Class 9 Geography Chapter 1 Question Answers - Contemporary India - I
Q1. Which are the countries with which India shares land boundaries? Write a short note about India’s position among its neighbours.
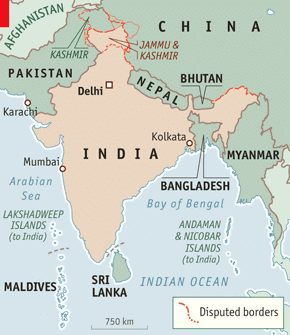 Fig: Neighbours of India
Fig: Neighbours of India
Ans: India shares its land boundaries with:
- Pakistan and Afghanistan in the northwest
- China (Tibet), Nepal, and Bhutan in the north
- Myanmar and Bangladesh in the east
The geographical position of India among its neighbours is significant:
- The Himalayas provide a natural barrier to the north and northwest.
- India holds a prominent position in the Indian subcontinent.
- Strong geographical and historical links exist with neighbouring countries.
India maintains robust relationships with its neighbours:
Q2. Write a note on the location and size of India [Important]
Ans: Location
- India is a vast country located in South Asia.
- It lies entirely in the Northern Hemisphere, extending from 8°04'N to 37°06'N latitude.
- The Tropic of Cancer (23°30'N) runs through the middle of the country.
- From west to east, India spans 68°07'E to 97°25'E longitude.
- To the southeast, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands are located in the Bay of Bengal, while the Lakshadweep Islands are in the Arabian Sea.
Size
- India covers an area of 3.28 million square km, making it the seventh-largest country in the world.
- This area represents about 2.4% of the world's total geographical area.
- The country has an east-west extent of 2,933 km (from Arunachal Pradesh to Kachchh) and a north-south extent of 3,214 km (from Kashmir to Kanniyakumari).
- India's land boundary measures approximately 15,200 km, with a coastline of 7,516.6 km, including the islands.
Geographically, India is bordered by the Himalayas to the northwest, north, and northeast. The southern region forms a peninsula that tapers towards the Indian Ocean, with the Arabian Sea on the southwest and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast.
With a population exceeding 1 billion, India is the second-most populous country in the world, following China.
Q3. Write a note on the Indian Standard Time? Why is there a time difference of almost 2 hours from Arunachal Pradesh to Gujarat? [Important]
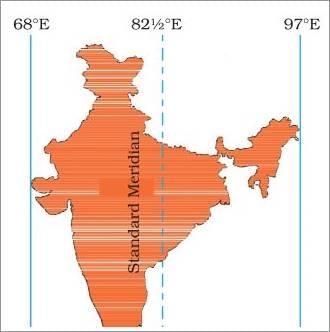 Fig: Indian standard time
Fig: Indian standard time
Ans: The vast longitudinal extent of India results in a time difference of nearly two hours between its eastern and western regions. To simplify this, a single standard time is used across the country.
The Standard Meridian of India is set at 82°30'E, which runs through Mirzapur in Uttar Pradesh. This time zone is calculated as:
- 82°30' × 4 minutes = 330 minutes
- Which equals 5 hours and 30 minutes ahead of GMT (Greenwich Mean Time).
India's longitudinal range exceeds 29°, from 68°07'E in Gujarat to 97°25'E in Arunachal Pradesh. The calculation for the time difference is as follows:
- For each degree of longitude, there is a time difference of 4 minutes.
- Thus, for 29°: 4 minutes × 29° = 116 minutes, or approximately 2 hours.
Consequently, the sun rises nearly two hours earlier in Arunachal Pradesh compared to Gujarat, despite both regions observing the same standard time.
Q5. What are the two groups of Indian islands? Write a note on each, describing its geographic position with relation to India.
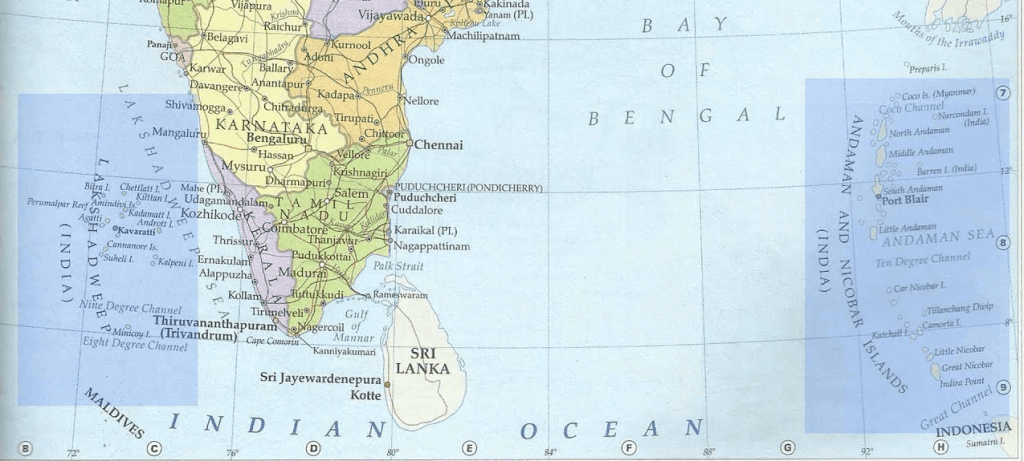 Fig: Andaman & Nicobar island and Lakshadweep island
Fig: Andaman & Nicobar island and Lakshadweep island
Ans: The two groups of islands that are part of the Indian Union are the Andaman & Nicobar Islands and the Lakshadweep Islands.
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands:
- Located to the southeast of the Indian mainland in the Bay of Bengal.
- Comprises the Great Andamans and Little Andamans in the north, and Nicobar Islands in the south.
- Includes numerous large and small islands, with Port Blair as the official headquarters.
- Strategically important, lying close to the equator with an equatorial climate.
- Located along the trans-Indian Ocean route, near south and southeast Asia.
- The southernmost point of India is found here.
- Lakshadweep Islands:
- Situated in the Arabian Sea to the southwest of India's mainland, near the Malabar coast of Kerala.
- Consists of small coral islands, covering an area of just 32 square kilometres.
- Kavaratti Island serves as the administrative headquarters.
Both island groups are rich in flora and fauna, contributing to India's natural beauty and geographical diversity.
Q6. How has India’s geographic location aided the nation?
Ans: India's geographic location has significantly aided its development in various ways:
- India is a southward extension of the Asian continent, centrally located between East and West Asia.
- The Himalayas to the north act as a natural barrier, facilitating cultural and commodity exchanges through ancient land routes.
- The Deccan Peninsula extends into the Indian Ocean, enhancing opportunities for maritime trade.
- Trans-Indian Ocean routes connect India with Europe and East Asia, providing a strategic position for trade.
- India maintains close contacts with oil-rich countries in West Asia and regions in Africa and Europe via the Arabian Sea.
- The Suez Canal offers the shortest maritime route to industrial Europe and America.
- From its eastern coast, India has favorable trade links with Southeast Asia, East Asia, and Australia via the Bay of Bengal.
- Proximity to densely populated countries in Southeast Asia and China boosts trade and cultural relations.
Overall, India's geographical location has played a crucial role in its progress and development.
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Geography Chapter 1 Question Answers - Contemporary India - I
| 1. भारत का आकार और स्थिति क्या है? |  |
| 2. भारत की भौगोलिक स्थिति का महत्व क्या है? |  |
| 3. भारत के प्रमुख भूगोलिक क्षेत्र कौन से हैं? |  |
| 4. भारत की सीमाओं का विस्तार कैसे हुआ? |  |
| 5. भारत के समय क्षेत्र का क्या महत्व है? |  |

















