Livestock Class 4 Notes SST
| Table of contents |

|
| Livestock |

|
| Types of Livestock |

|
| Contributions of Livestock |

|
| Importance of Livestock in Farming and Indian Villages |

|
| Breeds of Cattle and Their Uses |

|
Livestock
Livestock are animals raised on farms for different uses, except for chickens. They help farmers with tasks like plowing fields and provide food like milk and meat.

They include cows, buffaloes, bullocks, sheep, goats, camels, mules, and yaks, and they help in many ways.
Types of Livestock
Livestock come in various types, including cattle, sheep, pigs, goats, horses, donkeys, mules, buffaloes, oxen, and camels. They can be found in different parts of the world, adapted to various environments.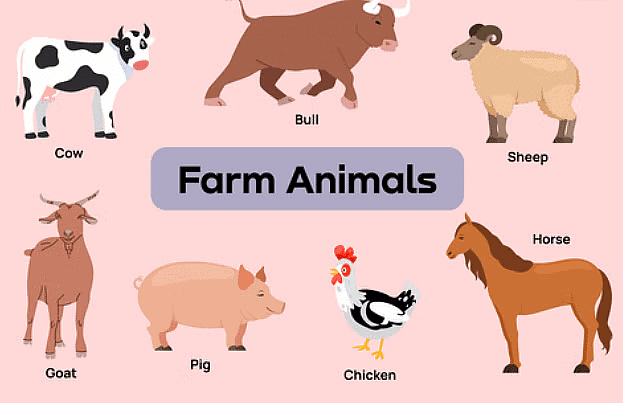
Contributions of Livestock
Here's a brief overview of some common types of livestock along with their contributions:
- Cattle: Cattle, including both beef and dairy cattle, are among the most widely raised livestock worldwide. They are adapted to various climates and environments and provide meat, milk, leather, and other products.

- Sheep: Sheep are primarily raised for their wool, meat (lamb and mutton), and milk. They are found in diverse regions, from temperate to arid climates, and are well-adapted to grazing on grasslands.

- Pigs: Pigs are highly adaptable animals raised for pork production. They can thrive in a range of environments and are known for their efficient conversion of feed into meat.

- Goats: Goats are versatile animals raised for meat, milk, and fiber (such as cashmere and mohair). They are well-suited to rugged terrain and can graze on a variety of vegetation, making them valuable for land management.

- Horses: Horses have been used by humans for thousands of years for transportation, agriculture, sport, and recreation. They come in various breeds adapted to different purposes, climates, and terrains.

- Donkeys and Mules: Donkeys and mules are often used as working animals in agriculture and transportation. They are known for their strength, endurance, and ability to navigate rough terrain, particularly in arid regions.

- Buffaloes: Water buffalo are commonly raised in parts of Asia for their milk, meat, and as draft animals. They are well-adapted to wetland environments and are important for rice cultivation in some regions.

- Oxen: Oxen are cattle trained as draft animals for plowing fields and hauling heavy loads. They have historically played a crucial role in agriculture, particularly in regions where mechanized equipment is less common.

- Camels: Camels are well-suited to arid environments and are primarily raised in desert regions of Africa and Asia. They are valued for their ability to travel long distances without water, provide milk, meat, and hides, and serve as pack animals.

