Conductors & Insulators | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Any object can be broadly classified in either of the following two categories on the basis of their electrical properties:
(i) Conductors
(ii) Insulators
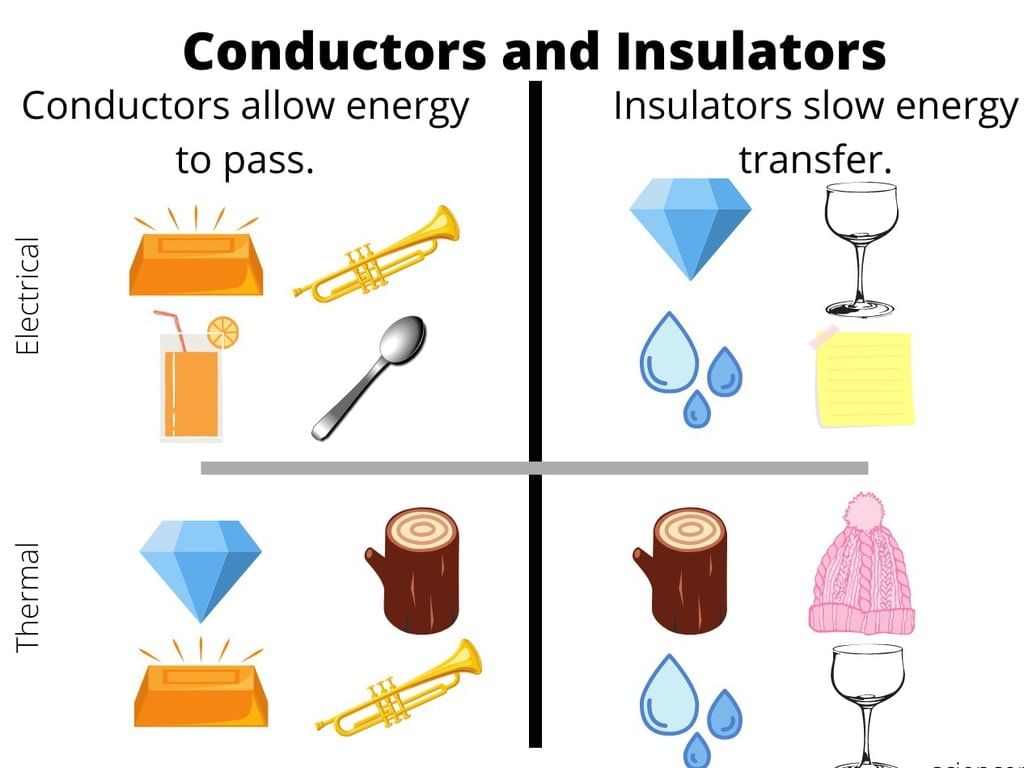
(i) Conductors: The materials or substances which allow electricity to flow through them are called Conductors. Conductors are able to conduct electricity because they allow electrons to flow inside them very easily.
The general property of conductor is to allow the transition of heat or light from one source to another. Metals, humans, earth and animal bodies fall in the category of conductors. This category generally comprises of metals but may sometimes contain non-metals too.
Example: Carbon in the form of graphite. Conductors have free electrons on its surface which allows current to pass through, that’s why conductors are able to conduct electricity.
APPLICATIONS OF CONDUCTORS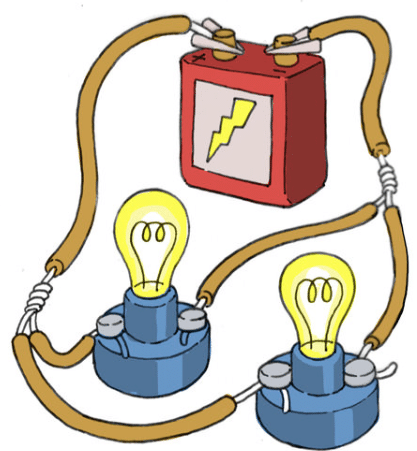
Fig: Use of conductors in lightning a bulb
Conductors are quite useful in many ways and used in many real life applications like:
- Mercury is used in thermometer to check temperature of body.
- Aluminium is used in making foils to store food and also in production of fry pans to store heat quickly.
- Iron is used in vehicle engine to conduct heat.
- The plate of an iron is made up of steel to absorb heat briskly.
- Conductors are used in car radiators to eradicate heat away from the engine.
 Fig: Insulators
Fig: Insulators
(ii) Insulators: The materials or substances which resist or don’t allow the current to flow through them are called Insulators. Insulators are mostly solid in nature and are used in a variety of systems. Insulators don’t allow the flow of heat as well.
The property which makes insulators different from conductors is its resistivity. Wood, cloth, glass, mica, and quartz are some good examples of insulators. Insulators are also called Protectors as they give protection against heat, sound and of course passage of electricity.
Insulators don’t have any electrons in its and that’s why insulators don’t conduct electricity.
Examples
- Glass is the best insulator as it has the highest resistivity.
- Plastic is a good insulator and is used in making number of things.
- Rubber which is used to make tyres, fire-resistant clothes and slipper is a very good insulator.
APPLICATIONS OF INSULATORS
 Fig: An insulator is used to protect wire opening
Fig: An insulator is used to protect wire opening
Being resistive to flow of electron, insulators are used worldwide in a number of ways.
Some are as follows
- Thermal Insulators, disallow heat to move from one place to another and is used in making thermoplastic bottles, in fireproofing ceilings and walls.
- Sound Insulators help in controlling noise level, as they are good in absorbance of sound and are used in buildings, conference halls, and buildings to make them noise free.
- Electrical Insulators, which hinders flow of electron or passage of current through them are extensively used in circuit boards, high-voltage systems and also in coating electric wire and cables.
|
297 videos|946 docs|172 tests
|
FAQs on Conductors & Insulators - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is the difference between conductors and insulators? |  |
| 2. Why are metals good conductors of electricity? |  |
| 3. How does the conductivity of a material affect its use as a conductor or insulator? |  |
| 4. What factors determine the conductivity of a material? |  |
| 5. Can insulators conduct electricity under certain conditions? |  |





















