NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science - Transportation in Animals and Plants
Q1. Match structures given in Column I with functions given in Column II.

Ans:

- Stomata - Transpiration
Stomata are tiny openings on plant leaves that facilitate transpiration by allowing water vapor to escape, promoting the flow of water from roots to leaves. This process cools the plant and enables the uptake of essential nutrients and minerals. - Xylem - Transport of water
Xylem helps in the transport of water by conducting it from the roots to the rest of the plant through specialized, elongated cells, and providing support to the plant through its lignified cell walls. - Root hairs - Absorption of water
Root hairs increase the surface area of plant roots, allowing for greater water absorption. They also penetrate the soil, helping to draw water and nutrients into the plant more efficiently. - Phloem - Transport of food
Phloem helps in the transport of food by conducting sugars and other organic nutrients, synthesized in the leaves during photosynthesis, to different parts of the plant. This process, known as translocation, ensures that energy and essential building blocks are distributed throughout the plant.
Q2. Fill in the blanks
(i) The blood from the heart is transported to all parts of the body by the _____________
Ans: Arteries
Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to all of the body's tissues. They branch several times, becoming smaller and smaller as they carry blood further from the heart and into organs.
(ii) Haemoglobin is present in _____________ cells.
Ans: Red Blood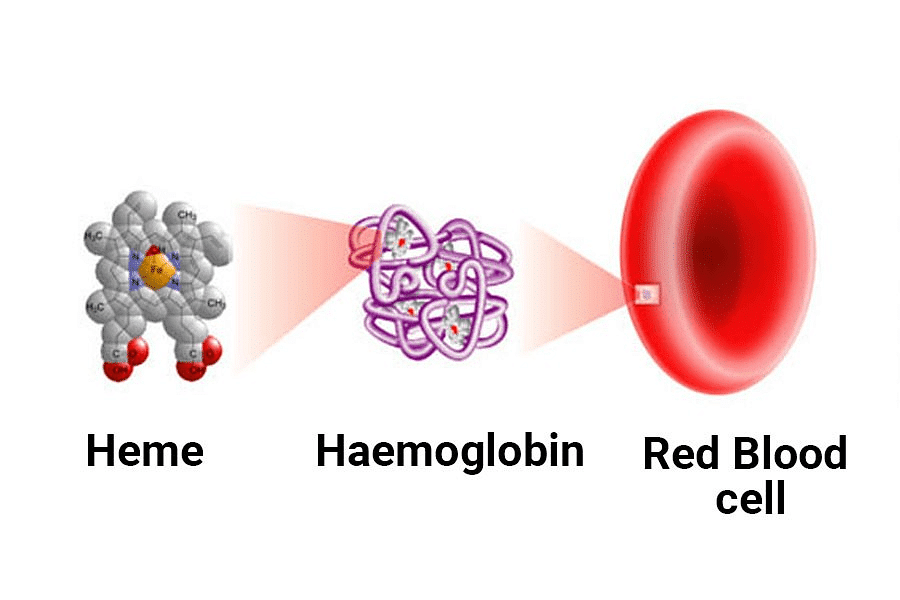 RBC contain Haemoglobin
RBC contain Haemoglobin
(iii) Arteries and veins are joined by a network of _____________
Ans: Capillaries
The human circulatory system consists of a network of arteries, veins, and capillaries, with the heart pumping blood through it.
 Capillaries connecting arteries and veins
Capillaries connecting arteries and veins
(iv) The rhythmic expansion and contraction of the heart is called _____________
Ans: Cardiac cycle
The cardiac cycle is the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart.
(v) The main excretory product in human beings is _____________
Ans: Urea
The major wastes produced by humans are Carbon dioxide and Urea. Carbon dioxide is produced by the process of respiration, and urea is produced by the decomposition of unused proteins in the liver. In humans, the main excretory product is Urea.
(vi) Sweat contains water and _____________
Ans: Salts
Sweat is mostly water, but it also contains some salts. The body makes sweat to cool itself down.
(vii) Kidneys eliminate the waste materials in the liquid form called _____________
Ans: Urine
The kidneys remove wastes and extra water from the blood to form urine. An adult human excretes, on average, 1 to 1.5 litres of urine per day. The urine formed is a light yellow-coloured watery fluid which is slightly acidic (pH-6.0) and has a characteristic odour.
