Mnemonics: Morphology of Flowering Plants | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Root System |

|
| Types of Root |

|
| Root Modifications |

|
| Shoot System |

|
| Stem Modifications |

|
| Leaf |

|
| Flower |

|
This document will help you remember important information about Morphology of Flowering Plants in a fun and easy way. Inside, you'll find mnemonics—memory tricks—that will make it easier for you to remember key concepts, examples related to Morphology of Flowering Plants.
Whether you're studying for an exam, preparing for a quiz, or simply looking to enhance your understanding of Morphology of Flowering Plants, these mnemonics will serve as valuable memory tools. Utilize them alongside your regular study routine to reinforce your knowledge and increase your recall ability.
Happy mnemonic learning!
Root System
A seed consists of a plumule and a radicle. While plumule gives rise to the shoot system of plants, radicle gives rise to the root system of plants. The roots invade into the soil and thus to protect the root tip from damage, a root cap is found on the root tip. It is a thimble-like structure that protects the root from damage while invading the hard surface of soil.
The root can be divided into three regions:
- Region of Meristematic Activity: It consists of actively dividing meristematic cells.
- Region of Elongation: The meristematic cells stop dividing and start elongating their vacuoles to accommodate more space and increase the length of root.
- Area of Maturation: In this area, the epidermal cells give rise to root hair which increases the surface area for better absorption of water and minerals through the root.
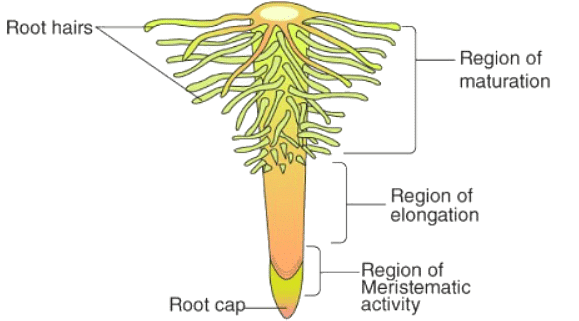
Types of Root
There are three types of root systems:
- Tap Root: The primary, secondary and tertiary roots that arise at first from the radicle are known as tap roots. They are commonly found in dicots.
- Fibrous Root: In many plants, the tap root is short lived. Instead it gives rise to thin fibre-like roots that are known as fibrous roots. They do not have a strong primary root like tap roots. They are seen in some monocots.
- Adventitious Root: The roots that arise from any other part of the plant except the roots are called adventitious roots. They are commonly seen in monocots.
Let us now see a mnemonic to remember the examples of types of roots:
Mnemonic: A Goat and Monkey Became Friends With The Man.
- A: Adventitious Roots
- G: Grass
- M: Monstera
- B: Banyan
- F: Fibrous Roots
- W: Wheat
- T: Tap Roots
- M: Mustard
Root Modifications
The tap roots modify themselves for storage and respiration purposes, whereas the adventitious roots can also modify them for storage and also mechanical support.
Tap Root Examples: Carrot forms conical roots for storage purposes. The root is broad at the surface but tapers at the end. Radish forms fusiform roots that are swollen in the middle and tapering at both ends for storage purposes. Turnip forms napiform roots that are very broad (almost spherical) at the base and fibre-like thin at the ends. Mangrove trees or Rhizophora have pneumatophores that are pores on roots that help in respiration.
Adventitious Root Examples: Sweet potato forms tuberous roots for storage. Banyan trees have prop roots that arise from the stem and give mechanical support to the plant. Maize forms stilt roots that arise from the base of the stem and also give mechanical support to the plant.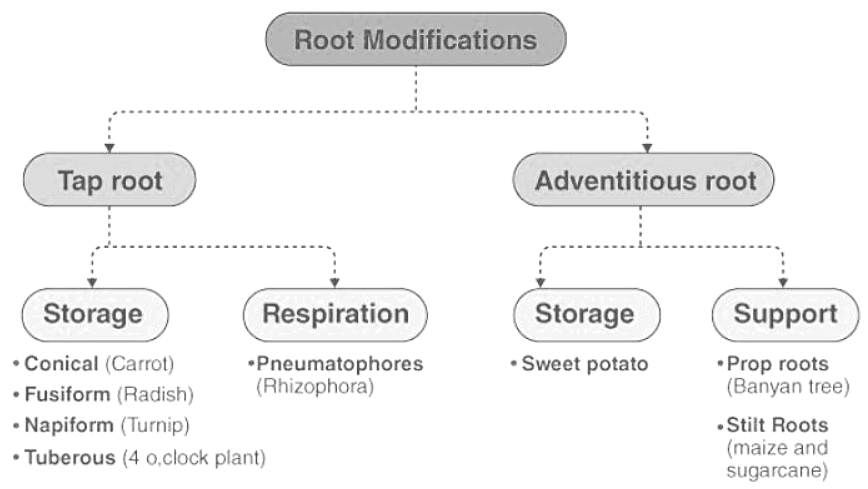
Mnemonics to remember the examples:
