Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Question Answers - Nutrition in Plants
Short Answer Questions
Q1: Differentiate between nutrients and nutrition.
Ans: Carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals are essential components of food. These components are called nutrients, but Nutrition is the mode of taking food by an organism and its utilisation by the body.
 Nutrients: Essential Components of Food
Nutrients: Essential Components of Food
Q2: Differentiate between autotrophs and heterotrophs.
Ans: Green plants are called autotrophs as they prepare their own food from simple substances, but animals and most other organisms are called heterotrophs as they take in ready-made food prepared by the plants.
Q3: Explain the food factory of plants.
Ans: Leaves are called the food factories of plants, as the synthesis of food takes place in the leaves of plants. Water and minerals present in soil are absorbed by roots and transported to leaves via the stem. Carbon dioxide from the air is taken in through tiny pores on the surface of leaves called stomata.
Q4: Draw a labelled diagram of the cell showing the nucleus and cytoplasm.
Ans :

Q5: How are water and minerals transported to leaves from roots?
Ans: There are vessels inside a plant that run like pipes throughout the root, stem branches, and leaves; by going through these vessels, water and minerals are transported to leaves from roots.
Q6: Define chlorophyll.
Ans: Chlorophyll is the green pigment that helps leaves capture energy from sunlight to carry out the food-making process of plants by the leaves.
Q7: Explain the role of chlorophyll in the process of photosynthesis.
Ans: Chlorophyll is the green pigment that helps leaves capture energy from sunlight to carry out the food-making process of plants by the leaves. It is the green photosynthesis pigment which provides the energy necessary for photosynthesis.
Q8: Define photosynthesis along with the equation for the same.
Ans: Photosynthesis is the food manufacturing process of green plants containing chlorophyll in the presence of sunlight, with the help of carbon dioxide and water, to synthesise carbohydrates. The equation for the process is as follows:
Carbon dioxide + water —————> carbohydrate + Oxygen
Q9: Draw a labelled diagram showing the process of photosynthesis.
Ans:
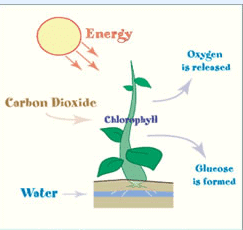 photosynthesis
photosynthesis
Q10: Draw a diagram of a leaf showing chlorophyll and stomata in it.
Ans :

