NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics - Employment: Growth, Informalisation and Other Issues
Q1: Who is a worker?
Ans:
- A worker is someone who engages in activities to earn a living by contributing to the production of goods and services.
- In simpler terms, a worker is an economic agent who plays a role in creating goods or providing services, which helps to generate income for themselves and adds to the country's GDP during a specific period.
- For example, a farmer growing crops, a teacher teaching students, and a factory worker manufacturing products are all considered workers.
Q2: Define the worker-population ratio.
Ans: The worker-population ratio is defined as the proportion of the population that is actively contributing to the production of goods and services. It is measured by the ratio between the country’s workforce and its total population. The worker-population ratio is estimated by dividing the total workforce by the total population and multiplying by 100. 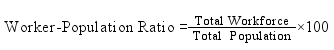
Q3: Are the following workers — a beggar, a thief, a smuggler, a gambler? Why?
Ans: No, a beggar, a thief, a smuggler, or a gambler cannot be considered a worker. A worker is someone who takes part in legal production activities that contribute to a country's GDP and national income. These individuals do not engage in any lawful economic activities that add value to the economy. Begging, theft, smuggling, and gambling are either illegal or non-productive activities that do not contribute to the country's economic growth. Therefore, they cannot be regarded as workers.
Q4: Find the odd man out
(i) owner of a saloon
(ii) a cobbler
(iii) a cashier in Mother Dairy
(iv) a tuition master
(v) transport operator
(vi) construction worker
Ans: The tuition master and the owner of a saloon are the odd man out. This is because all others are hired while these two are self-employed. The tuition master and the owner of a saloon are engaged in their own business and profession, whereas, the cobbler, the construction worker, the transport operator and the cashier in the Mother Dairy are hired and render their services to others in exchange for rewards in the form of salaries or wages.
Q5: The newly emerging jobs are found mostly in the ____________sector
(service/manufacturing).
Ans: The newly emerging jobs are found mostly in the service sector.
The service sector is taking a lead over the manufacturing sector as a source of employment. It includes trade, commerce, banking, insurance, health and other services. These services are developing at a faster pace than the manufacturing and other allied production activities. This is because of the globalisation of the economy.
Q6: An establishment with four hired workers is known as __________ (formal/informal) sector establishment.
Ans: An establishment with four hired workers is known as an informal sector establishment.
An informal sector is an unorganised sector of the economy. It includes all enterprises that hire less than 10 workers, except farming and self-employment ventures. Therefore, an establishment with four hired workers is known as an informal sector establishment.
Q7: Raj is going to school. When he is not in school, you will find him working on his farm. Can you consider him as a worker? Why?
Ans: Yes, Raj can be considered a worker. This is because his work is contributing to the total output of the farm. Further, as implied by the definition of worker, a person who is engaged in an economic activity or is assisting anyone in an economic activity and, thereby, is contributing to the GDP of the country.
Q8: Compared to urban women, more rural women are found working. Why?
Ans:
- Rural women make up 30% of the workforce, while urban women make up only 14%.
- This higher participation in rural areas is largely due to lower education and skill requirements for farm work, which allows women to support their families.
- Rural poverty also drives many women to take low-paying jobs.
- In contrast, urban families earn more, so there is less need for urban women to work.
- Additionally, family decisions often influence whether women work.
- Although female literacy is improving, it needs to rise further to increase urban women's participation in the workforce.
Q9: Meena is a housewife. Besides taking care of household chores, she works in the cloth shop which is owned and operated by her husband. Can she be considered as a worker? Why?
Ans: Yes, Meena can be considered a worker. Although she is a housewife, she contributes labour to her husband's cloth shop, which is productive work. Even though she is not formally employed or may not receive a wage, her efforts in the shop add economic value and support the family business. Therefore, her work qualifies her as a worker in economic terms.
Q10: Find the odd man out (i) a rickshaw puller who works under a rickshaw owner (ii) a mason (iii) a mechanic shop worker (iv) a shoeshine boy.
Ans: Shoeshine boy is the odd man out. All others (a rickshaw puller, a mason, and a mechanic shop worker) are hired workers. They render their services to their employers and receive rewards in the form of salaries or wages in return. On the other hand, the shoeshine boy is a self-employed worker and carries out his occupation himself. In other words, he is engaged in his own profession.
Q11: The following table shows the distribution of the workforce in India for the year 1972-73. Analyse it and give reasons for the nature of workforce distribution. You will notice that the data is pertaining to the situation in India 30 years ago!
