Magnetisation & Magnetic Intensity | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Magnetization, also termed as magnetic polarization, is a vector quantity that gives the measure of the density of permanent or induced dipole moment in a given magnetic material. As we know, magnetization results from the magnetic moment, which results from the motion of electrons in the atoms or the spin of electrons or the nuclei. The net magnetization results from the response of a material to the external magnetic field, together with any unbalanced magnetic dipole moment that is inherent in the material due to the motion in its electrons as mentioned earlier. The concept of magnetization helps us in classifying the materials on the basis of their magnetic property. In this section, we will learn more about magnetization and the concept of magnetic intensity.
What is Magnetization?
The magnetization of a given sample material M can be defined as the net magnetic moment for that material per unit volume.
Mathematically,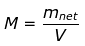
Let us now consider the case of a solenoid. Let us take a solenoid with n turns per unit length and the current passing through it be given by I, then the magnetic field in the interior of the solenoid can be given as,
B0 = μ0nl
Now, if we fill the interior with the solenoid with a material of non-zero magnetization, the field inside the solenoid must be greater than before. The net magnetic field B inside the solenoid can be given as,
B = B0 + Bm
Where Bm gives the field contributed by the core material. Here, Bm is proportional to the magnetization of the material, M. Mathematically,
Bm = μ0M
Here, µ0 is the constant of permeability of a vacuum.
Let us now discuss another concept here, the magnetic intensity of a material. The magnetic intensity of a material can be given as,
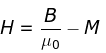
From this equation, we see that the total magnetic field can also be defined as,
B =μo(H+M)
Here, the magnetic field due to the external factors such as the current in the solenoid is given as H and that due to the nature of the core is given by M. The latter quantity, that is M is dependent on external influences and is given by,
M = χH
Where χ is the magnetic susceptibility of the material. It gives the measure of the response of a material to an external field. The magnetic susceptibility of a material is small and positive for paramagnetic materials and is small and negative for diamagnetic materials.
B=μ0(1+X)H=μ0μrH= μH
Here, the term µr is termed as the relative magnetic permeability of a material, which is analogous to the dielectric constants in the case of electrostatics. We define the magnetic permeability as,
μ=μ0μr=μ0(1+X)
|
289 videos|635 docs|184 tests
|
FAQs on Magnetisation & Magnetic Intensity - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is magnetisation and how does it relate to magnetic intensity? |  |
| 2. What factors affect the magnetisation of a material? |  |
| 3. How is magnetisation measured in a material? |  |
| 4. Can magnetisation be reversed or changed in a material? |  |
| 5. How does magnetisation play a role in magnetic materials and their applications? |  |






















