NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Data Handling | Mathematics (Maths) Class 7 (Old NCERT) PDF Download
Exercise Page: 72
In Questions 1 to 16, there are four options, out of which only one is correct. Write the correct answer.
Q.1. Let x, y, z be three observations. The mean of these observations is
(a) (x × y × z)/3
(b) (x + y + z)/3
(c) (x – y – z)/3
(d) (x × y + z)/3
Ans: (b)
Explanation: The average or Arithmetic Mean or mean of a given data is defined as Sum of all observations by the Number of observations.
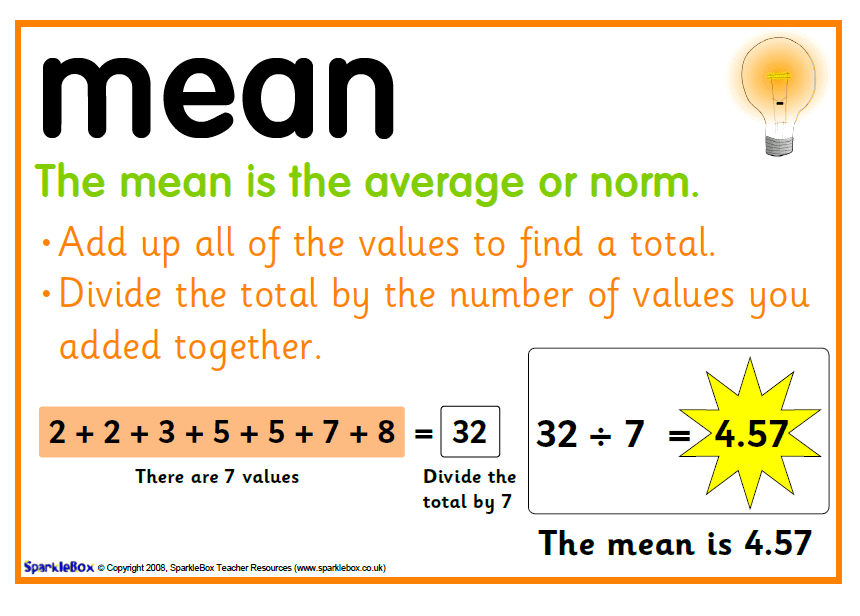 Mean of a dataQ.2. The number of trees in different parks of a city are 33, 38, 48, 33, 34, 34, 33 and 24. The mode of this data is
Mean of a dataQ.2. The number of trees in different parks of a city are 33, 38, 48, 33, 34, 34, 33 and 24. The mode of this data is
(a) 24
(b) 34
(c) 33
(d) 48
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Mode is the observation that occurs most frequently in the data.
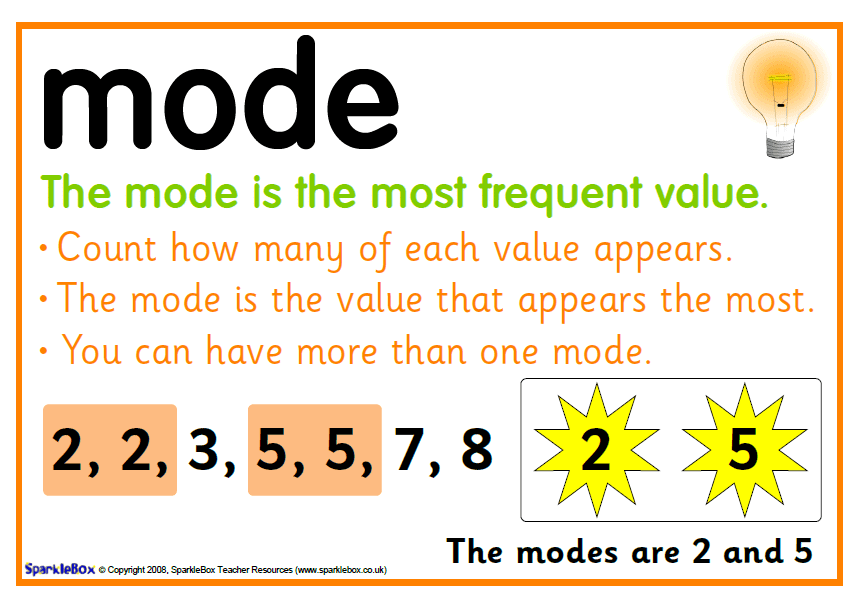 Mode of a dataQ.3. Which measures of central tendency get affected if the extreme observations on both the ends of a data arranged in descending order are removed?
