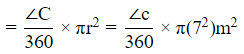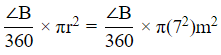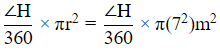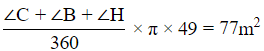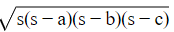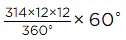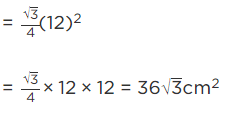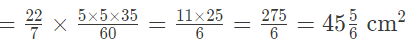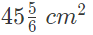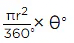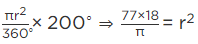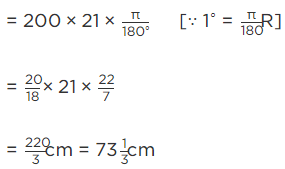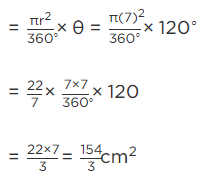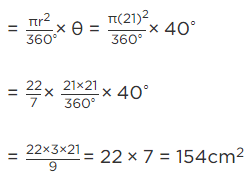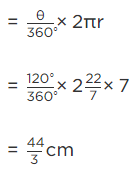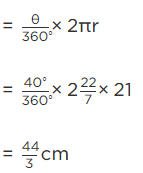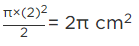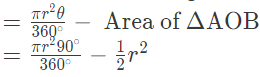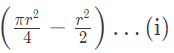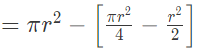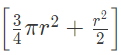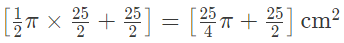NCERT Exemplar: Areas Related to Circles - 2 - Class 10 PDF Download
Exercise 11.4
Q.1. The area of a circular playground is 22176 m2. Find the cost of fencing this ground at the rate of Rs 50 per metre.
Given, area of circular playground is 22176 m²
We have to find the cost of fencing this ground at the rate of Rs 50 per metre.
Area of circle = πr²
Where r is the radius
22176 = (22/7)r²
r² = 22176(7)/22
r² = 7056
Taking square root,r = 84 m
Circumference of circle = 2πr
Circumference of circular playground = 2(22/7)(84)
= 2(22)(12)
= 44(12)
= 528 m
Given, cost of fencing per meter = Rs. 50
Cost of fencing 528 m = 528(50)
= Rs. 26400
Therefore, the cost of fencing is Rs. 26400
Q.2. The diameters of front and rear wheels of a tractor are 80 cm and 2 m respectively. Find the number of revolutions that rear wheel will make in covering a distance in which the front wheel makes 1400 revolutions.
Given, the diameter of front and rear wheels of a tractor are 80 cm and 2 m.
We have to find the number of revolutions that the rear wheel will make in covering a distance in which the front wheel makes 1400 revolutions.
Number of revolutions = total distance / distance covered in one revolution
Distance covered in one revolution = 2πr
Given, diameter of front wheel, 2r = 80 cm
Distance covered in one revolution by the front wheel = 80π
Given, diameter of rear wheel, 2r = 2 m
1 m = 100 cm
So, diameter of rear wheel, 2r = 200 cm
Distance covered in one revolution by the rear wheel = 200π
Given, total number of revolutions by front wheel = 1400
So, total distance covered by front wheel = number of revolutions × distance covered in one revolution
= 1400(80π)
= 112000π cm
Let the number of revolutions by the rear wheel be c
Distance travelled by rear wheel = number of revolutions × distance covered in one revolution
= c × 200π
Both the wheels travel the same distance.
So, 112000π = c × 200π
112000 = c × 200
c = 112000/200
c = 1120/2
c = 560
Therefore, the number of revolutions made by the rear wheel is 560.
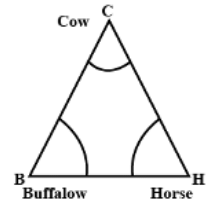
Q.3. Sides of a triangular field are 15 m, 16 m and 17 m. With the three corners of the field a cow, a buffalo and a horse are tied separately with ropes of length 7 m each to graze in the field. Find the area of the field which cannot be grazed by the three animals.