Mnemonics:
- She Cuts The Sheet
- SMS
She Cuts The Sheet
- S: Storage
- C: Carrot
- T: Turnip
- S: Sweet potato
SMS
- S: Support
- M: Maize
- S: Sugarcane
Shoot System
The shoot develops from the plumule of the seed. A shoot or stem is made up of nodes and internodes. Space between two nodes is called an internode. Leaves arise from the nodes. The basic function of the stem is to keep the plant erect but it undergoes a number of modifications to fulfill other functions as well.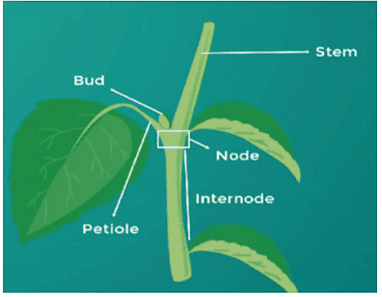
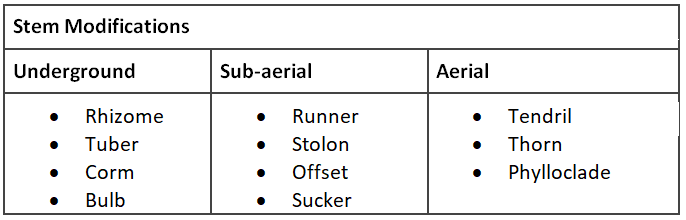
Stem Modifications
Underground Stem Modifications with Examples: Underground stems modify for food storage purposes that are mainly used by humans for eating. For example, Ginger (rhizome), Potato (Tuber), Colocasia (Corm) and Onion (Bulb).
Mnemonic: Uma Fooled Sunny and ate Pie, Garlic bread, Tacos with Zucchini and Custard.
- U: Underground
- F: Food storing
- S: Stem
- P: Potato
- G: Ginger
- T: Turmeric
- Z: Zaminkand
- C: Colocasia
Sub Aerial Stem Modifications: Sub aerial stem modifications are partially below and partially above the ground. Examples of such modifications include mint, jasmine (stolon), Eicchornia, Pistia (offset), strawberry (runner) and pineapple, Chrysanthemum, banana (sucker).
Mnemonics:
- One Egg Please (Offset: Eicchornia, Pistia)
- She Made Jam (Stolon: Mint, Jasmine)
- Sweet Pancakes with Cream and Butter (Sucker: Pineapple, Chrysanthemum, Banana)
Aerial Stem Modifications: Tendrils are aerial stem modifications that are formed from axillary buds. They are slender and coil spirally to help the plant climb. (Eg., cucumber, watermelon and pumpkin). Thorns are modifications of axillary buds of stems that develop into a straight, pointed and woody structure to protect the plants from animals. (Eg., Citrus, Bougainvillaea). Lastly, phylloclade is an important modification that shows both leaf and stem modification. Leaf gets modified into the spine and thus the stem takes over the function of photosynthesis and storage and becomes swollen (Eg., Cactus, Opuntia).
Mnemonics:
- Cool People With Gadgets (Tendril: Cucumber, Pumpkin, Watermelon, Grapevines)
- Tom Cried like a Baby (Thorn: Citrus, Bougainvillaea)
- Photosynthesis (Phylloclade: Opuntia, Euphorbia)
Leaf
A leaf arises from the nodes of a stem. It consists of a midrib from which the veins and veinlets arise. It is attached at the node by leaf base and flutters in the air on a thin structure called petiole. The broad, flat and expanded part of the leaf is called the lamina.
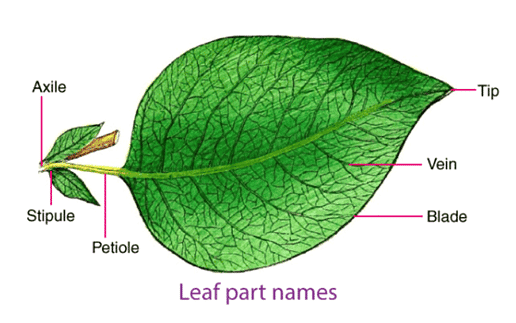
Types of Leaf
The leaves are of two types based on the division of lamina:
- Simple Leaf: A leaf which does not show any incisions near the midrib is called a simple leaf. In cases when the leaves are incised, it does not touch the midrib and does not form leaflets.
- Compound Leaf: When a leaf shows incisions touching the midrib such that it creates leaflets, it is known as a compound leaf. Compound leaves are of two types:
- Palmately Compound: When the leaflets arise from a common point, it is known as palmately compound leaf.
- Pinnately Compound: When the leaflets arise from a common axis, it is known as pinnately compound leaf.
Phyllotaxy
The arrangement of leaves on an axis or stem is termed as phyllotaxy. It is of three types:
- Alternate: When the leaves are present alternatively on either side of the stem, it is known as alternate phyllotaxy. E.g, Hibiscus