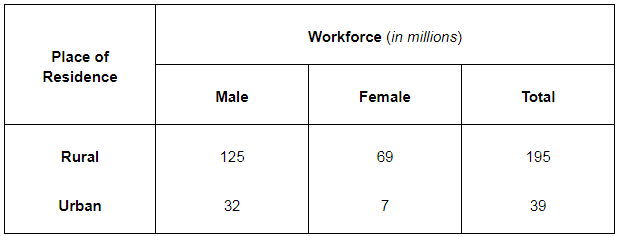 Ans: (i) In 1972-73, India's workforce was 234 million, with 83% (195 million) from rural areas and 17% (39 million) from urban areas, due to the high rural involvement in agriculture.
Ans: (i) In 1972-73, India's workforce was 234 million, with 83% (195 million) from rural areas and 17% (39 million) from urban areas, due to the high rural involvement in agriculture.(ii) The rural workforce was 64% male and 36% female, while the urban workforce was 82% male and 18% female. Male participation was higher in both areas due to limited education and job opportunities for women, along with family discouragement.
(iii) Rural females made up 36% of their workforce, compared to 18% in urban areas. Rural areas relied on low-productivity agriculture, leading to low earnings and widespread poverty.
In summary, the Indian economy at the time faced low productivity, unemployment, poverty, and low female workforce participation.
Q12: The following table shows the population and worker population ratio for India in 1999-2000. Can you estimate the workforce (urban and total) for India?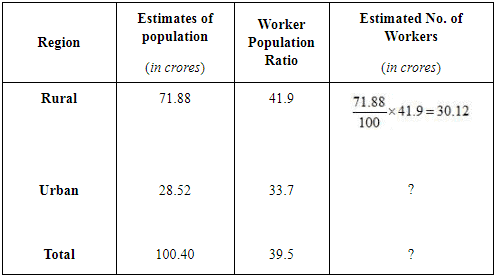 Ans:
Ans: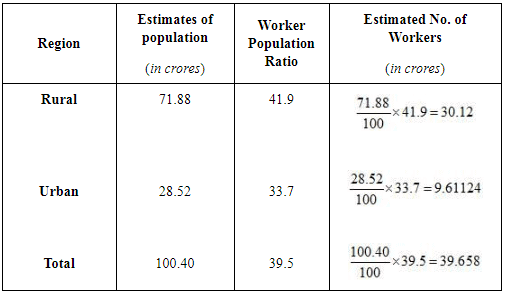
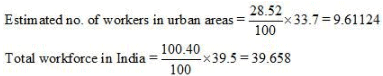
Q13: Why are regular salaried employees more in urban areas than in rural areas?
Ans: Regular salaried employees are permanent, skilled workers who receive social security benefits. These jobs are more common in urban areas, where training and education are more accessible, allowing workers to acquire specialized skills. Urban areas also host most large companies due to better infrastructure, banks, transport, and communication facilities. This concentration of jobs in cities leads to a higher number of regular salaried employees in urban areas compared to rural areas.
Q14: Why are less women found in regular salaried employment?
Ans:
- Fewer women are in regular salaried employment than men because many women work in economic activities without stable contracts or steady income, key features of regular salaried jobs.
- Women are often employed in informal sectors without social security benefits and tend to work in more vulnerable conditions with less bargaining power, resulting in lower pay compared to men.
- Consequently, women are more likely to be found in self-employment and casual work rather than regular salaried positions.
Q15: Analyse the recent trends in the sectoral distribution of the workforce in India.
Ans:
- The three main economic sectors—Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary—form an economy's occupational structure.
- The primary sector includes agriculture, forestry, and fishing, employing the largest portion of India’s workforce at 57.3%.
- The secondary sector (manufacturing and construction) employs 17.6%, while the tertiary sector (services like transport and trade) employs 25.1%.
- Urban workers are mostly in the secondary and tertiary sectors, while rural workers are mainly in the primary sector.
- The tertiary sector is also growing as a significant employment source and contributor to GDP.
- More women are employed in the primary sector than in the secondary and tertiary sectors.
Q16: Compared to the 1970s, there has hardly been any change in the distribution of workforce across various industries. Comment.
Ans:
- India’s agrarian economy relies heavily on agriculture for livelihoods, with a large population dependent on this sector.
- Although India aimed to reduce this dependence, the change has been slow.
- From 1972-73 to 1999-00, the workforce in the primary sector dropped from 74% to 60%, while the secondary and tertiary sectors grew from 11% to 16% and 15% to 24%, respectively.
- Over these years, many workers shifted from self-employment and salaried jobs to casual wage work, a trend known as casualisation of the workforce.
- Despite these shifts, the industrial and tertiary sectors need to grow further to absorb excess agricultural labor and create more employment opportunities.