Given radius of each sector = 7m
Now area of sector with ∠C
Area of the sector with ∠B =
And area of the sector with ∠H =
Therefore sum of the areas =
Semiperimeter = 24 m
Therefore area of the triangular field =
= 24√21m2
So area which can not be grazed =(24√21 −77)m2
Q.4. Find the area of the segment of a circle of radius 12 cm whose corresponding sector has a central angle of 60° (Use π = 3.14).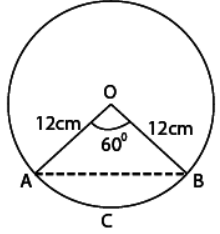
Given that, radius of a circle (r) = 12 cm
And central angle of sector OBCA (θ) = 60∘
∴ Area of sector OBCA
= πr2/360 × θ [here, OBCA = sector and ABCA = segment]
= 314 × 2 × 12
= 3.14 × 24 = 75.36 cm2
Since, ΔOAB is an isosceles triangle.
Let ∠OAB = ∠OBA = θ1
and OA = OB = 12cm
∠AOB = θ = 60∘
∴ ∠OAB + ∠OBA + ∠AOB = 180∘
[∵ Sum of all interior angles of a triangle is 180∘]
⇒ θ1 + θ1 + 60∘ = 180∘
⇒ 2θ1 = 120∘
⇒ θ1 = 60∘
∴ θ1 = θ = 60∘
So, the required ΔAOB is an equilateral triangle.
Now, area of ΔAOB = √3/4 (side)2
[ ∵ area of an equilateral triangle. = √3/4 (side)2]
Now, area of the segment of a circle i.e
ABCA = Area of sector OBCA - Area of ΔAOB
= ( 75.36 − 36√3)cm2
Hence, the required of segment of a circle is: (75.36 − 36√3)cm2.
Q.5. A circular pond is 17.5 m is of diameter. It is surrounded by a 2 m wide path. Find the cost of constructing the path at the rate of Rs 25 per m2.
Diameter of the pond = 17.5 m
Radius of the pond = 8.75 m
Radius of the pond with the path = 8.75 + 2 = 10.75 m
Area of the path = Area of the pond along with the path − area of the pond
Area of the path = π[R2 - r2]
= π[(10.75)2 - (8.75)2]
= π[(2)(19.5)]
= 122.46m2
Cost of constructing the path =25 × 122.46 = Rs 3061.5
Q.6. In Fig. 11.17, ABCD is a trapezium with AB || DC, AB = 18 cm, DC = 32 cm and distance between AB and DC = 14 cm. If arcs of equal radii 7 cm with centres A, B, C and D have been drawn, then find the area of the shaded region of the figure.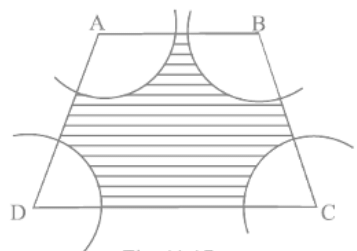
Given, ABCD is a trapezium with sides
AB = 18 cm
DC = 32 cm
The distance between AB and DC = 14 cm
Also, AB||DC
Radii of arcs with centres A, B, C and D = 7 cm
We have to find the area of the shaded region.
Area of the shaded region = area of trapezium - area of 4 sectors.
since AB||DC, ∠A + ∠D = 180° and ∠B + ∠C = 180°
Area of sector = πr²θ/360°
Area of sectors with angles A and D = π(7)²[(∠A+∠D)/360°]
= 49π(180°/360°)
= 49π(1/2)
= 49(22/7)(1/2)
= 7(11)
= 77 cm²
Area of sectors with angles B and C = π(7)²[(∠B+∠C)/360°]
= 49π(180°/360°)
= 49π(1/2)
= 49(22/7)(1/2)
= 7(11)
= 77 cm²
Area of 4 sectors = 77 + 77
= 154 cm²
Area of trapezium = 1/2[(sum of parallel sides) × height]
From the figure,
The parallel sides are AB and CD
Given, AB = 18 cm and CD = 32 cm
Height = distance between AB and CD
So, height = 14 cm
Now, the area of trapezium = 1/2[(18 + 32) × 14]
= 1/2[(50) × 14]
= 1/2(700)
= 350 cm²
Area of shaded region = 350 - 154
= 196 cm²
Therefore, the area of the shaded region is 196 cm²
Q.7. Three circles each of radius 3.5 cm are drawn in such a way that each of them touches the other two. Find the area enclosed between these circles.
Given that, three circles are in such a way that each of them touches the other two.
Now, we join centre of all three circles to each other by a line segment. Since, radius of each circle is 3.5 cm.
So; AB = 2 x Radius of circle
= 2 x 3.5 = 7 cm.
⇒ AC = BC = AB = 7cm
which shows that, ΔABC is an equilateral triangle with side 7 cm.
We know that, each angle between two adjacent sides of an equilateral triangle is 60°
∴ Area of sector with angle ∠A = 60°.
