What is hoe? What is its use?
Ans. Hoe is a simple tool which is used for removing weeds and for loosening the soil. It has a long rod of wood or the iron. A strong broad and bent plate of iron is fixed to one of its ends and works like a blade. It is also pulled by animals.
Q.26. Explain the preparation of manure by the farmers.
Ans. Manure is an organic substance obtained from decomposition of plant or animal wastes. Farmers dump plant and animal wastes in pits at open places and allow it to decompose. The decomposition is caused by some microorganisms. The decomposed matter is used as organic manure.
Q.27. What are fertilizers? How do they differ from manure on the basis of their formation?
Ans. Fertilizers are the chemical substances which are rich in a particular nutrient. Fertilizers are produced in the factories while manure can be made by farmers themselves in the fields. Some fertilizers are urea, ammonium sulphate, super‑phosphate, potash, N.P.K. (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium). Fertilizers are used to get better yield of crops.
Q.28. What is the role of water in the production of crops?
Ans. Water is essential for plants. It helps in the germination of seeds because seeds cannot germinate under dry conditions. Nutrients dissolved in water get transported to each part of the plant. It protects the crop from frost and hot air currents. Water is important for proper growth and development of flowers, fruits and seeds of plants. Along with water minerals and fertilizers are also absorbed. Plants contain nearly 90% water. The time and frequency of irrigation varies from crop to crop, soil to soil and season to season.
Q.29. Explain traditional methods of irrigation.
Ans. The water available in wells, lakes and canals is lifted up by different methods in different regions, for taking it to the fields. Cattle or human labour is used in these methods. These methods are cheaper but less efficient. The various traditional ways are:
(a) Moat (Pulley system)
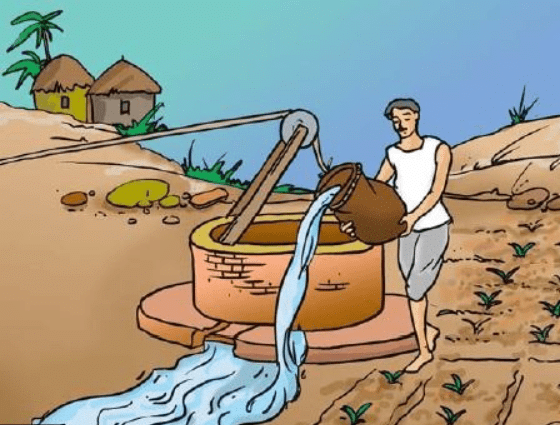

Fig: Moat
(b) Chain pump
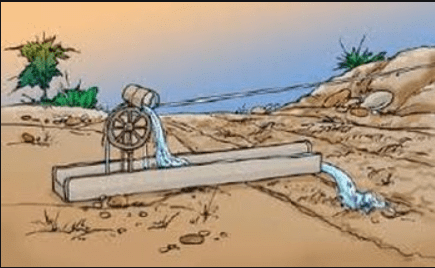
Fig: Chain pump
(c) Dhekli
 Fig: Dhekli
Fig: Dhekli
(d) Rahat (Lever system)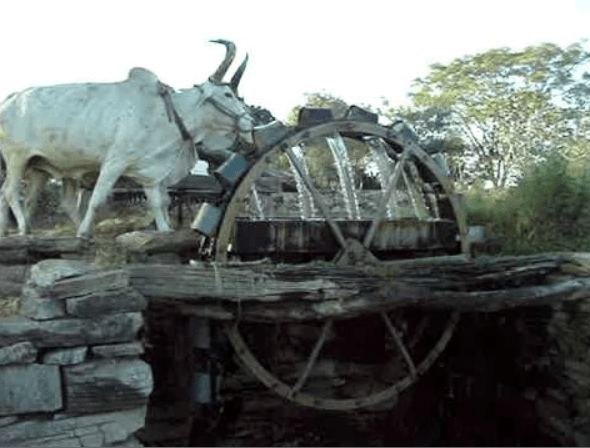
Fig: Rahat
Q.30. What is weeding? Why is it necessary?
Ans. The process of removal of weeds is called weeding. Weeding is necessary since weeds compete with crop plants for water, nutrients, space and sunlight. Thus they affect the growth of crop. Some weeds interfere even in harvesting and may be poisonous for animals and human beings.
Q.31. Explain the various methods of weeding.
Ans. Farmers use many ways to remove weeds and control their growth. Tilling before sowing of crops helps in uprooting and killing weeds, which may then dry up and get mixed with the soil. The best time for the removal of weeds is before they produce flowers and seeds. The khurpi is used to remove weeds by uprooting or cutting them from time to time. A seed drill is also used to uproot weeds. Weeds are also controlled by using weedicides like 2, 4‑D.

