Surface Area and Volumes Class 10 Notes Maths Chapter 12
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Surface Area of a Combination of Solids |

|
| Volume of Combination of Solids |

|
| Summary |

|
Introduction
Imagine you’re on a road trip and you spot a truck carrying a huge container of water. Ever wondered what shape that container is? It’s likely a combination of a cylinder with hemispheres capping each end. Or think about a test tube in your science lab—it's a perfect blend of a cylinder and a hemisphere. We see these combined shapes all around us, from water tanks to magnificent monuments.

But how do we calculate the surface areas and volumes of these fascinating shapes? In this chapter, we’ll explore the methods to do just that, bringing together the basics you’ve learned about cuboids, cones, cylinders, and spheres to tackle these more complex shapes. Get ready to dive into the world of combined solids!
Surface Area of a Combination of Solids
Surface area is the measurement of the space taken up by a flat two-dimensional surface. This measurement is expressed in terms of square units. For three-dimensional objects, the surface area represents the space occupied by their outer surfaces. Similar to the flat surface area, it is also measured in square units.
In general, there are two types of surface area

(a) Total Surface Area
- Total surface area is the combined measurement of an object's base(s) and the curved portion.
- It represents the sum of the object's surface coverage.
- In cases where the object's shape includes both a curved surface and a base, the total surface area is calculated by summing up the measurements of these two areas.

TSA of new solid = CSA of one hemisphere + CSA of cylinder + CSA of other hemisphere
(b) Curved Surface Area or Lateral Surface Area
- Curved surface area pertains to the measurement of only the curved portion of a shape, excluding any base(s).
- This aspect is also referred to as the lateral surface area, particularly for shapes like a cylinder.

Formulas for Total Surface Area and Lateral Surface Area
(i) Surface Area of a Cube
A cube is a solid shape having 6 equal square faces of length a.

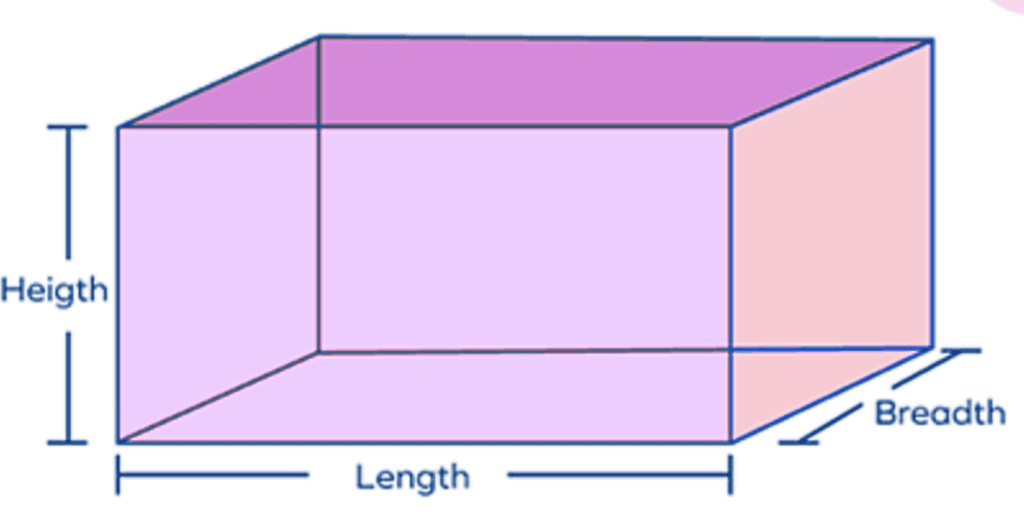
(ii) Surface Area of a Cuboid
Cuboid is a solid shape having 6 rectangular faces at a right angle with length l, breadth b and height h.

Example1: Two cubes each of volume 64 cm3 are joined end to end. Find the surface area of the resulting cuboid.
Ans:
Given: The Volume (V) of each cube is = 64 cm3
This implies that a3 = 64 cm3
∴ a = 4 cm
Now, the side of the cube = a = 4 cm
Also, the length and breadth of the resulting cuboid will be 4 cm each, while its height will be 8 cm.
So, the surface area of the cuboid = 2(lb+bh+lh)
substituting the values
= 2(8×4+4×4+4×8) cm2
= 2(32+16+32) cm2
= (2×80) cm2 = 160 cm2
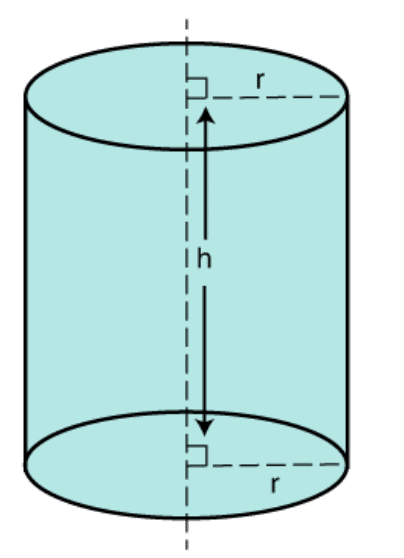
(iii) Surface Area of a Right Circular Cylinder
If we fold a rectangular sheet with one side as its axis then it forms a cylinder. It is the curved surface of the cylinder. And if this curved surface is covered by two parallel circular bases then it forms a right circular cylinder. For a cylinder of height h and with base radius r.

(iv) Surface Area of a Hollow Right Circular Cylinder
If a right circular cylinder is hollow from inside then it has a different curved surface.