Mode of a dataQ.3. Which measures of central tendency get affected if the extreme observations on both the ends of a data arranged in descending order are removed?
(a) Mean and mode
(b) Mean and Median
(c) Mode and Median
(d) Mean, Median and Mode
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Removing extreme values affects the mean (as it depends on all data points) and may affect the median if the number of observations is small. The mode is unaffected unless the extreme value is the mode itself.
Q.4. The range of the data: 21, 6, 17, 18, 12, 8, 4, 13 is
(a) 17
(b) 12
(c) 8
(d) 15
Ans: (a)
Explanation: The difference between the highest and lowest observations in a given data is called its Range.
Range = Highest – lowest
= 21 – 4
= 17
Q.5. The median of the data: 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 3, 4 is
(a) 5
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 6
Ans: (c)
Explanation: When the given data is arranged in ascending (or descending) order, then the middle most observation is the median of the data.
So, now arrange the given observation into ascending order 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 7
Therefore, 4 is the middle most observation and it is the median of the data.
Q.6. Out of 5 brands of chocolates in a shop, a boy has to purchase the brand which is most liked by children. What measure of central tendency would be most appropriate if the data is provided to him?
(a) Mean
(b) Mode
(c) Median
(d) Any of the three
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Mode is the observation that occurs most frequently in the data.
Q.7. There are 2 aces in each of the given set of cards placed face down. From which set are you certain to pick the two aces in the first go?
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans: (c)
Explanation: The probability of picking the two aces in the first go is in option (c).
Q.8. In the previous question, what is the probability of picking up an ace from set (d)?
(a) 1/6
(b) 2/6
(c) 3/6
(d) 4/6
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Probability of picking up an ace from set = Number of ace in the set/ Total number of cards in the set.
Q.9. The difference between the highest and the lowest observations in a data is its
(a) frequency
(b) width
(c) range
(d) mode
Ans: (c)
Q.10. In a school, only 2 out of 5 students can participate in a quiz. What is the chance that a student picked at random makes it to the competition?
(a) 20%
(b) 40%
(c) 50%
(d) 30%
Ans: (b)
Explanation: From the question it is given that, in a school, only 2 out of 5 students can participate in a quiz.
So, the chance that a student picked at random = 2/5
Then percentage = 2/5 × 100
= 0.4 × 100
= 40 %
Q.11. Some integers are marked on a board. What is the range of these integers?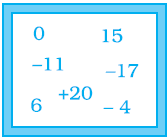
(a) 31
(b) 37
(c) 20
(d) 3
Ans: (b)
Explanation: The difference between the highest and lowest observations in a given data is called its Range.
Range = Highest – lowest
= 20 – (- 17)
= 20 + 17
= 37
Q.12. On tossing a coin, the outcome is
(a) only head
(b) only tail
(c) neither head nor tail
(d) either head or tail
Ans: (d)
Q.13. The mean of three numbers is 40. All the three numbers are different natural numbers. If lowest is 19, what could be highest possible number of remaining two numbers?
(a) 81
(b) 40
(c) 100
(d) 71
Ans: (a)
Explanation: From the question it is given that,
The mean of three numbers is 40.
Lowest number = 19
Let us assume the other two numbers be P, Q.
Then,
Mean = (P + Q + 19)/3
40 = (P + Q + 19)/3
By cross multiplication we get,
120 = P + Q + 19
120 – 19 = P + Q
Then, P + Q = 101
So, 81 + 20 = 101
Therefore, the highest number is 81
Q.14. Khilona earned scores of 97, 73 and 88 respectively in her first three examinations. If she scored 80 in the fourth examination, then her average score will be
(a) increased by 1
(b) increased by 1.5
(c) decreased by 1
(d) decreased by 1.5
Ans: (d)
Explanation: From the question,
Khilona earned scores in 3 exam = 97, 73, 88
Then, Mean = (97 + 73 + 88 +)/3
Mean = 86 marks
Khilona earned scores in 4 exam = 97, 73, 88, 80
Then, Mean = (97 + 73 + 88 + 80)/4
Mean = 84.5 marks
Then, her average score will be 86 – 84.5 = 1.5, decreased by 1.5
Q.15. Which measure of central tendency best represents the data of the most popular politician after a debate?