Hence, the required area enclosed between these circles is 1.967 cm2 (approx).
Q.8. Find the area of the sector of a circle of radius 5 cm, if the corresponding arc length is 3.5 cm.
Given, radius of circle = 5 cm
Corresponding arc length = 3.5 cm
We have to find the area of the sector of a circle.
Find the area of the sector of a circle of radius 5 cm, if the corresponding arc length is 3.5 cm Length of the arc = θ/360°(2πr)3.5 = (θ/360°)(2π)(5)3.5 = (θ/360°)(2)(22/7)(5)θ/360° = 3.5(7)/(22)(10)
θ/360° = 24.5/220
θ/360° = 0.1114
Area of sector = πr²θ/360°
= (22/7)(5)²(0.1114)
= 61.27/7
= 8.75 cm²
Therefore, the area of the sector is 8.75 cm².
Q.9. Four circular cardboard pieces of radii 7 cm are placed on a paper in such a way that each piece touches other two pieces. Find the area of the portion enclosed between these pieces.
Given, four circular cardboard pieces of radii 7 cm are placed on a paper such that each piece touches the other two pieces.
We have to find the area of the portion enclosed between these pieces.
Four circular cardboard pieces of radii 7 cm are placed on a paper in such a way that each piece touches other two pieces. Find the area of the portion enclosed between these pieces
From the figure,A, B, C and D are the four circular cardboard pieces of radii 7 cm.On joining the centres, A, B, C and D form a square.
The side of square = 7 + 7 = 14 cm
Thus, the sides AB = AC = BD = CD = 14 cm
Area of the portion enclosed between these cardboard pieces = area of square - area of 4 sectors.
Area of square = (side)²
= (14)²
= 196 cm²
We know that the angle between the two adjacent sides of a square is 90°
So ∠A = ∠B = ∠C = ∠D = 90°
Area of sector = πr²θ/360°
Area of sector with angle A = (22/7)(7)²(90°/360°)
= (22)(7)(1/4)
= 154/4
= 38.5 cm²
Area of 4 sectors = 4(area of sector with angle A)
= 4(38.5)
= 154 cm²
Area of shaded region = 196 - 154
= 42 cm²
Therefore, the area of the shaded region is 42 cm².
Q.10. On a square cardboard sheet of area 784 cm2, four congruent circular plates of maximum size are placed such that each circular plate touches the other two plates and each side of the square sheet is tangent to two circular plates. Find the area of the square sheet not covered by the circular plates.
Given, four congruent circular plates of maximum size are placed on a square cardboard sheet of area 784 cm².
The circular plates are placed such that each plate touches the other two plates and each side of the square sheet is tangent to two circular plates.
We have to find the area of the square sheet not covered by the circular plates.
On a square cardboard sheet of area 784 cm² , four congruent circular plates of maximum size are placed such that each circular plate touches the other two plates and each side of the square sheet is tangent to two circular plates. Find the area of the square sheet not covered by the circular plates
From the figure,
ABCD is a square sheet.
Given, area of square sheet = 784 cm²
Area of square = (side)²
784 = (side)²
Taking square root,
side = √784
side = 28 cm
Given, the four circular plates are congruent.
The diameter of each plate = 28/2 = 14 cm
Radius of each plate = 14/2 = 7 cm
Area of circle = πr²
Area of one circular plate = (22/7)(7)²
= 22(7)
= 154 cm²
Area of 4 congruent circular plates = 4(area of one circular plate)
= 4(154)
= 616 cm²
Area of the square sheet not covered by the plates = area of square - area of 4 circular plates.
= 784 - 616
= 168 cm²
Therefore, the area of the square sheet not covered by the circular plates is 168 cm².
Q.11. Floor of a room is of dimensions 5 m × 4 m and it is covered with circular tiles of diameters 50 cm each as shown in Fig. 1 1.18. Find the area of floor that remains uncovered with tiles . (Use π = 3.14)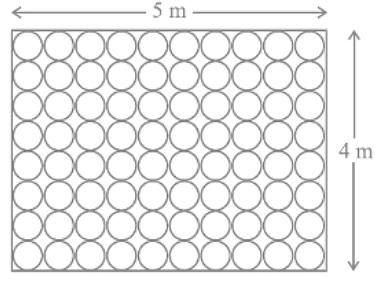
Given, the floor of a room with dimensions 5 m × 4 m is covered with circular tiles of diameters 50 cm.
We have to find the area of the floor that remains uncovered with tiles.