Q17: Do you think that in the last 50 years, employment generated in the country is commensurate with the growth of GDP in India? How?
Ans:
- Economic growth refers to an increase in GDP, or total output, within a country.
- Ideally, this growth comes from creating more jobs and using better technology.
- However, in recent years, India has experienced jobless growth—where GDP rises but employment does not increase proportionally.
- This is largely due to advanced technology replacing labour in the industrial and tertiary sectors, preventing these sectors from absorbing surplus agricultural labour.
- As a result, disguised unemployment persists in agriculture, leading to low productivity and widespread poverty.
- Additionally, MNCs contribute to growth by using skilled labour and advanced technology, but they create limited jobs, mainly for educated workers.
- Consequently, India's employment growth does not match its GDP growth.
Q18: Is it necessary to generate employment in the formal sector rather than in the informal sector? Why?
Ans:
- The formal sector is the organized part of the economy, including government, public enterprises, and private establishments with 10 or more workers.
- Workers here enjoy social security benefits and are protected by labour laws.
- In contrast, the informal sector is unorganized, with workers lacking social security, trade unions, and bargaining power, making them more vulnerable to market uncertainties.
- Increasing jobs in the formal sector can absorb workers from the informal sector, helping reduce poverty and income inequality.
- Therefore, generating more formal sector employment is crucial for economic growth and safeguarding workers' interests.
Q19: Victor is able to get work only for two hours in a day. Rest of the day, he is looking for work. Is he unemployed? Why? What kind of jobs could persons like Victor is doing?
Ans: Yes, Victor is an unemployed worker. He works for two hours a day but a major portion of the day he is looking for work and is unemployed. This implies that he is an underemployed worker. The situation of underemployment refers to a situation in which a person gets work for less time than the time he actually can and wants to work. According to the National Sample Survey Statistics, a person who is employed for less than 28 hours a week is called underemployed. Victor could do jobs that are part-time in nature like dropping newspapers, working in a restaurant, delivering couriers, bank tellers, etc.
Q20: You are residing in a village. If you are asked to advice the village panchayat, what kinds of activities would you suggest for the improvement of your village which would also generate employment.
Ans: The following are the suggestions that can generate employment opportunities in a village:
- Increase Production: Boost production in agriculture and industry by promoting small-scale and cottage industries, which will create jobs and support the industrial sector.
- Increase Productivity: Higher productivity leads to higher profits, investment, and demand for labour. Rural workers should be trained in modern techniques to improve productivity and accept modernization.
- Control Population: Population growth hampers economic progress. Rural populations should be educated about family planning and birth control to manage growth and reduce unemployment.
- Create Non-agricultural Employment: With a large part of the workforce in agriculture, it's crucial to create non-agricultural jobs like pottery and handicrafts, especially during the off-season, to reduce disguised unemployment and increase farmers' income.
- Easy Credit and Finance: Rural areas face challenges accessing finance due to a lack of institutions and high lending rates. Setting up financial institutions can provide affordable credit to support rural development.
- Education and Health Facilities: Improving education and healthcare in rural areas can boost productivity and quality of life. Establishing schools, night schools for adults, technical education, sanitation, and healthcare services are vital for long-term development.
Q21: Who is a casual wage labourer?
Ans: Casual workers refer to those workers who do not work throughout the year. They only work for a few months. Casual workers are not hired by employers on a regular basis. They do not enjoy social security benefits like provident fund, gratuity, etc. They are generally unskilled workers. For example: workers working at a construction site.
Q22: How will you know whether a worker is working in the informal sector?
Ans: The following features help to recognise a worker working in the informal sector:
- A worker working in an enterprise (other than the public sector establishments and the private sector establishments) hiring 10 or less than 10 workers.
- This sector includes millions of farmers, agricultural labourers, owners of small enterprises and self-employed. These sections of people are not hired workers.
- A worker working in the informal sector does not enjoy social security benefits such as provident fund, gratuity, pension, etc.
- The economic interest of the workers working in the informal sector is not protected by any Labour Laws other than the Minimum Wages Act. Therefore, workers in the informal sector are highly exposed to the uncertainties of the market and have low bargaining power.
|
64 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics - Employment: Growth, Informalisation and Other Issues
| 1. What are the main factors contributing to employment growth in India? |  |
| 2. How does informalization of employment affect workers in India? |  |
| 3. What are the implications of informal employment on economic growth? |  |
| 4. What measures can be taken to formalize informal employment in India? |  |
| 5. How does the COVID-19 pandemic impact employment in the informal sector? |  |






