(a) Mean
(b) Median
(c) Mode
(d) Any of the above
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Mode is the observation that occurs most frequently in the data.
Q.16. Which of the following has the same mean, median and mode?
(a) 6, 2, 5, 4, 3, 4, 1
(b) 4, 2, 2, 1, 3, 2, 3
(c) 2, 3, 7, 3, 8, 3, 2
(d) 4, 3, 4, 3, 4, 6, 4
Ans: (d)
Explanation: Mean of the given data = (4 + 3 + 4 + 3 + 4 + 6 + 4)/7
= 4
Mode is the observation that occurs most frequently in the data i.e. 4.
When the given data is arranged in ascending (or descending) order, then the middle most observation is the median of the data.
Arranging the given data, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 6.
So, the median is 4.
In Questions 17 to 31, fill in the blanks to make the statements true.
Q.17. The difference between the highest and the lowest observations of a data is called _________.
Solution: The difference between the highest and the lowest observations of a data is called range.
Q.18. The mean of a data is defined as _________.
Solution: The average or Arithmetic Mean or mean of a given data is defined as Sum of all observations by the Number of observations.
Q.19. In a set of observations, the observation that occurs the most often is called _________.
Solution: Mode
Mode is the observation that occurs most frequently in the data.
Q.20. In a given data, arranged in ascending or descending order, the middle most observation is called _________.
Solution: Median.
When the given data is arranged in ascending (or descending) order, then the middle most observation is the median of the data.
Q.21. Mean, Median, Mode are the measures of _________.
Solution: Central tendency
Mean, median and mode are the representative values of a group of observations. They are also called the measures of central tendency of the data.
Q.22. The probability of an event which is certain to happen is _________.
Solution: The probability of an event which is certain to happen is 1.
Q.23. The probability of an event which is impossible to happen is _________.
Solution: The probability of an event which is impossible to happen is 0.
Q.24. When a die is thrown, the probability of getting a number less than 7 is _________.
Solution: When a die is thrown, the probability of getting a number less than 7 is 1.
Let us assume that 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 are the possible outcomes when the die is thrown.
Probability of getting a number less than 7 = Number less than 7/number of sides in die.
= 6/6
= 1
Q.25. In throwing a die the number of possible outcomes is _________.
Solution: In throwing a die the number of possible outcomes is 6.
Q.26. _________ can be used to compare two collections of data.
Solution: A double bar graph can be used to compare two collections of data.
Q.27. The representation of data with bars of uniform width is called _________.
Solution: The representation of the data in the form of rectangles (bars) of uniform width is called a bar graph.
Q.28. If the arithmetic mean of 8, 4, x, 6, 2, 7 is 5, then the value of x is _________.
Solution: If the arithmetic mean of 8, 4, x, 6, 2, 7 is 5, then the value of x is 3.
Q.29. The median of any data lies between the _________ and _________ observations.
Solution: The median of any data lies between the minimum and maximum observations.
30. Median is one of the observations in the data if number of observations is _________.
Solution: Median is one of the observations in the data if number of observations is odd.
Q.31. Rohit collected the data regarding weights of students of his class and prepared the following table: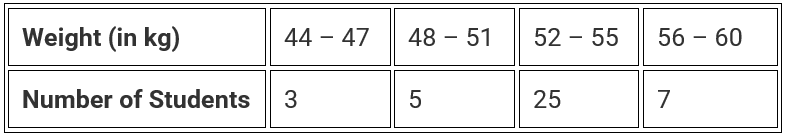
A student is to be selected randomly from his class for some competition. The probability of selection of the student is highest whose weight is in the interval.
Solution: A student is to be selected randomly from his class for some competition. The probability of selection of the student is highest whose weight is in the interval 52 – 55.
