Class 10 Economics Chapter 2 Extra Question Answers - Sectors of the Indian Economy
Short Answer Questions
Q1: Explain the difference in employment conditions in organised and unorganized sectors.
Ans:
Organised Sector | Unorganized Sector |
Working conditions are regulated on the basis of government rules and regulations, | There are rules but they are not strictly implemented for the benefit of workers |
Workers have job security. | Worker have no job security. |
Workers get weekly holidays, medical facilities, retirement benefits, etc. | There are no such benefits at work. |
Q2: Explain the objectives of implementing the MGNREGA 2005.
Ans:
(i) To provide work to those who are able and are in need of work, in rural areas.
(ii) They are to be provided guaranteed 100 days of employment in a year.
(iii) If government fails in its duty to provide employment, it will give unemployment allowance to the worker.
(iv) The types of work that would in future help to increase agricultural production will be given preference under the Act.
Q3: Explain the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors by giving examples of each.
Ans:
Primary Sector:- All those economic activities that are undertaken by directly using natural resources are included in primary sector. For example, mining, forestry, fishing, poultry etc.
Secondary sector:- It cover activities in which natural products are changed into other forms through ways of manufacturing that we generally associate with industrial activities. For example, after obtaining a crop, say cotton, we need machines to change it into yarn and cloth.
Tertiary Sector:- These are the activities that help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors. These activities, by themselves do not produce any good but they are an aid or a support to the production process. For example, any good produced in primary or secondary sector need to be transported to the market. That will be done by tertiary sector. It is also called service sector.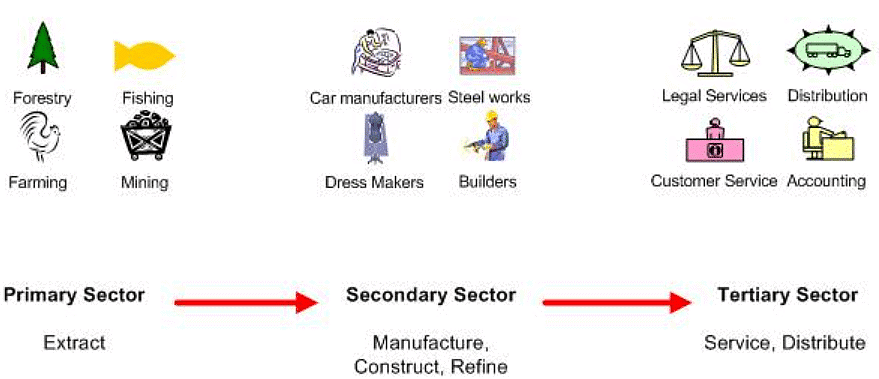
Q4: Describe the role played by National Rural Employment Guarantee Act in improving the employment situation in India.
Ans: The National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, which is now called Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act or ‘MGNREGA’, has improved employment situation in rural India in the following ways —
(i) As this Act provides minimum 100 days of work guarantee to a member of each rural family, it means no family will be without the opportunity of work although only for 100 days.
(ii) By providing jobs some assets are being created in rural areas which are further creating jobs like tree plantation, pool construction, etc.
(iii) MNREGA has checked mass rural migration to urban centers for jobs and other livelihood opportunities.
Q5: ‘Economic activities, though grouped into three different categories, are highly interdependent.’ - Discuss.
Ans: All Economic activities are interdependent as no activity can sustain itself alone –Economic activities in all sectors are interdependent. The primary sector provides raw materials for the secondary sector. For example, tobacco is needed for the cigarette industry, sugarcane is needed for sugar industry. To provide transportation, banking facilities, and management to the primary and secondary sectors, the tertiary sector is needed.
Q6: Write three ways to increase employment opportunities for people in India.
Ans: Employment opportunities for people can be increased in the following ways:–
(a) In villages more irrigation facilities should be provided so that farmers can grow more crops and they would be engaged throughout the year.
(b) Agro-based industries should be set up in villages so that farmers could get good prices for their products. For example, sugar mills.
(c) People should be given easy loan facilities which would help them to start their own enterprises.
Q7: Describe any three problems faced by workers in the unorganized sector.
Ans: The workers of unorganized sector face following problems:–
(a) They are not paid according to government rules. They are underpaid.
(b) They are not given other facilities like holidays, medical facility, gratuity, etc.
(c) They can be asked to leave without any reason. There is no job security. Workers are hired as and when needed and then asked to leave job without any compensation.
Q8: Explain the term GDP. Why are only ‘final goods and services’ counted in GDP?
Ans: GDP means Gross Domestic Product of a country. It is the value of all final goods and services produced within a country during a particular year. Only the final goods and services are counted in the GDP. For example, if wheat is sold at Rs. 8 per kg. to flour mill, which sells flour to Biscuit company which then uses flour to make biscuits. Then the value of biscuits would be counted, not the value of flour. This is to avoid double-counting. The value of biscuits contains the value of intermediary goods their production.
Q9: Explain what is meant by disguised unemployment. Give examples from rural and urban areas where disguised unemployment exists.