- Opposite: When two leaves are present on a single node on either side of the stem, it is known as opposite phyllotaxy. E.g, Calotropis, guava
- Whorled: If there are more than one leaf present at a common point, it is known as whorled phyllotaxy. E.g., Alstonia
Mnemonics:
- All – Must See Cell (A: Alternate – Mustard, Sunflower, Chinarose
- One Chicken Gravy (O: Opposite – Calotropis, Guava)
- WAll: Whorled – Alstonia
Leaf Modifications
- Tendril: It is a spirally-coiled structure that helps the plant in climbing. E.g., Pea
- Storage Leaves: Leaves that become fleshy for storage purposes. E.g., Garlic
- Spines: Spines are modified leaves that protect the plant from grazing herbivores. E.g., Cactus
- Carnivorous Leaves: The leaves that can trap and prey on insects to fulfil their nitrogen requirements are called carnivorous leaves. E.g., Pitcher plant
- Phyllode: When the leaves are short lived, the petiole region gets modified and becomes swollen called phyllode. E.g., Acacia
Flower
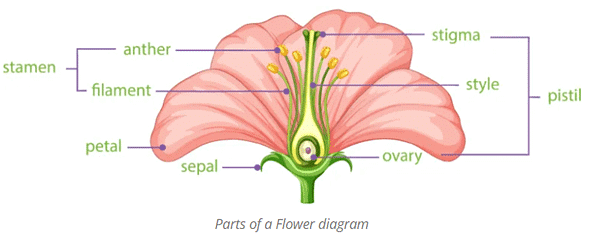
Flower is a modified shoot. Four floral whorls are found in a flower:
- Calyx: whorl of sepals
- Corolla: whorl of petals
- Androecium: male sex organs (stamen)
- Gynoecium: female sex organ (pistil)
Note: Both androecium and gynoecium are essential whorls as they are reproductive parts of the flower, whereas calyx and corolla are non-essential whorls.
Calyx
It is the outermost whorl of the flower. It is made up of leaf-like structures called sepals. When the flower is in its budding stage, calyx provides protection to the bud from the external environment. It is represented by the letter K in floral diagrams.
If there are five fused sepals, it is known as gamosepalous and is denoted by K(5). If there are 5 free sepals, it is known as polysepalous and is denoted by K5.
Corolla
A whorl of brightly coloured petals is known as corolla. It functions to attract insects for pollination. It is denoted by letter C in floral diagrams.
If there are five fused petals, it is known as gamopetalous and is denoted by C(5). If there are five free petals, it is known as polypetalous and is denoted by C5.
 |
Download the notes
Mnemonics: Morphology of Flowering Plants
|
Download as PDF |
Perianth
It is a condition where the sepals and petals are fused together and known as tepals. The whorl of tepals is known as perianth. It is commonly seen in monocots. It is represented by the letter P in floral diagrams.
Inflorescence
The arrangement of flowers on a branch or axis of stem is known as inflorescence. It is of two types:
- Racemose: This type of inflorescence shows indefinite growth on the floral axis because older flowers are the bottom and younger ones keep growing on the apex. This type of flower arrangement is called acropetal.
- Cymose: An arrangement that shows definite growth of flowers where the floral axis terminates into a flower is known as cymose inflorescence. It shows basipetal arrangement of flowers where older flowers are found at the apex.
Aestivation
The arrangement of sepals or petals in the floral bud with respect to other whorls of the same flower is called aestivation. It is of four types:
- Valvate: In this type of aestivation, the sepals or petals do not touch each other at the margin.
- Twisted: In this type, the sepals or petals overlap each other.
- Imbricate: This is also an overlapping arrangement of sepals or petals but in a specific manner such that two of the petals or sepals have both their margins on the inside.
- Vexillary: It is a unique arrangement where a bigger sepal or petal covers smaller petals or sepals.