Because, more number of students comes under this interval.
In Questions 32 to 49, state whether the statements are True or False.
Q.32. If a die is thrown, the probability of getting a number greater than 6 is 1.
Solution: False.
The possible outcomes when the die is thrown are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6.
Q.33. When a coin is tossed, there are 2 possible outcomes.
Solution: True.
When a coin is tossed, there are 2 possible outcomes i.e. either Head (H) or Tail (T).
Q.34. If the extreme observations on both the ends of a data arranged in ascending order are removed, the median gets affected.
Solution: False.
When the given data is arranged in ascending (or descending) order, then the middle most observation is the median of the data.
So, if the extreme observations on both the ends of a data arranged in ascending order are removed, the median is not affected.
Q.35. The measures of central tendency may not lie between the maximum and minimum values of data.
Solution: False.
The measures of central tendency lies between the maximum and minimum values of data.
Q.36. It is impossible to get a sum of 12 of the numbers on both dice when a pair of dice is thrown together.
Solution: True.
The possible outcomes when the die is thrown are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6.
If both dice get 6, then sum of the number is 12.
Q.37. The probability of the spinning arrow stopping in the shaded region is ½.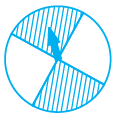
Solution: True.
Probability of spinning arrow stopping in the shaded region = Number of shaded part in circle/total number of parts
= 2/4
= ½
Q.38. A coin is tossed 15 times and the outcomes are recorded as follows:
H T T H T H H H T T H T H T T. The chance of occurence of a head is 50 per cent.
Solution: False.
The chance of occurence of a head = occurence of a head /total number of trials
= 7/15 × 100
= 46.6 %
Q.39. Mean, Median and Mode may be the same for some data.
Solution: True.
Let us consider the data 4, 3, 4, 3, 4, 6, 4
Mean of the given data = (4 + 3 + 4 + 3 + 4 + 6 + 4)/7
= 4
Mode is the observation that occurs most frequently in the data i.e. 4.
When the given data is arranged in ascending (or descending) order, then the middle most observation is the median of the data.
Arranging the given data, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, and 6.
So, the median is 4.
Q.40. The probability of getting an ace out of a deck of cards is greater than 1.
Solution: False.
The probability of getting an ace out of a deck of cards is less than 1.
Q.41. Mean of the data is always from the given data.
Solution: False.
The average or Arithmetic Mean or mean of a given data is defined as Sum of all observations by the Number of observations.
Q.42. Median of the data may or may not be from the given data.
Solution: True.
When the given data is arranged in ascending (or descending) order, then the middle most observation is the median of the data.
Q.43. Mode of the data is always from the given data.
Solution: True.
Mode is the observation that occurs most frequently in the data.
Q.44. Mean of the observations can be lesser than each of the observations.
Solution: False.
Q.45. Mean can never be a fraction.
Solution: False.
Q.46. Range of the data is always from the data.
Solution: False.
The difference between the highest and lowest observations in a given data is called its range.
Q.47.
The data 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 has every observation as mode.
Solution: True
Data is 12, 13, 14, 15, 16
Since, every observation occurs one time.
∴ Every observation can taken as mode.
Q.48. The range of the data 2,-5, 4, 3, 7, 6 would change if 2 was subtracted from each value in the data.
Solution: False
Data is 2, -5, 4, 3, 7, 6
Range = Highest value – Lowest value = 7 – (-5) = 7 + 5 = 12
After subtracting 2 from each value, data becomes 0, -7, 2, 1, 5, 4
Now, range = Highest value – Lowest value = 5 – (-7) – 5 + 7 = 12
Hence, in both cases range is same.
Q.49. The range of the data 3, 7, 1, -2, 2, 6, -3, -5 would change if 8 was added to each value in the data.
Solution:
False
Data is 3, 7, 1,-2, 2, 6, -3, -5
Range = Highest value – Lowest value = 7 – (-5) = 12
After adding 8 to each value, data becomes 11, 15, 9, 6, 10, 14, 5, 3
∴ Range = Highest value – Lowest value = 15 – 3 = 12
Hence, in both cases range is same.
