NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 - Exercise 11.1 Constructions
Basic Constructions
A geometrical construction means to draw geometrical figures, such as an angle, a circle, a triangle, a quadrilateral, and a polygon, etc.
We normally use all or some of the following instruments for drawing geometrical figures: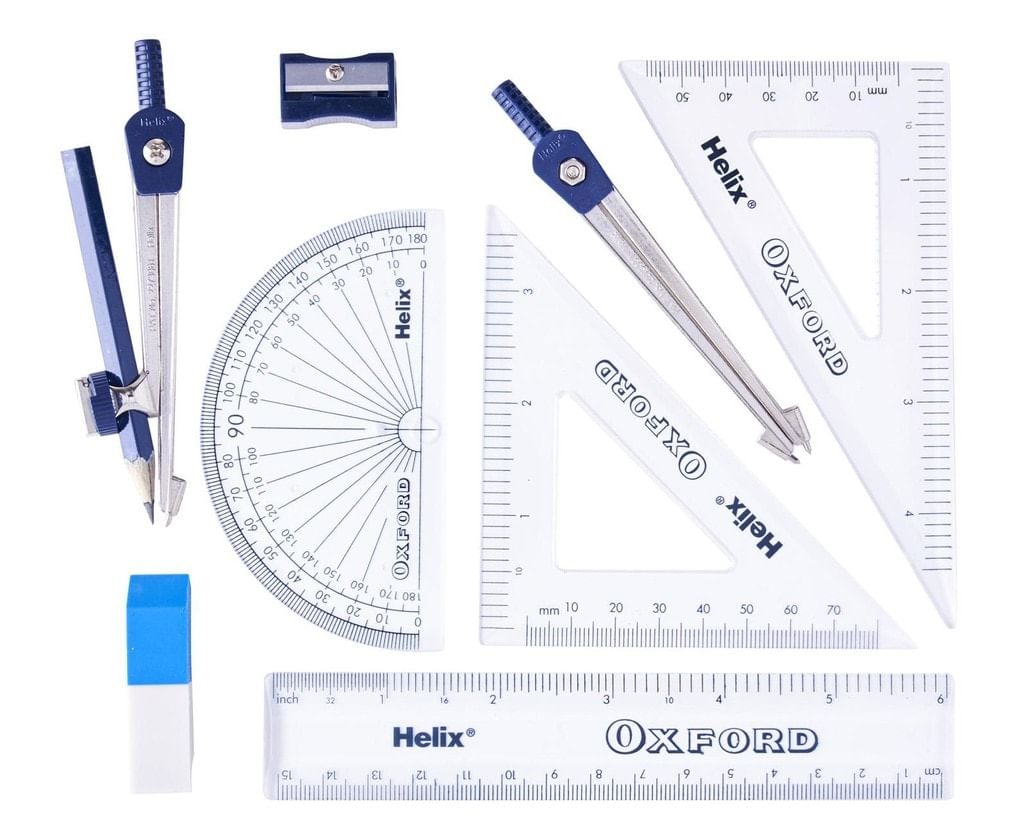
- A protractor
- A pair of compasses
- A pair of set squares
- A pair of dividers
- A graduated scale
Exercise 11.1
Q1. Construct an angle of 90º at the initial point of a given ray and justify the construction.
Ans: Steps of construction:
- Draw a ray OA.
- Taking O as the centre and suitable radius, draw a semicircle, which cuts OA at B.
- Keeping the radius the same, divide the semicircle into three equal parts such that
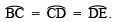
- Draw
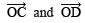
- Draw
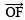 , the bisector of ∠COD.
, the bisector of ∠COD.
Thus, ∠AOF = 90º.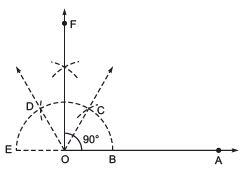
Justification:
∵ O is the centre of the semicircle and it is divided into 3 equal parts.
∴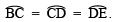
∠BOC = ∠COD = ∠DOE
∵ Equal chords subtend equal angles at the centre
∴ ∠BOC + ∠COD + ∠DOE = 180º
∠BOC + ∠BOC + ∠BOC = 180º
3∠BOC = 180°
∴ ∠BOC = 60º
Similarly, ∠COD = 60º and ∠DOE = 60º
∵ OF is the bisector of ∠COD.
∴ 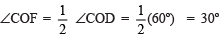 = 30º
= 30º
Now, ∠BOC + ∠COF = 60º + 30º
∠BOF = 90º or ∠AOF = 90º
Q2. Construct an angle of 45º at the initial point of a given ray and justify the construction.
Ans: Steps of construction:
- Draw a ray
 .
. - Taking O as the centre and with a suitable radius, draw a semicircle such that it intersects
 at B.
at B.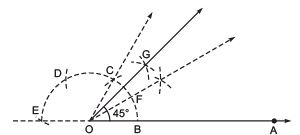
- Taking B as centre and keeping the same radius, cut the semicircle at C. Similarly, cut the semicircle at D and E, such that
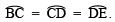 . Join OC and produce.
. Join OC and produce. - Divide
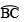 into two equal parts, such that
into two equal parts, such that 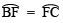
- Draw OG, the angle bisector of ∠FOC.
Thus, ∠BOG = 45º or ∠AOG = 45º
Justification:
∵ 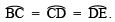
∴ ∠BOC = ∠COD = ∠DOE
∵ Equal chords subtend equal angles at the centre
∴ ∠BOC + ∠COD + ∠DOE = 180º
∠BOC = 60º
∵  is the bisector of ∠BOC/
is the bisector of ∠BOC/
∴ 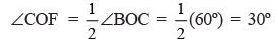 .. (1)
.. (1)
Also, 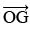 is the bisector of ∠COF.
is the bisector of ∠COF.