Dogs and Cats: Not Livestock
Dogs aren't livestock, but they're helpful pets, offering services like guarding homes or guiding the blind. Similarly, cats are good companions but aren't considered livestock. They offer emotional support, loyalty, and friendship to their owners, making them valued members of many households.
Uses of Cow Dung
Cow dung has several uses. These are listed below.
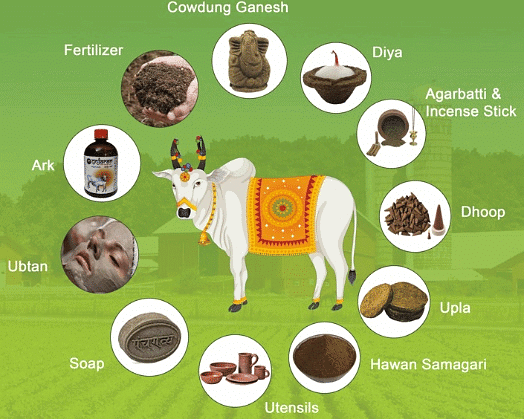
- Fertilizer:
- Cow dung is rich in organic matter and nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, making it an excellent natural fertilizer for crops.
- When applied to fields, it improves soil structure, enhances water retention, and promotes plant growth.
- Fuel: Dried cow dung, known as "cow dung cakes," is commonly used as a fuel for cooking and heating in many rural areas, particularly in regions where other sources of energy are scarce or expensive.
- Biogas Production:
- Cow dung is also a valuable feedstock for biogas production through anaerobic digestion.
- Biogas generated from cow dung can be used for cooking, lighting, and even electricity generation, offering a renewable and environmentally friendly energy source.
Utilization of Animal By-Products
Leather Production: The hides of cattle are processed to produce leather, a durable and versatile material used in various industries, including fashion, furniture, and automotive manufacturing. This demonstrates how even after the death of livestock, their by-products continue to serve human needs.
Importance of Livestock in Farming and Indian Villages
- Farming Operations:
- Livestock, particularly bullocks (castrated male cattle), have traditionally been essential for various farming operations, such as plowing, tilling, and transporting agricultural produce.

- They provide traction power in regions where mechanized equipment may not be suitable or accessible.
- Livestock, particularly bullocks (castrated male cattle), have traditionally been essential for various farming operations, such as plowing, tilling, and transporting agricultural produce.
- Daily Life:
- Livestock, especially cattle, hold immense cultural, economic, and practical significance in rural Indian communities.
- They are integral to agricultural activities, transportation, and religious ceremonies, highlighting the interconnectedness between humans and animals in village life.
Breeds of Cattle and Their Uses
Different cattle breeds are bred for specific purposes based on their traits and characteristics.
For example:
- Dairy Breeds: Dairy Breeds such as Holstein, Jersey, and Guernsey, are selectively bred for high milk production.

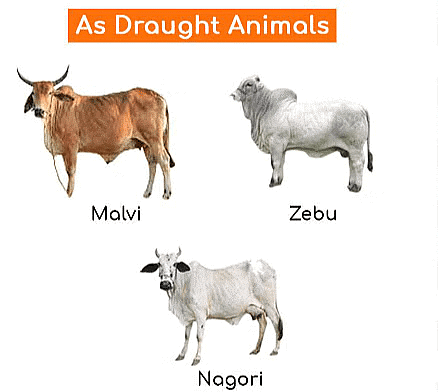
- Draught Breeds: Draught Breeds like Oxen, are bred for their strength and endurance to perform heavy agricultural tasks.
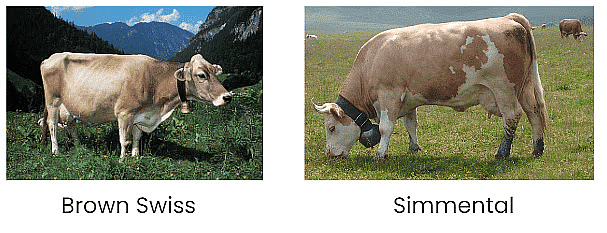
- Dual-Purpose Breeds: Dual-purpose Breeds such as Brown Swiss and Simmental, are raised for both milk and meat production.
Ensuring Livestock Health
Keeping livestock healthy is very important for making sure they stay strong and healthy. This means giving them good food, clean water, a safe place to live, making sure they get their shots to stay healthy, and giving them medicine to get rid of worms. It's also important to have a vet check them regularly to make sure they're okay and to help them if they get sick.
Ethical Treatment of Animals
Because animals help people in important ways, like providing food and other products, it's really important to take good care of them and treat them nicely all the time. This means giving them a comfortable place to live, making sure they're not scared or suffering, and using farming methods that let them act like they naturally would.
|
50 videos|246 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Livestock Class 4 Notes SST
| 1. What are the common types of livestock? |  |
| 2. How can livestock be managed for optimal health? |  |
| 3. What are some important considerations when selecting livestock breeds? |  |
| 4. How can livestock contribute to sustainable agriculture practices? |  |
| 5. What are some common challenges faced by livestock farmers? |  |