Q.50. Calculate the Mean, Median and Mode of the following data:
5, 10, 10, 12, 13.
Are these three equal?
Solution: Data is 5, 10, 10, 12, 13
Since, 10 occurs most frequently i.e., two times.
∴ Mode = 10
Observations are odd in number.
∴ Median = Middle most observation i.e., 3rd observation
∴ Median = 10
Mean = Median = Mode = 10
Yes, these three are equal.
Q.51.
Find the mean of the first ten even natural numbers.
Solution:
First ten even natural numbers are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20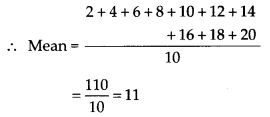
Q.52. A data constitutes of heights (in cm) of 50 children. What do you understand by mode for the data?
Solution: Mode is the height that occurs most frequently in the set of heights of 50 children.
Q.53.
A car seller collects the following data of cars sold in his shop.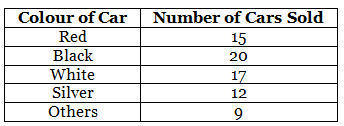
(a) Which colour of the car is most liked?
(b) Which measure of central tendency was used in (a)?
Solution:
(a) Black colour of car is most liked because number of cars sold of black car is greatest.
(b) Mode is used in (a) part.
Q.54. The marks in a subject for 12 students are as follows: 31, 37, 35, 38, 42, 23, 17, 18, 35, 25, 35, 29 For the given data, find the
(a) Range
(b) Mean
(c) Median
(d) Mode
Solution: Arranging the data in ascending order, we get 17, 18, 23, 25, 29, 31, 35, 35, 35, 37, 38, 42
(a) Range – Highest value – Lowest value = 42 – 17 = 25
(c) Observations are even in number.
∴ Median = Mean of two middle most observations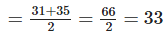
(d) Since, 35 occurs most frequently i.e., 3 times.
∴ Mode = 35.
Q.55. The following are weights (in kg) of 12 people.
70, 62, 54, 57, 62, 84, 75, 59, 62, 65, 78, 60
(a) Find the mean of the weights of the people.
(b) How many people weigh above the mean weight?
(c) Find the range of the given data.
Solution: Arranging the data in ascending order, we get
54, 57, 59, 60, 62, 62, 62, 65, 70, 75, 78, 84
(b) Since, mean = 65.6 kg
∴ 4 people have weight above mean weight.
(c) Range = Highest weight – Lowest weight
= (84 – 54) kg = 30 kg
Q.56. Following cards are put facing down: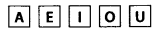
What is the chance of drawing out
(a) a vowel
(b) A or
(c) a card marked U
(d) a consonant
Solution:
Total cards = 5
(a) Here, all cards are vowel.
∴ Chance of drawing out a vowel is 1.
(b) Chance of drawing out a card marked A or I =2/5
(c) Since, one card has marked U.
∴ Chance of drawing out a card marked U is =1/5
(d) Since, there is no consonant.
∴ Chance of drawing out a consonant is 0.
Q.57. For the given data given below, calculate the mean of its median and mode.
6, 2, 5, 4, 3, 4, 4, 2, 3
Solution: Arranging the data in a ascending order, we get
2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 5, 6
Since, observations are odd in number.
∴ Median = Middle most observation = 4
Since, 4 occurs most frequently i.e., 3 times
∴ Mode = 4
Now, mean of median and mode is given by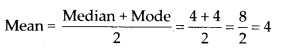
Q.58. Find the median of the given data if the mean is 4.5.
5, 7, 7, 8, x, 5, 4, 3, 1, 2
Solution:
The data is 5, 7, 7, 8, 1,5, 4, 3, 1, 2
⇒ 45 = x + 42
⇒ x = 45 – 42 =3
Now, arranging the data in ascending order, we get
1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5, 7, 7, 8
Since, observations are even in number.
∴ Median = Mean of two middle most observations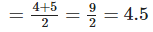
Q.59. What is the probability of the sun setting tomorrow?
Solution:
It is certain that sun setting every evening
∴ Probability of sun setting tomorrow is 1.