Area of floor of a room = length × breadth
= 5 × 4
= 20 m²
Given, diameter of each circular tile = 50 cm
Number of tiles in each row = 5m/50cm
1 m = 100 cm
= 500/50
= 10
Number of tiles in each column = 4m/50cm
= 400/50
= 8
Total number of tiles in the floor = 10 × 8 = 80
Radius of tiles = 50/2 = 25 cm
r = 25/100
r = 0.25 m
Area of circle = πr²
Area of circular tile = (3.14)(0.25)²
= 0.19625 m²
Area of 80 tiles = 80(area of one tile)
= 80(0.196)
= 15.7 m²
Area of the floor that remains uncovered with the tiles = area of floor - area of 80 tiles
= 20 - 15.7
= 4.3 m²
Therefore, the area of the floor that remains uncovered with the tiles is 4.3 m².
Q.12. All the vertices of a rhombus lie on a circle. Find the area of the rhombus, if area of the circle is 1256 cm2 . (Use π = 3.14)
Given, all the vertices of a rhombus lie on a circle.
Area of the circle = 1256 cm²
We have to find the area of the rhombus.
All the vertices of a rhombus lie on a circle. Find the area of the rhombus, if area of the circle is 1256 cm². (Use π = 3.14)
From the figure,ABCD is a rhombus whose vertices lie on a circle.d₁ and d₂ are the diagonals of the rhombus.
Area of circle = πr²
1256 = 3.14r²
r² = 1256/3.14
r² = 400
r = 20 cm
Therefore, the radius of the circle is 20 cm
Since all the vertices of the rhombus lie on the circle. The diagonal of the rhombus is equal to the diameter of the circle.
Diameter of circle = 2(20) = 40 cm
Area of rhombus = 1/2 × d₁ × d₂
= 1/2 × 40 × 40
= 20 × 40
= 800 cm²
Therefore, the area of rhombus is 800 cm²
Q.13. An archery target has three regions formed by three concentric circles as shown in Fig. 11.19. If the diameters of the concentric circles are in the ratio 1: 2:3, then find the ratio of the areas of three regions.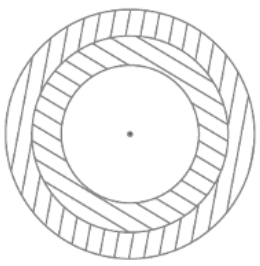
Given, an archery target has three regions formed by three concentric circles.
The diameters of the concentric circles are in the ratio 1:2:3
We have to find the ratio of the areas of three regions.
The diameter of the first circle = d
Radius = d/2
The diameter of the second circle = 2d
Radius = 2d/2 = d
The diameter of third circle = 3d
Radius = 3d/2
Area of circle = πr²
Area of first circle = π(d/2)²
= πd²/4
Area of second circle = πd²
Area of third circle = π(3d/2)²
= 9πd²/4
Area of the region enclosed between first and second circle = area of second circle - area of first circle
= πd² - πd²/4
= (4πd² - πd²)/4
= 3πd²/4
Area of the region enclosed between second and third circle = area of third circle - area of second circle
= 9πd²/4 - πd²
= (9πd² - 4πd²)/4
= 5πd²/4
Ratio of the areas of three regions = πd²/4 : 3πd²/4 : 5πd²/4
= 1 : 3 : 5
Therefore, the ratio of the areas of three regions is 1:3:5
Q.14. The length of the minute hand of a clock is 5 cm. Find the area swept by the minute hand during the time period 6 : 05 a m and 6 : 40 a m.
Time difference = (6 : 40 am – 6 : 05 am) = 35 min.
Time swept by min hand is 35 min.
Length of min. hand will be radius of circle swept.
∴ r = 5 cm
In 60 minutes time, area swept by min. hand = πr2
In 1 minute time, area swept by min. hand = πr2/60
In 35 minutes time, area swept by min. hand = πr2/60 × 35
∴ Required area swept by min. hand
Hence, the required area swept by him min. hand is
Q.15. Area of a sector of central angle 200° of a circle is 770 cm2. Find the length of the corresponding arc of this sector.
Let the radius of the sector AOBA be r.
Given: Central angle of sector AOBA = θ = 200∘
Area of the sector AOBA = 770 cm2 [Given]
We know that, area of the sector =
∴ Area of the sector, 770 =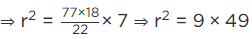
⇒ r = 3 × 7
∴ r = 21 cm
So, radius of the sector AOBA = 21 cm.
