Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Question Answers - Reproduction in Animals
Q1: Define Sexual reproduction.
Ans: Sexual reproduction: Reproduction which begins with the fusion of male and female gamete is called Sexual reproduction.
Q2: Define Fertilisation.
Ans: Fertilisation: Fusion of egg with sperm is called Fertilisation.
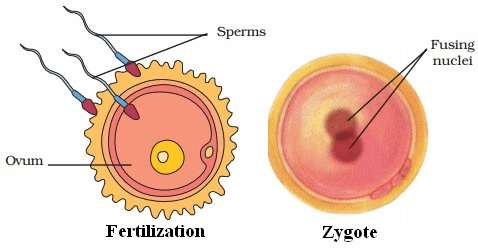
Q3: Define internal fertilisation.
Ans: Fertilisation which takes place inside female body is called internal fertilisation.
Q4: How do the hundreds of egg of frog remain protected even if laid on open aquatic system?
Ans: A layer of Jelly holds the eggs together and provides them protection.
Q5: What is External fertilisation?
Ans: The type of fertilisation in which fusion of male and female gametes takes place outside the body of female is called External fertilisation. It takes place in animals like frog, lizard, fish etc.
Q6: Give two examples of organisms showing both internal and external mode of fertilisation.
Ans: Internal fertilisation: Human and Hen.
External fertilisation: Frog and Starfish.
Q7: What are the common difference between zygote and embryo? .
Ans: Zygote: Single fertilizes egg and found in oviducts.
Embryo: Ball of cells and gets embedded in the wall of uterus for development.
Q8: Define Embryo.
Ans: Zygote divides repeatedly to give ball of cell called Embryo.
Q9: What is Foetus?
Ans: The stage of embryo in which all body part can be identified is a Foetus. When the development of foetus is complete, the mother gives birth to the baby.
Q10: What is the basic difference between reproduction mechanism in human being and hen?
Ans: Human being gives birth to baby, they are viviparous whereas hen lays egg and they are oviparous.
Q11: Why do frogs and fish lay eggs in hundred, whereas a hen lays only one egg at a time?
Ans: Organisms having internal fertilisation like hen, produce one egg at a time. This is so because here there is less chance of failure of fusion between male and female gamete. After the gametes are fertilized there is just the need of development of animal in the form of egg.
Frog like aquatic organisms who shows external mode of reproduction have to lay egg in hundred. The first reason behind this is the single egg is so small in size that it will not be possible to stay to definite position and which in turns make hard for sperm to found and fuse them. Whereas, when large number of eggs make them stick together this makes fertilisation possible. Another reason behind this is there is a lot of organisms who feed on these eggs, so larger number of eggs gives more possibility of giving birth to young ones
Q12: What is Viviparous animal?
Ans: The animals which give birth to young one are called Viviparous animal. Like cow, dog etc.
Q13: Explain Metamorphosis.
Ans: The transformation of larva into adult through drastic changes is called Metamorphosis.
Q14: Differentiate between internal fertilisation and external fertilisation.
Ans:
Internal fertilization
- It involves the fusion of the male and the female gamete inside the female body.
- Chances of the survival of the offspring are more. Therefore, a small number of eggs are produced.
- Humans, cows, hens are organisms showing internal fertilization.
External fertilization
- It involves the fusion of the male and the female gamete outside the female body.
- Chances of survival of the offspring are less. Therefore, a large number of eggs are produced.
- Fish, frog, starfish are organisms showing external fertilization.
Q15: Differentiate between zygote and foetus.
Ans:
Zygote | Foetus |
|
|
Q16: Name some animals in which young ones are different from adult.
Ans: Silkworm and Frog have young ones different from adult.
Q17: Does all kind of asexual mode of reproduction can also be called Budding?
Ans: No, there is another mode of asexual reproduction apart from Budding, which is Binary fission.
Q18: Define Binary fission and give name of at least one organism following it.
Ans: The mode of asexual reproduction in which an animal reproduce itself by dividing into two individual is called Binary fission. Amoeba follows this mode for its reproduction.
Q19: Differentiate between Budding and Binary fission.
Ans: In Budding new organism develops from bud, whereas, in Binary fission organism reproduce by dividing itself into two.
Q20: Define metamorphosis. Explain it in human beings.
Ans: The transformation of the larva into an adult through drastic changes is called as metamorphosis. This is the matter of contradiction that human beings undergo metamorphosis or not. Some people say humans don't go through metamorphosis. We just change size and appearance, but we are not considered to go through metamorphosis. On the other hand some people say Of course we go through metamorphosis! When you are born you are a big foot-long worm and as a young toddler you start to make a cocoon. Then, when you break out at about age 10 you are a normal looking person.
Q21: Define asexual reproduction. Describe two methods of asexual reproduction in animals.
Ans. Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction where fertilisation does not take place as only a single parent is involved. Offspring produced is identical to the parent because they are produced as clones. Types of asexual reproduction are as follows: fission, budding and fragmentation.
A. Fission: This type is mainly seen in unicellular prokaryotes. A full-grown organism at a certain stage splits into two identical daughter organisms.