Q.60. When a spinner with three colours (see figure) is rotated, which colour has more chance to show up with arrow than the others?
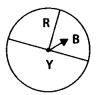
Solution:
Colour Y has more chance to show up with arrow than the others because Y has more region than both colours B and R.
Q.61. What is the probability that a student chosen at random out of 3 girls and 4 boys is a boy?
Solution: Total number of students 3 + 4 = 7
Total number of boys = 4
∴ Probability (student chosen is a boy) =4/7
Q.62. The letters written on paper slips of the word MEDIAN are put in a bag. If one slip is drawn randomly, what is the probability that it bears the letter D?
Solution: Total letters in the word MEDIAN = 6 D occurs only at once.
∴ Probability (Drawn slip bears the letter D) =1/6
Q.63. Classify the following events as certain to happen, impossible to happen, may or may not happen:
(a) Getting a number less than 1 on throwing a die.
(b) Getting head when a coin is tossed.
(c) A team winning the match.
(d) Christmas will be on 25 December.
(e) Today moon will not revolve around the earth.
(f) A ball thrown up in the air will fall down after some time.
Solution:
(a) Since, no number is less than 1 on a die.
∴Getting a number less than 1 on throwing a die is impossible to happen.
(b) When a coin is tossed two outcomes are possible i.e., Head or Tail.
∴ Getting head when a coin is tossed may or may not happen.
(c) A team winning the match may or may not happen because a team can lose the match.
(d) Christmas will be on 25 December is certain to happen.
(e) Since, moon always revolves around the earth.
∴Today moon will not revolve around the earth is impossible to happen.
(f) A ball thrown up in the air will fall down after some time is certain to happen due to gravity of earth.
Q.64. A die was thrown 15 times and the outcomes recorded were 5, 3, 4, 1, 2, 6, 4, 2, 2, 3, 1, 5, 6, 1, 2 Find the mean, median and mode of the data.
Solution: Arranging the data in ascending order, we get
1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 6, 6
Since, observations are odd in number,
∴ Median = Middle most observation i.e., 8th observation = 3
Since, 2 occurs most frequently i.e., 4 times
∴ Mode = 2
Q.65. Find the mean of the first six multiples of 4.
Solution: First six multiples of 4 are 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24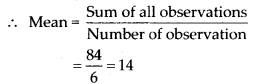
Q.66. Find the median of the first nine even natural numbers.
Solution: First nine even natural numbers are
2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18
Since, observations are odd in number.
∴ Median = Middle most observation i.e., 5th observation = 10
Q.67. The mean of three numbers is 10. The mean of other four numbers is 12. Find the mean of all the numbers.
Solution: Mean of 3 numbers = 10
Mean of 4 numbers = 12
⇒ Sum of 3 observations = 30 —— (1)
⇒ Sum of 4 observations = 48 ——- (2)
From (1) and (2), we get
Sum of 7 observations = 30 + 48 = 78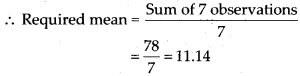
Q.68. Find the mode of the given data:
10, 8, 4, 7, 8, 11, 15, 8, 4, 2, 3, 6,8
Solution: Arranging the data in ascending order, we get
2, 3, 4, 4, 6, 7, 8, 8, 8, 8, 10, 11, 15
Since, 8 occurs most frequently in the data
i.e., 4 times. ∴Mode – 8
Q.69. Given below are heights of 15 boys of a class measured in cm:
128, 144, 146, 143, 136, 142, 138, 129, 140, 152, 144, 140, 150, 142, 154.
Find
(a) The height of the tallest boy.
(b) The height of the shortest boy.
(c) The range of the given data.
(d) The median height of the boys.
Solution: Arranging the heights in ascending order, we get
128, 129, 136, 138, 140, 140, 142, 142, 143, 144, 144, 146, 150, 152, 154
(a) Height of the tallest boy is 154 cm.
(b) Height of the shortest boy is 128 cm.
(c) Range = Highest value – Lowest value
= (154 – 128) cm = 26 cm
(d) Since, observations are odd in number
∴ Median height = Middle most height = 142 cm
Q.70. Observe the data and answer the questions that follow:
16, 15, 16, 16, 8, 15, 17
(a) Which data value can be put in the data so that the mode remains the same?