Mnemonics
- Velvet Chair (V: Valvate – Calotropis)
- Chinese Lady Twisted her Cotton shirt (Twisted – China Rose, Ladyfinger, Cotton)
- Imran the Gully boy lost his Casio (Imbricate – Gulmohar, Cassia)
- V.P. of Britannia (V: Vexillary – Pea, Bean)
Flower Symmetry
- Actinomorphic: In this type, the flowers can be cut in any plane to get equal halves. It is represented by ⊕ in floral diagrams. Examples: mustard, datura, chilli.
- Zygomorphic: In this type, the flower can be cut only in one plane to get equal halves. It is represented by % in floral diagrams. Examples: gulmohar, cassia, pea and bean.
Androecium
- It is the male sex organ. The collective whorls of stamen are known as androecium. It is denoted by A in floral diagrams.
- Stamen is the male reproductive organ that is made up of three parts: anther (a bilobed structure), filament (stalk) and connective (a sterile tissue that connects anther lobes).
- When the stamen is fused to petals, it is known as epipetalous. Example: brinjal. When the stamens are attached to the perianth, it is known as epiphyllous. Example: Lily.
- When the filaments of stamen are free, it is known as polyandrous. Example: Lotus.
- When the filaments of stamen are fused, it is known as adelphous. The stamens may be fused in one bunch, called monadelphous. Example: China rose. The stamens might be fused in two bunches, known as diadelphous. Example: pea. The stamens might be fused in more than two bunches, known as polyadelphous. Example: lemon.
Gynoecium
- The whorl of pistils is known as gynoecium. It is the female sex organ. It is denoted by G in floral diagrams.
- The pistil is the female sex organ that is made up of thee parts: stigma (the receptive surface for pollen grains), ovary (the enlarged basal part that possesses ovules) and style (stalk that connects ovary to the stigma).
- When the carpels are free, it is known as apocarpous. Example: lotus. When the carpels are fused, it is known as syncarpous. Example: mustard.
- Hypogynous: It is a floral arrangement of whorls where the calyx, corolla and androecium are situated below the gynoecium, i.e., the ovary is superior.
- Perigynous: The calyx, corolla and androecium are situated at the same level at the rim of thalamus and the ovary is half inferior to the other whorls.
- Epigynous: The calyx, corolla and androecium are situated above the gynoecium, i.e., the ovary is superior.
Mnemonics
- Evil Saints Circulated Germs (E: Epigynous – Sunflower, Cucumber, Guava)
- Pretty Puppies Rest Peacefully (P: Perigynous – Plum, Rose, Peach)
- He Made Cheese Burgers (H: Hypogynous – Mustard, China rose, Brinjal)
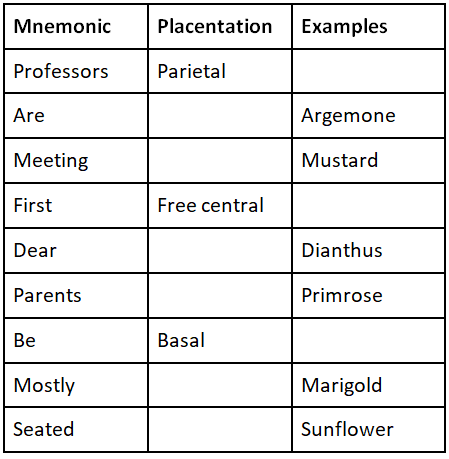
Placentation
Placentation is the arrangement of ovules within the ovary. There are five types of placentation known – axile, parietal, free central, basal and marginal placentation.
- In axile placentation, the ovules are attached in a multilocular ovary and the placenta is present axially.
- In parietal placentation, the ovules either develop on the periphery of the ovary or inner walls of the ovary.
- In free central placentation type the ovules are borne on the central axis and there is no septa in the ovary.
- In basal placentation, the placenta develops at the base of the ovary and only a single ovule is attached to it.
- Lastly, marginal placentation is characterised by the formation of a ridge by the placenta on the margins of which the ovules are borne.

|
180 videos|362 docs|148 tests
|


