∴ 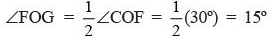 ... (2)
... (2)
Adding (1) and (2), we get∠COF + ∠FOG = 30º + 15º = 45º
∠BOF + ∠FOG = 45º [∵ ∠COF = ∠BOF]
∠BOG = 45º
Q3. Construct the angles of the following measurements:
(a) 30º
(b) 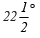
(c) 15º
Ans:
(a) Angle of 30º
Steps of construction:
- Draw a ray OA.
- With O as the centre and a suitable radius, draw an arc, cutting
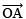 at B.
at B.
- With centre at B and the same radius as above, draw an arc to cut the previous arc at C.
- Join
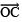 and produce, such that ∠BOC = 60º.
and produce, such that ∠BOC = 60º.  bisector of ∠BOC, such that
bisector of ∠BOC, such that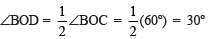
Thus, ∠BOD = 30º
(b) Angle of 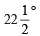
Steps of construction:
- Draw a ray
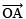
- Draw an angle ∠AOB = 90º
- Draw OC, the bisector of ∠AOB, such that
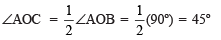
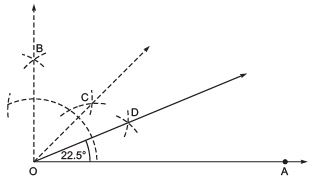
- Now, draw OD, the bisector of ∠AOC, such that
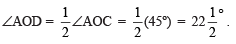
Thus, 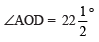
(c) Angle of 15º
Steps of construction:
- Draw a ray
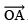 .
. - Construct ∠AOB = 60º.
- Draw
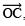 the bisector of ∠AOB, such that
the bisector of ∠AOB, such that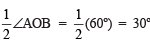 i.e. ∠AOC = 30º
i.e. ∠AOC = 30º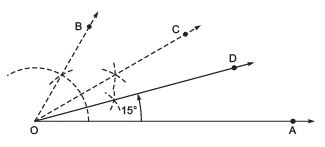
- Draw
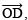 the angle bisector of ∠AOC such that
the angle bisector of ∠AOC such that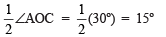
Thus, ∠AOD = 15º
Q4. Construct the following angles and verify by measuring them by a protractor:
(a) 75º
(b) 105º
(c) 135º
Ans:
(a) Angle of 75º (Hint: 75º = 60º + 15º)
Steps of construction:
- Draw
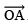 .
. - With O as centre and having a suitable radius, draw an arc which meets
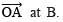
- With centre B and keeping the radius same, mark a point C on the previous arc.
- With centre C and the same radius, mark another point D on the arc of step 2.
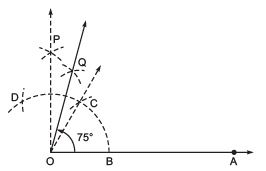
- Draw
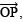 the bisector of
the bisector of 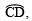 such that ∠COP
such that ∠COP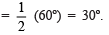
- Draw
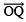 , the bisector of ∠COP, such that ∠COQ = 15º
, the bisector of ∠COP, such that ∠COQ = 15º
Thus, ∠BOQ = 60º + 15º = 75ºor ∠AOQ = 75º.
(b) Angle of 105º (Hint: 105º = 90º + 15º)
Steps of construction:
- Draw
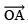
- With centre O and having a suitable radius, draw an arc that meets OA at B.
- With centre B and keeping the same radius, mark a point C on the arc of step 2.
- With centre C and keeping the same radius, mark another point D on the arc of step 2.
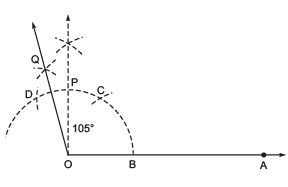
- Draw OP, the bisector of
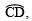
- Draw OQ, the bisector of
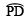 .
.
Thus, ∠AOQ = 105º
(c) Angle of 135º (Hint: 120º + 15º = 135º)
Steps of construction:
- Draw a ray
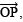
- With centre O and having a suitable radius draw an arc to meet OP at A.
- Keeping the same radius and starting from A, mark points Q, R and S on the arc of step 2.
- Draw
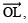 the bisector of
the bisector of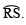 V. Draw
V. Draw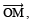 the bisector of
the bisector of 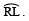
Thus, ∠POM = 135º.
Q5. Construct an equilateral triangle, given its side and justify the construction.
Ans: Let us construct an equilateral triangle, each of whose side = PQ
Steps of construction:
- Draw a ray
 .
.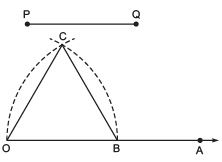
- Taking O as centre and radius equal to PQ, draw an arc to cut OA at B such that OB = PQ
- Taking B as centre and radius = OB, draw an arc, to intersect the previous arc at C.
- Join OC and OB.
Thus, ΔOBC is the required equilateral triangle.
Justification:
∵ The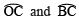 are drawn with the same radius.
are drawn with the same radius.
∴ 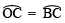 ⇒
⇒ 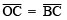
∵ Chords corresponding to equal arcs are equal.
∵ OC = OB = BC
∴ ΔOBC is an equilateral triangle.
|
82 videos|300 docs|69 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 - Exercise 11.1 Constructions
| 1. What are the basic constructions in geometry? |  |
| 2. How do you construct a perpendicular bisector of a line segment? |  |
| 3. What is the purpose of constructing an angle bisector? |  |
| 4. How can you construct a perpendicular from a point to a line? |  |
| 5. Can you explain how to construct parallel lines? |  |

