Fig: Spraying weedicide
Q.32. Explain various methods of harvesting in our country.
Ans. There are mainly two methods which are used to harvest the mature crops:
(a) Manual: A device called sickle is used to harvest mature crops manually.
(b) By Machine: A machine called harvester is also used to harvest crops. A machine called combine which is in fact, a combined harvester and thresher. This machine does both the functions of harvesting and threshing at the same time.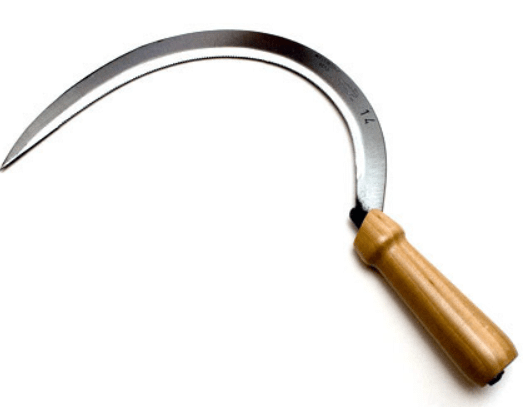
Fig: Sickle
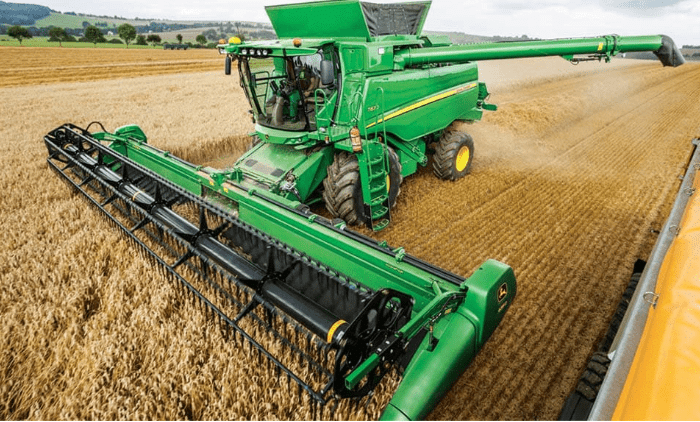

Fig: Combine
Q.33. What do you know about Harvest Festival?
Ans. After three or four months of hard work there comes the day of harvest. The sight of golden fields of standing crops, laden with grains fills the hearts of farmers with joy and a sense of well being. Men and women celebrate this period with great enthusiasm. This period of joy is called Harvest Festival. Pongal, Baishakhi, Holi, Diwali, Nabanya and Bihu are such Harvest Festivals.
Q.34. How do the grains stored and preserved?
Ans. Farmers store the grains in jute bags or metallic bins. However, large scale storage of grains is done in silos and granaries, to protect them from pests like rats and insects. Dried neem leaves are used for storing food grains at home. For storing large quantities of grains in big godowns, specific chemical treatments are required to protect them from pests and microorganisms.
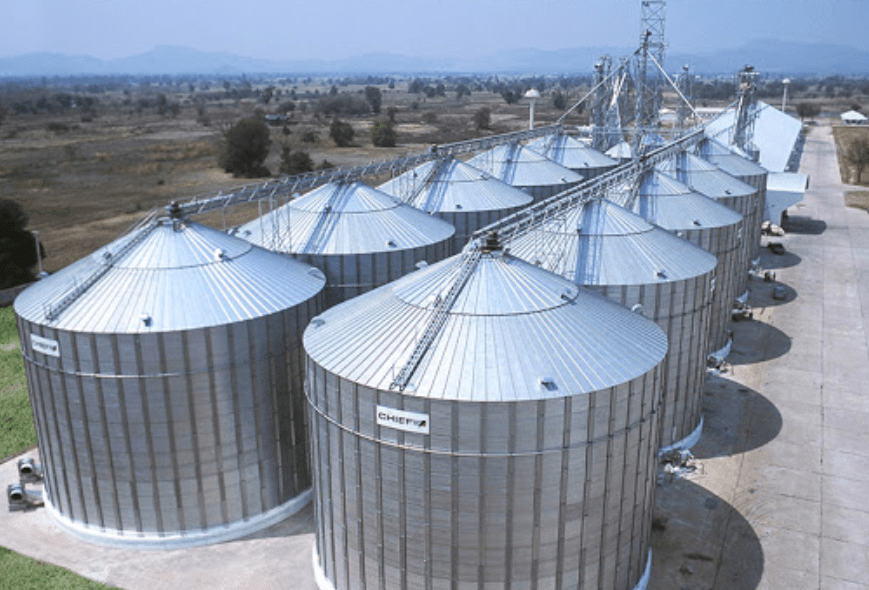

Fig: (a) Silos for storage of grains
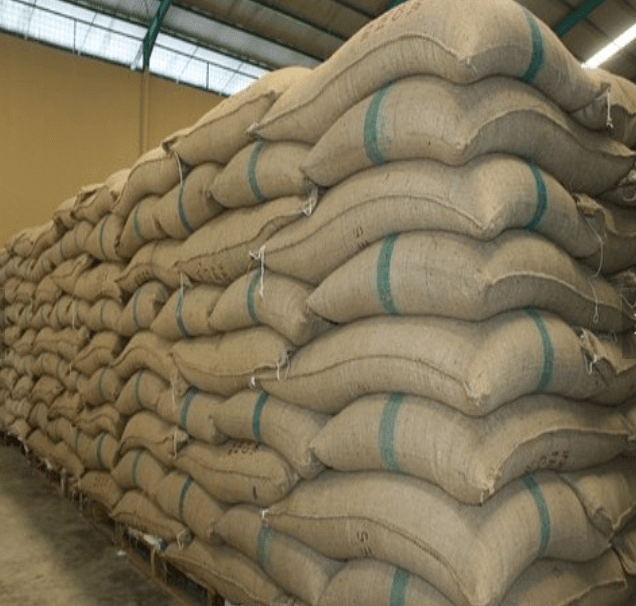

Fig: (b) Storage of grains in granaries
Q.35. Write the name of some food material, provided by animals.
Ans.
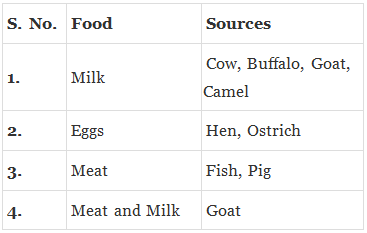
|
90 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Science - Question Answers Crop Production and Management- 2
| 1. What is crop production? |  |
| 2. How is crop production managed? |  |
| 3. What are the different methods of crop production? |  |
| 4. How does crop production contribute to the economy? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges faced in crop production? |  |
















