Class 9 Geography Chapter 1 Extra Question Answers - India - Size and Location
Q1. India's contacts with the world have continued through the ages due to its strategic position in Asia. The ideas of the Upanishads and the Ramayana, the stories of Panchtantra, the Indian numerals and the decimal system thus could reach many parts of the world. However, the Indian system of values is somewhat different from the values of the Western countries and has remained so despite these ancient contacts. Only during the last few years has our value system been significantly influenced by ideas from the West. What do you think may be the reasons for this system of values remaining intact for so many centuries, but is rapidly changing now? contacts were very limited. As a result, the Indian system of values was not influenced much. However, now there is quick transmission of ideas due to fast means of communication, so that the Indian system of values is being affected and also quite rapidly.
Ans: The ancient contacts between India and the West were limited to a small number of people due to restricted communication methods. Key points include:
- In the past, there were no telephones, aeroplanes, or the internet, which limited interactions.
- This lack of communication meant that the Indian system of values remained largely unaffected.
- Today, rapid communication allows for quick transmission of ideas, leading to significant changes in these values.
- The influence of Western ideas has increased in recent years, altering traditional perspectives.
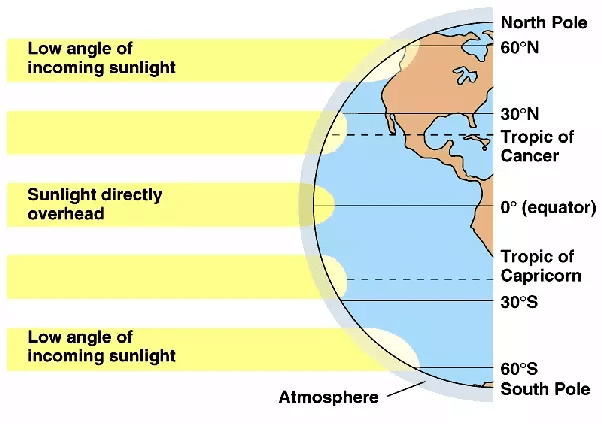
Q2. Why the latitudinal extent influences the duration of the day and night as one moves from North to South?
Ans: The latitudinal extent affects the duration of day and night as one moves from the equator towards the poles. Key points include:
- Near the equator, the Sun's rays strike directly, resulting in nearly equal lengths of day and night.
- As you move away from the equator, the Sun's rays become more slanted.
- This slanting causes nights to be longer and days to be shorter.
- Thus, regions close to the equator experience almost equal day and night durations.
Q3. Why is Indian Ocean named after our country? Give three reasons.
Ans: The Indian Ocean is named after India for several reasons:
- Longest coastline: India has the longest coastline along the Indian Ocean.
- Central location: India is centrally located between East and West Asia.
- Significant extension: The Deccan Peninsula extends into the Indian Ocean, enhancing its importance for international trade.
Q4. Why is India called a subcontinent? Name the countries which form a part of Indian subcontinent?
Ans: The term subcontinent refers to a large geographical area that has distinct features compared to the rest of the continent. The Indian subcontinent is characterised by the following:
- It covers approximately 2.4% of the Earth's total land area.
- India has a long land frontier of about 15,200 km and a coastline of nearly 7,500 km.
- Natural boundaries, such as the Himalayas to the north and the Deccan Peninsula, give it a unique identity.
- The subcontinent spans a longitudinal and latitudinal extent of about 30°.
Countries that are part of the Indian subcontinent include:
- India
- Pakistan
- Bangladesh
- Nepal
- Bhutan
- Sri Lanka
- Maldives
Q5. When was the Suez Canal opened? How it has benefitted India?
Ans: The Suez Canal was opened in 1869. It has significantly benefitted India by:
- Reducing the distance to Europe by 7,000 km.
- Eliminating the long sea route around the Cape of Good Hope.
- Facilitating faster trade and travel between India and Europe.
Q6. Which longitude has been selected as the Standard Meridian of India? Explain any two reasons for its selection.
Ans: 82°30' E longitude has been selected as the Standard Meridian of India for the following reasons:
- It runs through the middle of the country, ensuring a more uniform time across India.
- It is divisible by 7 hours and 30 minutes, aligning with the standard time used in other countries.
Q7. What influence did the land routes to India have on cultural exchanges in ancient times?
Ans: India's land routes have played a crucial role in cultural exchanges throughout history. Key points include:
- Land routes are older than maritime contacts, facilitating early interactions.
- Mountain passes in the north allowed ancient travellers to connect with India.
- These routes enabled the exchange of ideas and goods, such as:
- The philosophies of the Upanishads and stories from the Ramayana.
- Indian numerals and the decimal system spread to various regions.
- Spices and muslin were traded with many countries.
- Influences from other cultures, like Greek sculpture and architectural styles, also reached India.
Q8. Explain why the cities of Mumbai and Chennai are able to see the noon Sun exactly overhead twice a year, but Delhi never sees it exactly overhead.
Ans: Mumbai and Chennai experience the noon Sun directly overhead twice a year because:
- Both cities are located south of the Tropic of Cancer (23.5° N).
- Delhi, on the other hand, is situated north of this line.
- Due to the Earth's axial tilt of 23.5°, locations north of the Tropic of Cancer will never have the noon Sun directly overhead.