Q11: What is the function of stomata in a leaf of a plant?
Ans: Stomata are the tiny pores present on the surface of leaves which helps in exchange of gases, the pores in stomata are surrounded by guard cells.
Q12: Draw a diagram of stomata showing guard cells in it.
Ans : 
Q13: How would you test the presence of starch in leaves?
Ans :
- Take a potted plant which has been exposed to sunlight and pluck a leave from the plant.
- Then boil it in water for 5 min to soften it and then place the leaves in a test tube containing alcohol, place the test tube in a beaker containing water; gently heat the beaker till the alcohol dissolves in the chlorophyll and the leaves lose their green colour.
- Now wash the leaf with water and then place it on a plate, and add a few drops of iodine solution the parts that turn blue-black show the
Q14: How are humans and animals directly or indirectly dependent on plants?
Ans :
- All living organisms require food. Plants can make their food themselves by organic substances, but animals, including humans, cannot make their food themselves.
- They get it from plants or animals that eat plants.
- Thus, humans and animals are directly or indirectly dependent on plants.
Q15: Why do we need food?
Ans: Living organisms need food to build their bodies, grow, repair damaged parts of their bodies, and provide energy to carry out life processes.
Q16: Whether food is made in all parts of a plant or only in certain parts? Explain.
Ans :
- Only certain parts of plants, like leaves, have a green pigment called chlorophyll.
- So, Leaves are called the food factories of plants.
- Besides leaves, photosynthesis also takes place in other green parts of the plant, such as green stems and green branches.
- The desert plants have scale or spine-like leaves to reduce the loss of water through transpiration.
- These plants have green stems which carry out the process of photosynthesis.
Q17: What is cell?
Ans :
- The body of living organisms are made of tiny units called cells, therefore Cell are called the building blocks of living organism.
- Cells can be seen only under the microscope.
- Some organisms are made of single cells. They are called Unicellular. Ex. Amoeba, Paramecium etc.
- Others are made of multicellular material and are called multicellular. Ex. man, tree, etc.
Q18: What is the cell membrane?
Ans :
- The cell is enclosed by a thin outer boundary called the cell membrane. Many cells have a distinct, centrally located spherical structure called the nucleus.
- The nucleus is surrounded by a jelly-like substance called cytoplasm.
Q19: What are the main requirements of photosynthesis?
Ans: Chlorophyll, sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water are necessary to carry out photosynthesis.
Q20: Why are the colours of algae green?
Ans: Algae contain chlorophyll, which gives them a green colour, and because of chlorophyll, they can also prepare their own food by photosynthesis.
Q21: What are the main components present in carbohydrates?
Ans: The main components present in carbohydrates are carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
Q22: From where do the plants obtain nitrogen?
Ans :
- Soil has certain bacteria that convert gaseous nitrogen into a usable form and release it into the soil.
- These soluble forms are absorbed by the plants along with water.
- By adding fertilizers rich in nitrogen to the soil, farmers also made nitrogen available for plants.
Q23: What do you mean by parasitic nutrition?
Ans :
- The mode by which parasitic organisms get and synthesize their food is called parasitic nutrition. Example Cuscuta.
- It does not have chlorophyll; it takes readymade food from the plant on which it is climbing. The plant on which it climbs is called a host. In parasitic nutrition, only one of the partners is benefits, and the other is not.
Q24: Define insectivorous plants along with examples.
Ans :
- There are few plants which can trap insects and digest them.
- Such plants may be green or of some other colour.
- Such insect-eating plants are called insectivorous plants. Example: Venus Flytrap and Pitcher plant.
Q25: What is a saprotrophic mode of nutrition?
Ans :
- This mode of nutrition in which organisms take in nutrients in solution form from dead and decaying matter is called saprotrophic nutrition.
- Plants which use saprotrophic modes of nutrition are called saprotrophs. Example: Fungi that secrete digestive juices on the dead and decaying matter and convert it into a solution.
- Then, they absorb the nutrients from it.
Q26: What do you understand by symbiotic relationship present in some organisms?
Ans :
- Some organisms live together and share shelter and nutrients.
- This is called a symbiotic relationship. E.g. an alga and a fungus live together. Fungus provides shelter, water, and minerals to the alga, and, in return, the alga provides food, which is prepared by photosynthesis.
- In this kind of association, both partners are benefited.
Q27: How are nutrients replenished in soil?
Ans: Nutrients are replenished in soil in the following ways:
- By spreading manure or fertilizers that contain nutrients such as nitrogen in the fields
- The bacterium Rhizobium, which is commonly present in root nodules of leguminous plants, can take atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into a soluble form like nitrates.
Q28: What do you mean by Symbiosis?
Ans :
- Symbiosis is the type of nutrition in which two different kinds of organisms depend on each other for their nutrition.
- In this, both organisms benefit from each other. For example, lichen is a symbiotic association between algae and fungi.
- In this, one alga and one fungus live together and remain in a symbiotic relationship.
Q29: What is the role of leguminous plants in replenishing soil fertility?
Ans: Rhizobium is a type of bacteria that cannot make its own food and lives in the roots of gram, peas, moong beans and other legumes. It converts atmospheric nitrogen into usable form, which increases the fertility of soil and legumes provide food and shelter to the bacteria.
Q30: Distinguish between a parasite and a saprotrophs.
Ans:

Q31: Explain how Pitcher plants get their nutrition.
Ans: When an insect lands in the pitcher, the lid closes and the trapped insect gets entangled in the hair. The insect is digested by the digestive juices secreted in the pitcher.
Long Answer Questions
Q1: Sun is called the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms. Comments.
Ans: Solar energy is very important in the process of photosynthesis; it is captured by the leaves and stored in the plant in the form of food. This, in turn, is used by other organisms to get food to obtain energy. Thus, we say that the sun is the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms.
Q2: Explain the two modes of nutrition in plants.
Ans :

- Autotrophs or Autotrophic: - In this mode of nutrition, organisms make their food themselves from simple substances. All green plants are Autotrophs (Auto means self and trophic means nourishment)
- Heterotrophs or heterophobic: Heterotrophic organisms are those that obtain food from other organisms. Since these organisms depend on other organisms for their food, they are called consumers. All animals and non-green plants, like fungi, come under this category.
|
111 videos|246 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Question Answers - Nutrition in Plants
| 1. How do plants obtain nutrients? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of nutrients required by plants? |  |
| 3. How do plants transport nutrients within their body? |  |
| 4. What are the signs of nutrient deficiency in plants? |  |
| 5. How can plants be fertilized to ensure proper nutrition? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|


















