Dielectrics & Polarisation | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
What is a Dielectric?
Dielectrics are non-conducting substances. They are the insulating materials and are bad conductors of electric current. Dielectric materials can hold an electrostatic charge while dissipating minimal energy in the form of heat. Examples of dielectric are Mica, Plastics, Glass, Porcelain and Various Metal Oxides. You must also remember that even dry air is also an example of a dielectric.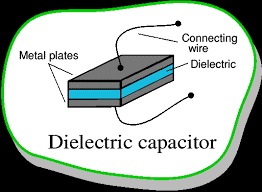
Classification of Dielectrics
Dielectrics are of two types
- Polar Molecules: Polar Molecules are those type of dielectric where the possibilities of the positive and negative molecules coinciding with each other are null or zero. This is because they all are asymmetric in shape. Examples: H2O, CO2, NO2 etc.
When the electric field is not present, it causes the electric dipole moment of these molecules in a random direction. This is why the average dipole moment is zero. If the external electric field is present, the molecules assemble in the same direction as the electric field. - Non-Polar Molecule: Unlike polar molecules, in non-polar molecules, the centre of positive charge and negative coincide, that is it is not zero. The molecule then has no permanent (or intrinsic) dipole moment. Examples: O2, N2, H2 etc.
Induced Electric Dipole Moment
When we apply an external electric field in a non-polar molecule, all the protons travel towards the direction of the electric field and electrons in opposite direction. Due to the presence of an electric field, this process continues unless the internal forces balance them.
Due to this, there is a creation of two centres of charge. They are Polarised and we call them as the Induced Electric Dipole. The dipole moment is the Induced Electric Dipole Moment.
Polarizability
Applied field is directly proportional to induced dipole moment and is independent of the temperature. The direction of induced dipole moment (x) is parallel to the direction of electric field Ê and for a single polar atom. The Polarisability determines the dynamical response of a bound system to external fields.
It also provides an insight into a molecule‘s internal structure. In a solid, polarizability is the dipole moment per unit volume of the crystal cell: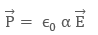
where ‘a’ is the Atomic Polarisability. The S.I. unit of polarizability is m3 and its dimensions are the same as it’s volume.
Electric Polarization
When we place a dielectric slab is in an electric field, then the molecule gains the dipole moment. In such cases, we say that the dielectric is polarised. The Electric Polarization is dipole moment per unit volume of a dielectric material. The polarization is denoted by P.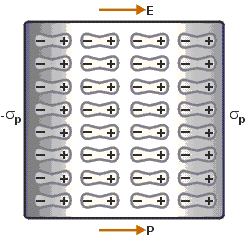 Polarisation
Polarisation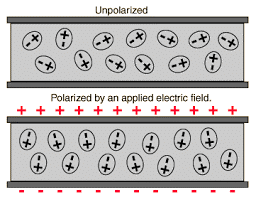 Polarisation Process
Polarisation Process
Dielectric Constant
When we place a dielectric slab between the parallel plates, the ratio of the applied electric field strength to the strength of the reduced value of electric field capacitor is the Dielectric Constant. The formula is: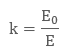
E is always less than or equal to E where Eo is dielectric and E is the net field. The larger the dielectric constant, the more charge can be stored. Completely filling the space between capacitor plates with a dielectric increase the capacitance by a factor of the dielectric constant. C = κCo, where Co is the capacitance with no dielectric between the plates.
Dielectric Strength
For an insulating material, the dielectric strength is the maximum electric field strength that it can withstand intrinsically without experiencing failure of its insulating properties.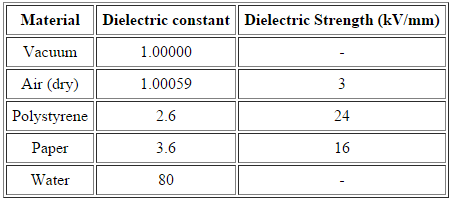
Dielectric Polarization
When we apply an external electric field to a dielectric material, we get the Dielectric Polarization. It is the displacement of charges (positive and negative) upon applying an electric field. The main task of the dielectric polarization is to relate macroscopic properties to microscopic properties.
Polarization occurs through the action of an electric field or other external factors, such as mechanical stress, as in the case of piezoelectric crystals. Piezoelectric crystals are those solid materials which accumulate electric charge within them.
Dielectric Polarization can also arise spontaneously in pyroelectric crystals, particularly in ferroelectrics. Ferroelectricity is a property of certain materials that have a spontaneous electric polarization that can be reversed by the application of an external electric field.
Solved Example for You
Question: Which of the following is/are non-polar dielectrics?
(a) HCl
(b) Water
(c) Benzene
(d) NH3
Solution: Option C – Benzene. Ammonia and HCl are polar molecules since they have a net dipole moment towards a particular direction. Both water and benzene are non-polar molecules. But water is a conductor of electricity, whereas benzene is a dielectric (insulator).
|
268 videos|774 docs|209 tests
|
