B. Budding: In this type of asexual reproduction, a 'bud' or an outgrowth is formed on the mature adult body and eventually this bud separates and acts as an individual organism.
Q22. What is reproduction? Explain its various modes.
Ans. The process by which organisms produce new offsprings of same species is called reproduction.
Modes of reproduction: There are following two modes of reproduction.
(i) Sexual reproduction: The method of reproduction in which two parents male, and female are involved is called reproduction.
(ii) Asexual reproduction: The method of reproduction in which only one parent (male or female) is involved is called asexual reproduction.
Q23. What is sperm? Explain its structure.
Ans. Sperm is a male reproductive cell. It is also called male gamete. There are mainly three parts of sperm:
(i) Head
(ii) Middle piece and
(iii) A long tail.
Indeed each sperm is a single cell with all the usual cell components.
Q24. What are the female reproductive organs?
Ans. The female reproductive organs are a pair of ovaries, oviducts (fallopian tubes) and a uterus. The ovary produces female gametes called ova or eggs. In human beings only one matured egg is released into oviduct by one of the ovaries every month. The development of baby takes place in uterus.
Q25. What is ovum? Explain its structure.
Ans. The female reproductive cell is called egg or ovum (plural ova). It is produced by ovaries. Like sperm, ovum is also a single cell and contains nucleus and other usual components.
Q26. What do you understand about test-tube baby?
Ans. Some women are unable to bear babies because sperms cannot reach the egg for fertilisation. In such cases, doctors collect freshly released egg and sperm and keep them together for few hours for IVF or in vitro fertilisation. In case fertilisation occurs the zygote is allowed to develop for a week and then it is placed in the mother’s uterus. Complete development takes place in the uterus and the baby is born like any other baby. Babies born through this technique are called test-tube babies.
Q27. Why is it necessary to produce large number of eggs and sperms by the animals which reproduce by external fertilisation?
Ans. The animals in which external fertilisation takes place produces a large number of eggs sperms. This is because the eggs and sperms get exposed to water movement, wind and rainfall. There are some other animals that may feed on eggs in the pond. Thus, production of large number of eggs and sperms is necessary to ensure fertilisation of at least a few of them.
Q28. Explain the terms viviparous and oviparous with examples.
Ans. Viviparous: The animals which give birth to young ones are called viviparous animals. For example: cat, dog, cow and human beings.
Oviparous: The animals which lay eggs are called oviparous animals. In such animals development of embryo take place outside the female body. For example: All birds and reptiles.
Q29. Explain the life-cycle of silkworm in brief.
Ans. In silkworm, the young ones may look very different from the adults. We can write the life-cycle of a silkworm as follows:
Egg → Larva or caterpillar → Pupa → Adult.
The caterpillar or pupa of silkworm looks very different from the adult moth.
Q30. Explain the asexual reproduction in hydra with diagram.
Ans. In hydra, reproduction takes place by budding. A part of the organism starts bulging out. Slowly it grows and develops into a separate individual.
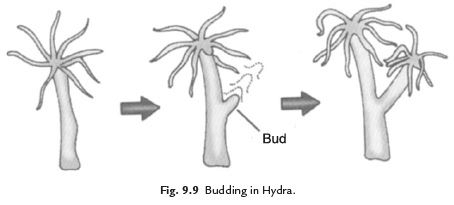
Q31. What is asexual reproduction? Write various methods of asexual reproduction.
Ans. The type of reproduction in which only a single parent is involved is called asexual reproduction.
There are following methods of asexual reproduction:
(i) By budding
(ii) By binary fission
(iii) By vegetative reproduction.
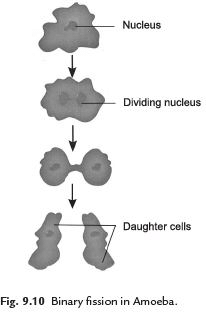
Q32. Explain the asexual reproduction in amoeba.
Ans. The reproduction in amoeba takes place by binary fission. In this process amoeba reproduces by dividing into two individuals. The nucleus of amoeba cell is divided into two. This is followed by division of its body into two, each part receiving a nucleus. Finally two amoebae are produced from one parent amoeba.
Q33. Explain Metamorphosis.
Ans. The transformation of larva into an adult through drastic changes is called metamorphosis. For example: The tadpole which develops from the eggs laid by the frog is entirely different from the frog. But when it grows, it becomes just like the frog. This drastic change in tadpole is called metamorphosis.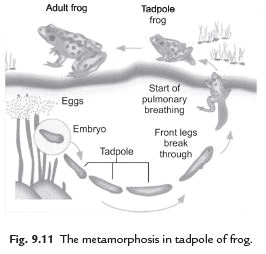
|
92 videos|419 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Question Answers - Reproduction in Animals
| 1. What are the different methods of reproduction in animals? |  |
| 2. How do animals reproduce sexually? |  |
| 3. What is the role of hormones in animal reproduction? |  |
| 4. Can animals reproduce without mating? |  |
| 5. How do animals ensure successful reproduction? |  |

