Now, the length of the corresponding arc of this sector
= Central angle × Radius [∵ θ = l/r]
Hence, the required length of the corresponding arc is
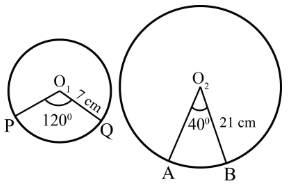
Q.16. The central angles of two sectors of circles of radii 7 cm and 21 cm are respectively 120° and 40°. Find the areas of the two sectors as well as the lengths of the corresponding arcs. What do you observe?
Let the lengths of the corresponding arc be l1 and l2
Given that, radius of sector PO1QP = 7 cm
And radius of sector AO2BA = 21 cm
And central angle of the sector AO2B A = 40∘
∴ Area of the sector with central angle O1and area of the sector with central angle
Now, corresponding arc length of the sector
Now, corresponding arc length of the sector AO2BA
Hence, we observe that arc lengths of two sectors of two different circles may be equal but their area need not be equal.
Q.17. Find the area of the shaded region given in Fig. 11.20.
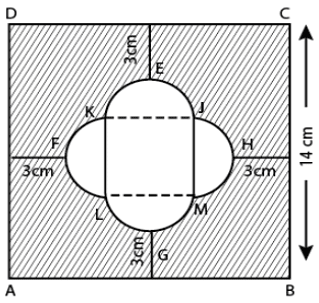
Join JK, KL, LM and MJ
There are four equal semi - circles and LMJK formed a square.
∴ FH = 14 – ( 3 +3 ) = 8cm
So, the side of square should be 4 cm and radius of semi - circle of both ends are 2 cm each.
∴ Area of square JKLM = (4) 2 = 16 cm2
Area of semi - circle HJM = πr2/2
∴ Area of four semi-circle = 4 × 2π cm2 = 8 πcm2
Now, area of square ABCD = (14)2 = 196 cm2
∴ Area of shaded region = Area of square ABCD - [Area of four semi-circle + Area of square JKLM]
= 196 − [8π + 16] = 196 − 16 − 8 π
= (180 − 8 π) cm2
Hence, the required of the shaded region is (180 − 8 π) cm.
Q.18. Find the number of revolutions made by a circular wheel of area 1 .54 m2 in rolling a distance of 176 m.
Given, area of circular wheel = 1.54 m²
Total distance covered by the wheel = 176 m
We have to find the number of revolutions made by a circular wheel.
Area of circle = πr²
1.54 = (22/7)r²
r² = 1.54(7)/22
r² = 0.07(7)
r² = 0.49
Taking square root,
r = 0.7 m
Circumference of the circle = 2πr
Circumference of the wheel = 2(22/7)(0.7)
= 44(0.1)
= 4.4 m
Number of revolutions = total distance / circumference
= 176/4.4
= 40
Therefore, the total number of revolutions made by the wheel is 40.
Q.19. Find the difference of the areas of two segments of a circle formed by a chord of length 5 cm subtending an angle of 90° at the centre.
Chord AB = 5 cm divides the circle in two segments minor segment APB and major segment AQB. We have to find out the difference in area of major and minor segment.
Here, θ = 90°
Area of ΔOAB = 1/2 Base × Altitude = 1/2r × r = 1/2r2Area of minor segment APB
Area of minor segment =
Area of major segment AQB = Area of circle – Area of minor segment
Area of major segment AQB =
Difference between areas of major and minor segment
In right angle ΔOAB , r2 + r2 = AB2
⇒ 2r2 = 52
⇒ r2 =25/2
So, required area =
Q.20. Find the difference of the areas of a sector of angle 120° and its corresponding major sector of a circle of radius 21 cm.
Given, central angle = 120°
Radius of circle = 21 cm
We have to find the difference between the areas of a sector and corresponding major sector of a circle.Find the difference of the areas of a sector of angle 120° and its corresponding major sector of a circle of radius 21 cmConsidering circle with radius 21 cm
Area of circle = πr²
= (22/7)(21)²
= 1386 cm²
Considering sector AOBA
Area of a sector = πr²θ/360°
Area of minor sector AOBA = (22/7)(21)²(120°/360°)
= (22)(3)(21)(1/3)
= (22)21
= 462 cm²
Area of major sector = area of circle - area of minor sector
= 1386 - 462
= 924 cm²
Area of major sector and its corresponding major sector ABOA = area of major sector - area of minor sector
= 924 - 462
= 462 cm²
Therefore, the difference between the areas of a sector and corresponding major sector of a circle is 462 cm²