Ans: Disguised employment is a hidden unemployment. It means a person seems to be doing a job but actually he is not required there. If he is taken out of the job, no difference in the productivity would be felt.
In rural areas all family members work on the agricultural field but all the work can be done only by one person alone. Rest are just engaged. In urban areas, casual workers do petty jobs. They are not employed adequately.
Q10: Service sector in India employs different kinds of people. Explain with example. Ans: Service sector employ different kinds of people. There are a very large number of workers engaged in services such as small shopkeepers, repair persons, transport persons etc. These people barely manage to earn a living. services like management, banking, finance, marketing, insurance, transport and communication are included in the tertiary sector. So, obviously different kinds of people are engaged in the service sector or tertiary sector.
Ans: Service sector employ different kinds of people. There are a very large number of workers engaged in services such as small shopkeepers, repair persons, transport persons etc. These people barely manage to earn a living. services like management, banking, finance, marketing, insurance, transport and communication are included in the tertiary sector. So, obviously different kinds of people are engaged in the service sector or tertiary sector.
Q11: Why is agriculture an activity of unorganized sector in India?
Ans: Agriculture is a sector which is not regulated by the government because land belongs to an individual. Hence farmer or whoever owns the land hires workers as and when required. So government cannot intervene in hiring or regulating work conditions. Agriculture is fully dependent on natural factors, and these factors are not within control of any human being or government. Moreover, most of the fields are small and scattered being cultivated by small and marginal farmers. It is just not possible to put agriculture in organised sector.
Q12: Differentiate between the public sector and private sector by giving examples.
Ans: In the public sector, the government owns most of the assets and provides all the services. In the private sector, ownership of assets and delivery of services is in the hands of private individuals or companies. Railways and Post Office is an example of the public sector whereas companies like Tata Iron and Steel Company Limited (TISCO) and Reliance Industries Limited (RIL) are in private sector.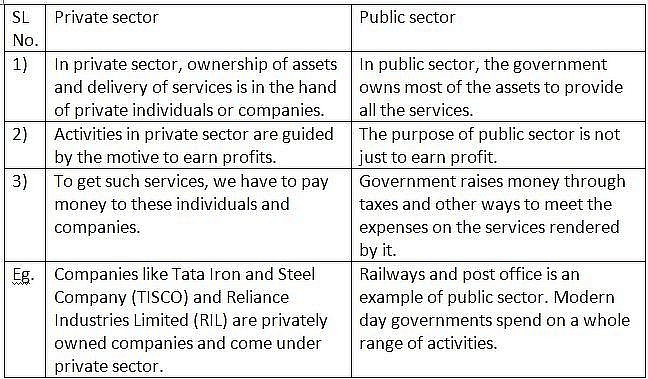
Q13: Suggest any three ways to create more employment avenues in Urban sector.
Ans:
(i) Industrialization– Developing private sector industries by giving more incentives
(ii) Creating Special Economic Zones in urban areas.
(iii) Laying more emphasis on export of goods.
(iv) Developing new sectors like tourism-promoting regional craft industry.
(v) Expanding IT sector.
Q14: How can the workers in the unorganized sector be protected? Explain.
Ans: In the rural areas, the unorganized sector mostly comprises of landless labourers, small and marginal farmers, artisans, etc. These people need to be supported through adequate facility for timely delivery of seeds, agricultural inputs, credit, storage facilities and marketing outlets. In the urban areas, unorganized sector comprises mainly workers in small-scale industry, casual workers in trade, transport and construction, etc. Small scale industries need government support for procuring raw material and marketing of output. The casual workers need to be protected by law. A separate body of rules and regulations need to be made to manage activities in the unorganized sector.
Long Answer Questions
Q1: What steps should be taken to create more employment? Explain.
Ans: Following steps can be taken to create more employment:—
(i) Increase in irrigation facilities:- Without irrigation only a single crop is grown in most agricultural fields. It means less working opportunities, but if irrigation is provided two or three crops can be grown on the same field. So more people will be employed. (ii) Improved Roads and Transportation:- If village roads are better built, good transportation facilities are provided then, surplus produce could be sold in city market. This would fetch more income.
(ii) Improved Roads and Transportation:- If village roads are better built, good transportation facilities are provided then, surplus produce could be sold in city market. This would fetch more income.
(iii) Provide them easy loan:- If people are provided easy bank loans then they could start small business which will make them self dependent.
Q2: Study the data given in the table and answer the following questions.
Workers in different sectors (in millions)
Sector | Organised Sector | Unorganized Sector | Total |
Primary | 4 | 236 | 240 |
Secondary | 12 | 55 | 67 |
Tertiary | 24 | 75 | 99 |
Total | 40 | 366 | 406 |
(i) Which sector provides maximum number of jobs?
(ii) How many workers are working in the unorganized sector?
(iii) Which organised sector is the most important and why?
Ans:
(i) Primary Sector
(ii) 366 million workers
(iii) Tertiary Sector is the most important organised sector because it provides maximum number of jobs.
Q3: Explain how public sector contributes to the economic development of India.
Ans: Public sector is an important sector for the development of economy.