(viii) Water reaches great heights in the trees because of suction pull caused by _____________
Ans: Transpiration
Transpiration is mainly responsible for the loss of water that is absorbed by the plants. However, it is important for plants as it helps in the movement of water to the top of tall trees.
 Transpiration in Plants
Transpiration in Plants
Q3. Choose the correct options:
(a) In plants, water is transported through
(i) Xylem
(ii) Phloem
(iii) Stomata
(iv) Root hair
Ans: (i) Xylem
The xylem moves water from the roots to the leaves, and the phloem moves food from the leaves to the rest of the plant. It transports water and mineral salts from the roots up to other parts of the plant.
(b) Water absorption through roots can be increased by keeping the plants
(i) in the shade
(ii) in dim light
(iii) under the fan
(iv) covered with a polythene bag
Ans: (iii) Under the fan
Water absorption through the roots can be increased by keeping the plants under the fan. By keeping the plants under the fan, the transpiration process is boosted. Therefore, more amount of water and other minerals are absorbed by the plant roots from the soil. The higher the rate of evaporation of water from the plants, the greater is the rate of transpiration.
Q4. Why is the transport of materials necessary in a plant or an animal? Explain.
Ans:
Transport of materials is vital for plants and animals, ensuring nutrients and oxygen reach all body parts. Without this transport, survival is impossible.
Cells in various organs require diverse substances for metabolic activities, leading to the creation of different waste products.
Essential materials like food, water, oxygen, carbohydrates, and hormones are crucial for organism survival.
In plants, transport involves gases, water, hormones, minerals, and organic materials through processes such as diffusion and active transport.
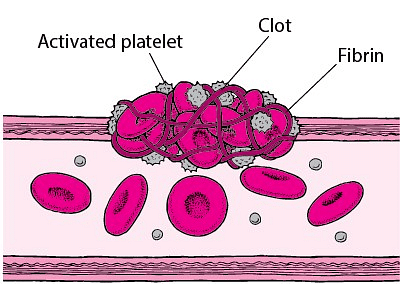
Q5. What will happen if there are no platelets in the blood?
Ans: Platelets, or thrombocytes, play a crucial role in blood clotting. Without platelets, the absence of a clot would cause uncontrollable bleeding, resulting in severe blood loss and ultimately the death of the individual.
Q6. What are stomata? Give two functions of stomata.
Ans: Stomata are small, microscopic openings or pores found on the surface of leaves and stems in plants.
 Stomata
Stomata
Two primary functions of stomata are :
(i) Gas Exchange: they help the plant take in carbon dioxide from the air. This carbon dioxide is crucial for a process called photosynthesis, which is how plants make their own food. So, stomata act like little breathing holes for plants.
(ii) Transpiration: Stomata play a role in controlling the amount of water in plants. This happens through a process called transpiration, where water is released from the plant in the form of vapor through these stomata. It's like the plant is sweating to cool itself down and also to move water around.
Q7. Does transpiration serve any useful function in plants? Explain.
Ans: In the process of transpiration, water evaporates through the tiny openings called stomata on the surface of leaves. This evaporation leads to the loss of water that the plant absorbs from its surroundings. Surprisingly, this process is vital for plants.
Transpiration plays a key role in tall trees by helping to move water to their uppermost parts. This upward flow of water is essential for distributing water throughout the entire plant. Additionally, transpiration has a cooling effect on the plant. So, despite the loss of water, transpiration is crucial for maintaining the proper functioning and health of plants, especially in larger and taller ones.
Q8. What are the components of blood?
Ans: Blood, a fluid connective tissue, comprises plasma, red blood cells (RBC), white blood cells (WBC), and platelets.
- Plasma Function: Plasma, the liquid part of blood, is a mixture of water, sugar, fat, protein, and salts. Its role is to transport blood cells, nutrients, waste products, antibodies, clotting proteins, and chemical messengers throughout the body.
- Red Blood Cells (RBC): RBCs, constituting 40-45% of blood volume, are the most abundant cells. They have a distinctive biconcave disk shape, resembling a doughnut, facilitating their function in oxygen transport.