(v) Surface Area of a Right Circular Cone
If we revolve a right-angled triangle about one of its sides by taking other as its axis then the solid shape formed is known as a Right Circular Cone.
Curved surface area of a Right Circular Cone = πrl= πrh2+r2
Total surface area of a Right Circular Cone= πr2+πrl [CSA of cone + circular area of base]= πr(r+l)

(vi) Surface Area of a Sphere
A sphere is a solid shape which is completely round like a ball. It has the same curved and total surface
area.
Curved or Lateral surface area of a Sphere=4πr2
Total surface area of a Sphere=4πr2

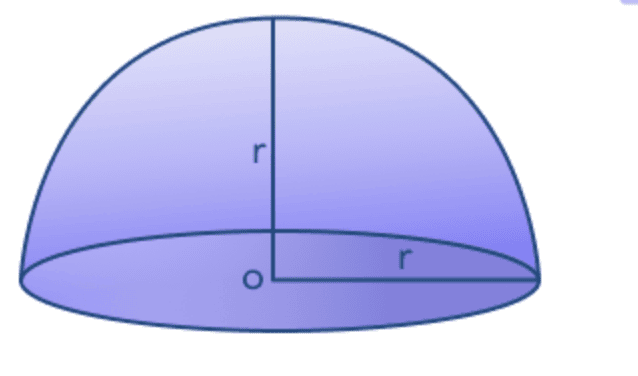
(vii) Surface Area of a Hemisphere
If we cut the sphere in two parts then it is said to be a hemisphere.

Example2: A vessel is in the form of a hollow hemisphere mounted by a hollow cylinder. The diameter of the hemisphere is 14 cm, and the total height of the vessel is 13 cm. Find the inner surface area of the vessel.
Solution:
The diagram is as follows:
Now, the given parameters are:
The diameter of the hemisphere = D = 14 cm
The radius of the hemisphere = r = 7 cm
Also, the height of the cylinder = h = (13-7) = 6 cm
And the radius of the hollow hemisphere = 7 cm
Now, the inner surface area of the vessel = CSA of the cylindrical part + CSA of the hemispherical part
(2πrh+2πr2) cm2 = 2πr(h+r) cm2
2×(22/7)×7(6+7) cm2 = 572 cm2
Example 3: A toy is in the form of a cone of radius 3.5 cm mounted on a hemisphere of the same radius. The total height of the toy is 15.5 cm. Find the total surface area of the toy.
Answer:
The diagram is as follows:
Given that the radius of the cone and the hemisphere (r) = 3.5 cm or 7/2 cm
The total height of the toy is given as 15.5 cm.
So, the height of the cone (h) = 15.5-3.5 = 12 cm
∴ The curved surface area of the cone = πrl
(22/7)×(7/2)×(25/2) = 275/2 cm2
Also, the curved surface area of the hemisphere = 2πr2
2×(22/7)×(7/2)2
= 77 cm2
Now, the Total surface area of the toy = CSA of the cone + CSA of the hemisphere
= (275/2)+77 cm2
= (275+154)/2 cm2
= 429/2 cm2 = 214.5cm2
So, the total surface area (TSA) of the toy is 214.5cm2
Volume of Combination of Solids
The volume of the solid formed by joining two basic solids will actually be the sum of the volumes of the constituents.

required volume = volume of the cuboid + 1/2 volume of the cylinder
Formulas of volume of each figure
(i) Volume of Cube
Volume = a3
Side of Cube = a

(ii) Volume of Cuboid
Volume = lbh
l=length, b= breadth, h=height
(iii) Volume of Cylinder
Volume = πr2h
r = Radius of Cylinder
h = Height of Cylinder
(iv) Volume of Cone
Volume = 1/3πr2h
h= height of cone
r = radius of cone
l = slant height of cone =√ (h2+r2)

Example 4: A vessel is in the form of an inverted cone. Its height is 8 cm and the radius of its top, which is open, is 5 cm. It is filled with water up to the brim. When lead shots, each of which is a sphere of radius 0.5 cm, are dropped into the vessel, one-fourth of the water flows out. Find the number of lead shots dropped in the vessel.
Solution:
For the cone,
Radius = 5 cm,
Height = 8 cm
Also,
Radius of sphere = 0.5 cm
The diagram will be like
It is known that,
The volume of cone = volume of water in the cone
= ⅓πr2h = (200/3)π cm3
Now,
Total volume of water overflown= (¼)×(200/3) π =(50/3)π
The volume of lead shot
= (4/3)πr3
= (1/6) π
Now,
The number of lead shots = Total volume of water overflown/Volume of lead shot
= (50/3)π/(⅙)π
= (50/3)×6 = 100
(v) Volume of Sphere
Volume = 4/3πr3
r= radius

(vi) Volume of Hemi-Sphere
Volume = 2/3πr3
r= radius
Example 5: A solid is in the shape of a cone standing on a hemisphere, with both their radii being equal to 1 cm and the height of the cone being equal to its radius. Find the volume of the solid in terms of π.
Solution:
Here r = 1 cm and h = 1 cm.
The diagram is as follows.
Now, Volume of solid = Volume of conical part + Volume of hemispherical part
We know the volume of cone = ⅓ πr2h
And,
The volume of the hemisphere = ⅔πr3
So, the volume of the solid will be
= π cm3
Summary

|
126 videos|457 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Surface Area and Volumes Class 10 Notes Maths Chapter 12
| 1. What is the formula to calculate the surface area of a cylinder? |  |
| 2. How do you find the volume of a combination of solids? |  |
| 3. What is the surface area of a sphere? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the difference between the surface area and volume of a solid? |  |
| 5. What is the volume of a cone and how is it calculated? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
