(i) There are several things needed by the society as a whole but which the private sector will not provide at a reasonable cost. As huge sum of amount is needed which private sector can not afford, so public sector is needed there. For example, building bridges, railway etc.
(ii) There are several basic activities which government has to support, for example, selling electricity at lower cost, providing drinking water at affordable rate etc.
(iii) There are some activities which government has to perform like providing health and education facilities. So public sector is needed.
Q4: Study the graph given below and answer the following questions:

(i) Which was the largest producing sector in 1973?
(ii) Which was the largest producing sector in 2003?
(iii) Which sector has grown the most over thirty years?
(iv) What was the GDP of India in 2003?
Ans:
(i) Primary Sector
(ii) Tertiary Sector
(iii) Tertiary Sector
(iv) Rs. 2,100,00 crore
Q5: Explain four features of an organised sector.
Ans: Four features of organised sectors:–
(i) Workers have job security.
(ii) Government rules are followed properly in terms of employment.
(iii) Post retirement facilities are provided.
(iv) Workers get paid holidays, medical facilities, bonus, gratuity, etc.
Q6: In which sector are most of the people employed and why?
Ans: Most of the workers are employed in Primary Sector, because :—
(i) Not enough jobs have been created in the secondary and tertiary sectors.
(ii) More than half of the workers in the country are working in the primary sector although Primary sector contributes only one third of G.D.P.
Q7: What do you mean by tertiary sector? Explain the role of this sector in the Indian economy.
Ans:
- The economic activities that support primary and secondary sectors are included in tertiary sector. This includes transport facilities, banking facilities, medical facilities, education facilities etc. This sector is very important for an economy.
- It is going to be more important for India because due to rapid industrialization several activities are needed like, transport, banking, marketing, insurance etc. Skilled educated class is required for all sector which has to be provided by education sector. When income level increase people demand more services like catering, tourism etc.
- Several new services like information technology have come up which are providing great employment opportunities.
Q8: Why is the tertiary sector growing so rapidly in India? Explain it with four reasons.
Ans: Tertiary sector is growing rapidly because:
(i) India’s economy is growing fast. Several services like hospital, educational institutions, post, telegraph, police, courts, municipality, transport, banks, insurance etc are needed.
(ii) Development of agriculture and industry lead to the development of services such as transport, trade, storage etc, so these would be in greater demand.
(iii) As income level increases certain sections of people start demanding many more services like eating out, tourism, shopping, private hospital etc.
(iv) Certain new services have emerged like information and communication technology which have become important.
Q9: What is an organised sector? Describe its working conditions
Ans:
Organised Sector: This sector covers those enterprises or places of work where the terms of employment are regular. They are registered by the government and have to follow the rules and regulations. There people have job security.
Working Conditions:
(i) Fixed working hours an organised sector: In organised sector working hours are fixed. If employee is working after the fixed time, he would be paid extra money for it.
(ii) Wage structure divided under various heads : The wage structure is divided under various heads like provident fund, gratuity and various allowances. Employees get pension after retirement in organised sector.
Q10: Why is the tertiary sector becoming more important than other sectors in India? Give four reasons.
Ans: Tertiary sector has become important in India due to
(i) Basic services like hospitals, education, post and telegraph, courts etc. are the responsibility of the government.
(ii) Demand for services such as transport, trade, storage has increased with the development of primary and secondary sectors.
(iii) Demand for tourism, shopping, private schools, private hospitals etc. increased with the increase in the level of income.
(iv) Rapid growth of service sector also benefited from external demand such as software industry and call center services.
Q11: What is the significance of secondary sector in Indian economy? How does it help in the economic development of the country?
Ans: After independence secondary sector or manufacturing sector became the most important in total production and employment. In the past 30 years, service sector has taken a lead in terms of total production and employment. However, tertiary sector is largely dependent on secondary sector. Goods produced need to be sold, marketed and distributed. Banking activities and insurance sector get a boost by an expanding secondary sector. All sector are inter-related and expansion or shrinking of one sector has effects on other sectors too. As of now primary sector is the leading employer followed by tertiary and secondary sectors in that order. In terms of share in GDP tertiary sector is the leading sector followed by primary and secondary sectors.
Q12: Explain how a shift has taken place between sectors in developed countries?
Ans: About more than 100 years ago new methods of manufacturing and technological revolution took place. People who worked in farms began working in factories in large numbers in new urban centers. Secondary sector gradually became the most important in terms of production and employment. Hence, over a time, a shift had taken place from primary to secondary sector. In the past 100 years there has been a further shift from secondary to tertiary sector in developed countries. The service sector has become the most important in terms of total production. Most of the working people are currently employed in the service sector. This is the general pattern observed in developed countries.
|
63 videos|445 docs|87 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Economics Chapter 2 Extra Question Answers - Sectors of the Indian Economy
| 1. What are the different sectors of the Indian economy? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the primary sector in the Indian economy? |  |
| 3. How does the secondary sector contribute to the Indian economy? |  |
| 4. What are the major challenges faced by the tertiary sector in India? |  |
| 5. How does the Indian economy benefit from the growth of the tertiary sector? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|