- White Blood Cells (WBC): WBCs, primarily neutrophils and lymphocytes, defend against infections. T lymphocytes regulate immune function, attacking infected cells, while B lymphocytes produce antibodies targeting bacteria, viruses, and foreign materials.
- Platelets and Blood Clotting: Platelets play a crucial role in blood clotting. They accumulate at injury sites, adhere to the vessel lining, and create a platform for coagulation, preventing excessive bleeding.

Ans: Blood is needed by all body parts as:
- It carries oxygen to all the body parts and carries carbon dioxide back to the lungs.
- It carries digested food to various parts of the body for absorption.
- It contains platelets that help in the clotting of blood.
- It helps in maintaining a constant body temperature.
- It transports hormones and helps in fighting the body with germs and bacteria.
Q10. What makes the blood look red?
Ans: Blood is red because of the presence of a pigment called haemoglobin. Haemoglobin is a protein that forms a complex along with iron molecules and carries oxygen molecules across the body. Iron can reflect red light, and blood looks red because our blood contains so much iron. Thus, haemoglobin makes the blood look red. It is the carrier of oxygen in our body.
Q11. Describe the function of the heart.
Ans: The primary function of the heart is to pump blood throughout the body.
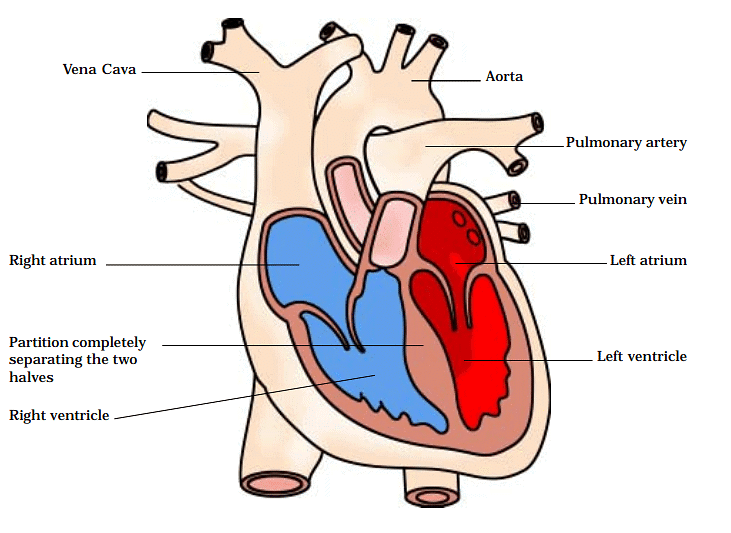
- It consists of four chambers: the upper ones are called atria (singular: atrium), and the lower ones are ventricles. The partition between these chambers prevents the mixing of oxygen-rich and carbon dioxide-rich blood. Blood travels from the heart to the lungs and back before being pumped to the rest of the body.
- It first receives deoxygenated, carbon dioxide-rich blood from different body regions through the right auricle and ventricle. This collected blood is then transported to the lungs for purification, where gases are exchanged.
- Following purification, the now oxygenated blood returns to the heart's left side, entering the left auricle.
- From there, it is pumped into the left ventricle. The left ventricle is a powerful chamber that propels the oxygenated blood into the arteries, facilitating its distribution to all body cells.
- This process ensures that essential nutrients and oxygen reach every part of the body, sustaining cellular functions and overall well-being.
Q12. Why is it necessary to excrete waste products?
Q13. Draw a diagram of the human excretory system and label the various parts.
Ans: Human Excretory SystemThe human excretory system organs include:
Human Excretory SystemThe human excretory system organs include:
- A pair of kidneys
- A pair of ureters
- A urinary bladder
- A urethra
|
111 videos|246 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science - Transportation in Animals and Plants
| 1. What is transportation in animals and plants? |  |
| 2. How does the circulatory system work in animals? |  |
| 3. What are xylem and phloem in plants? |  |
| 4. What is transpiration in plants? |  |
| 5. How do plants absorb nutrients from the soil? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|



