Q9. The central location of India at the head of the Indian Ocean is considered of great significance. Why?
Ans: The central location of India at the head of the Indian Ocean is significant for several reasons:
- India lies between East and West Asia, making it a crucial link.
- It serves as a southward extension of the Asian continent.
- The trans-Indian Ocean routes connect Europe and East Asia, enhancing India's strategic importance.
- The Deccan Peninsula extends into the Indian Ocean, facilitating contact with West Asia, Africa, and Europe from the west, and Southeast and East Asia from the east.
- No other country has as long a coastline on the Indian Ocean as India, underscoring its prominent position.
India's location justifies the naming of the ocean after it.
Q10. Describe the location and size of India in three points each.
Ans:
Location:
- India is the 7th largest country in the world, located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere.
- The mainland stretches from latitudes 8°04' N to 37°06' N and longitudes 68°07' E to 97°25' E.
- The Tropic of Cancer (23°30' N) nearly divides the country into two equal halves.
Size:
- India covers an area of 3.28 million sq km.
- This area represents about 2.4% of the world's total land area.
- India has a land boundary of approximately 15,200 km and a coastline of 7,516.6 km.
Q11. What is the longitudinal extent of India? What is its implication?
Ans: The longitudinal extent of India ranges from 68° 7'E to 97° 25'E. Key points include:
- The Earth rotates from West to East, causing the Sun to appear to move from East to West.
- There is a time difference of one hour for every 15° of longitude.
- This results in a time lag of two hours from Gujarat to Arunachal Pradesh.
- The Standard Meridian of India is 82° 30'E, which is used for the entire country.
- The latitudinal extent affects the duration of day and night as one moves from south to north.
Q12. India has a long coastline which is advantageous. Explain.
Ans: India's long coastline offers several advantages:
- It is the longest coastline along the Indian Ocean, enhancing India's maritime trade.
- Approximately 90% of India's international trade is conducted via sea routes.
- This strategic position facilitates easy access to global markets.
Furthermore, the opening of the Suez Canal in 1869 significantly reduced India's distance from Europe by 7,000 km, further boosting trade opportunities.
Q13. India said to enjoy a strategic position with reference to the International Trade Route. In your view which features provide India a strategic advantage?
Ans: India holds a strategic position in international trade due to several key features:
- It is centrally located between East and West Asia, making it a vital link for trade routes.
- India's landmass extends southward, forming the South-Central Peninsula of Asia.
- The Deccan Peninsula juts into the Indian Ocean, facilitating connections with West Asia, Africa, and Europe from the west, and with Southeast and East Asia from the east.
- India has the longest coastline along the Indian Ocean, enhancing its maritime trade capabilities.
These geographical advantages enable India to engage effectively in global trade.
Q14. What is the total area of India's land mass? What percentage of total geographical area of the world does it cover?
Ans: The total area of India is 3.28 million sq km. It represents approximately 2.4% of the world's total geographical area.
Q15. Which island countries are our Southern - neighbours?
Ans: Sri Lanka and Maldives are the two island countries that lie to the south of India.
- Sri Lanka is separated from India by the Palk Strait and the Gulf of Mannar.
- The Maldives is located south of the Lakshadweep Islands.
Q16. What is the total land boundary of India?
Ans: The total land boundary of India measures approximately 15,200 km.
Q17. What is the total length of India's coastline?
Ans: The total length of India's coastline, including its islands, is approximately 7,517 km.
Q18. Which neighbour country lies to the South-East of the Nicobar Islands?
Ans: The neighbour country to the south-east of the Nicobar Islands is Indonesia.
Q19. Which union territories (or part of them) are found on the West coast of India?
Ans: The union territories located on the West coast of India include:
- Daman and Diu
- Mahe (part of Puducherry)
Note that Lakshadweep is situated off the West coast, rather than on it.
Q20. Find out the number of union territories along the Western and Eastern coasts.
Ans: The Union Territories along the:
- Western Coast:
- Lakshadweep
- Daman and Diu
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Mahe (part of Puducherry)
- Eastern Coast:
- Puducherry
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
Q21. Find out area wise which is the smallest and which is the largest state.
Ans: Area-wise, the largest and smallest states in India are:
- Largest State: Rajasthan - 342,239 sq km
- Smallest State: Goa - 3,702 sq km
Q22. Name the group of island lying in the Arabian sea.
Ans: The group of islands located in the Arabian Sea is known as the Lakshadweep Islands.
Q23. Name the countries which are larger than India.
Ans: The countries larger than India are:
- Russia
- Canada
- USA
- China
- Australia
- Brazil
Q24. Which island group of India lies to its South-East?
Ans: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are located to the south-east of India.
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Geography Chapter 1 Extra Question Answers - India - Size and Location
| 1. भारत का आकार और स्थिति क्या है? |  |
| 2. भारत की भौगोलिक स्थिति का क्या महत्व है? |  |
| 3. भारत की सीमाएं किन-किन देशों के साथ मिलती हैं? |  |
| 4. भारत का कुल क्षेत्रफल किस प्रकार विभाजित है? |  |
| 5. भारत की जलवायु का क्या प्रभाव है? |  |






















