Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Question Answers - Motion and Measurement of Distances
Q1: The known fixed quantity of measurement is called __________.
Ans: Unit.
A unit is a standard quantity used for measurement, such as meter for length or kilogram for weight.
Q2: What do you mean by the term ‘measurement’?
Ans: The comparison of an unknown quantity with some known quantity is called measurement.
Measurement involves comparing an unknown quantity with a standard unit to determine its size, length, volume, etc.
Q3: What is the full form of SI units?
Ans: International System of Units.
SI units are the globally accepted standard units of measurement used in science and daily life.
Q4: What is the SI unit of length?
Ans: Metre.
The metre is the SI unit of length, used to measure distances and lengths.
Q5: Yard is a measure of distance between:
a) Two hands
b) The hand and the feet
c) Between the hand and the elbow
d) End of the arm and the chin
Ans: d
Yard is traditionally measured from the end of the arm to the chin.
Q6: In ancient India small length measurements used were angul and mutthi. (TRUE/FALSE)
Ans: True.
Angul and mutthi were traditional units of measurement for small lengths in ancient India.
Q7. Which of the following is the SI unit of length?
Ans: The SI unit of length is metre.
Q8: What is motion?
Ans: Motion refers to the movement of an object from one place to another over time.
Q9: 1 metre is equal to __cm.
Ans: 100.
One metre is equivalent to 100 centimetres.
Q10: We can measure the length of a curved line directly by using a metre scale. (TRUE/FALSE)
Ans: False.
A metre scale is straight and cannot measure the length of a curved line directly.
Q11: What are the different types of motion?
Ans: Rectilinear motion, circular motion, rotational motion and periodic motion. These are the four primary types of motion based on the path and pattern of movement.
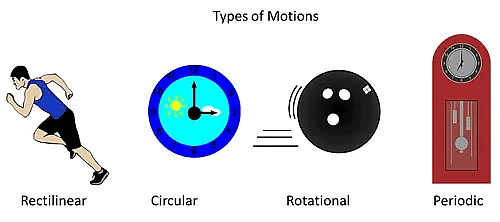
Q12: When objects move along a straight line such motion is called ______ motion.
Ans: Rectilinear motion.
Rectilinear motion occurs when objects travel in a straight path.
Q13: One centimetre is equal to _______millimetre.
Ans: 10.
One centimetre is equivalent to ten millimetres.
Q14: When an object moves in a circular path, such motion is called _________.
Ans: Circular motion.
Circular motion is the movement of an object along the circumference of a circle.
Q15: Give one example of periodic motion.
Ans: The motion of a pendulum is a periodic motion. A pendulum swings back and forth in a regular, repeating pattern, demonstrating periodic motion.
Q16: One kilometre is equal to __________ metre.
Ans: 1000.
One kilometre is equivalent to one thousand meters.
Q17. What is the motion of a spinning top called?
Ans: Rotational Motion
Rotational motion refers to an object rotating around its own axis. In the case of a spinning top, the top rotates around its central axis, demonstrating rotational motion. Unlike circular motion, which involves movement along the circumference of a circle, rotational motion focuses on the rotation around an internal axis, making it the correct description of a spinning top's motion.
Q18: 2 km is equal to _________m and ________cm.
Ans: 2000 m and 200000 cm.
Two kilometres are equal to two thousand meters and two hundred thousand centimetres.
Q19: In periodic motion, an object repeats its motion. (TRUE/FALSE)
Ans: True.
Periodic motion involves an object repeating its movement at regular intervals.
Q20: 8 km is equal to ___m.
Ans: 8000.
Eight kilometres are equivalent to eight thousand meters.
Q21: The length of a rope is 5m. Express it in cm.
Ans: 5 m = 500 cm.
Five meters are equal to five hundred centimetres.
Q22: A ball is rolling on the ground, rotating as well as moving forward on the ground. Therefore, it undergoes _____________ and ___________ motion.
Ans: Rectilinear and rotational.
The ball moves in a straight line (rectilinear) and rotates on its axis (rotational).
Q23: What were the early modes of transport before the invention of the wheel?
Ans: Early modes of transport included walking on foot and using animals to carry goods.
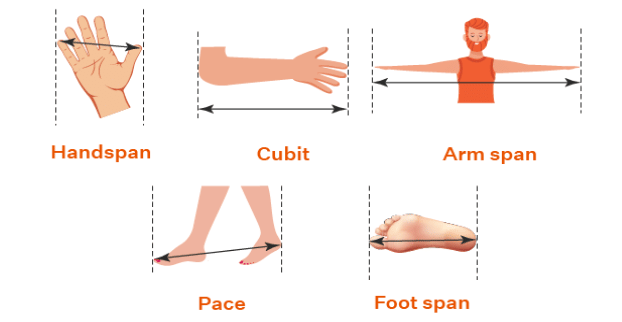
Q24: What did people use to measure lengths before standard scales were made?
Ans: People used their body parts such as the length of a foot, the width of a finger, and the distance of a step.
Q25: What is the importance of the correct position of the eye in taking measurements?
Ans: The correct position of the eye ensures an accurate reading of the measurement scale, avoiding parallax errors.
Q26: How can you measure a length if the zero mark on a scale is broken?
Ans: Use any other full mark on the scale, measure from that mark, and then subtract its reading from the reading at the other end.
Q27: How did ancient people use the 'cubit' for measurement?
Ans: The cubit was the length from the elbow to the fingertips and was used as a unit of length.
Q28: What is the SI unit for large distances?
Ans: Kilometre (km).
Kilometre is used for measuring large distances, with 1 km equal to 1000 meters.
Q29: Why are standard units of measurement important?
Ans: Standard units of measurement provide uniformity and consistency, allowing accurate and comparable measurements.
Q30: What type of motion does a sewing machine needle exhibit?
Ans: Periodic motion.
The needle of a sewing machine moves up and down continuously, repeating its motion.
FAQs on Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Question Answers - Motion and Measurement of Distances
| 1. What is motion? |  |
| 2. How is distance measured in physics? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between distance and displacement? |  |
| 4. How can we calculate speed? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between speed and velocity? |  |

