(b) At least how many and which value(s) must be put in to change the mode to 15?
(c) What is the least number of data values that must be put in to change the mode to 17? Name them.
Solution: The data is 16, 15, 16, 16, 8, 15, 17 (a) Since, 16 occurs most frequently in the data i.e., 3 times.
∴ Mode = 16
15 occurs two times, therefore if 15 will be put in the data, mode would be changed.
Hence, 8 or 17 or 16 can be put in the data so that mode remain the same.
(b) 15 occurs two times, therefore mode will be 15 if 15 occurs atleast 4 times.
∴ Atleast two times 15 must be put into the data to change the mode to 15.
(c) 17 occurs only once in the data.
∴ Atleast 3 times 17 must be put in to the data to change the mode to 17.
Q.71. Age (in years) of 6 children of two groups are recorded as below: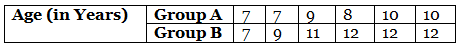
(a) Find the mode and range for each group.
(b) Find the range and mode if the two groups are combined together.
Solution: (a) For group A;
Both 7 and 10 occurs two times.
∴ Mode = 7 year and 10 year.
Range = Highest age – Lowest age
= (10 – 7) year = 3 year
For group B;
12 occurs most frequently i.e., 3 times.
∴ Mode = 12
Range – Highest age – Lowest age
= (12 – 7) year = 5 year
(b) If both groups A and B are combined, then arranging the data in ascending order, we get
7, 7, 7, 8, 9, 9, 10, 10, 11, 12, 12, 12
In this data both 7 and 12 occurs most frequently i.e., 3 times.
∴ Mode = 7 year and 12 year
Range = Highest age – Lowest age
= (12 – 7) year = 5 year
Q.72. Observe the given bar graph carefully and answer the questions that follow.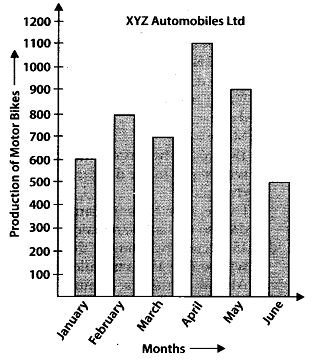
(a) What information does the bar graph depict?
(b) How many motor bikes were produced in the first three months?
(c) Calculate the increase in production in May over the production in January.
(d) In which month the production was minimum and what was it?
(e) Calculate the average (mean) production of bikes in 6 months.
Solution:
(a) The bar graph depicts the information about production of motor bikes by XYZ automobiles Ltd. during January to June.
(b) The motor bikes produced in first three months are = 600 + 800 + 700 = 2100
(c) Production in January = 600
Production in May = 900
∴ Increase in production in May over the production in January = 900 – 600 = 300
(d) In the month of June the production was minimum and it was 500.
Q.73. The bar graph given below shows the marks of students of a class in a particular subject: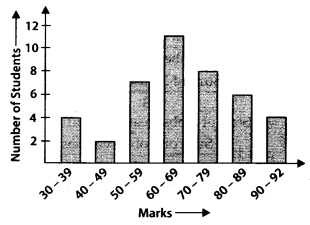
Study the bargraph and answer the following questions:
(a) If 40 is the pass mark, then how many students have failed?
(b) How many students got marks from 50 to 69?
(c) How many students scored 90 marks and above?
(d) If students who scored marks equal to or above 80 are given merits then how many merit holders are there?
(e) What is the strength of the class?
Solution:
(a) Number of students scored marks below 40 i.e., 30-39 ate 4 . 4 students have failed.
(b) Number of students got marks from 50 to 59 is 7 and number of students got marks from 60 to 69 is 11.
∴ 7 + 11 = 18 students got marks from 50 to 69.
(c) 4 students scored marks from 90 and above.
(d) Number of students got marks from 80 to 89 is 6. Number of students got marks from 90 to 92 is 4.
∴ 6 + 4 = 10 students are merit holders.
(e) Total number of students in the class = 4 + 2 +7 + 11 + 8 + 6 + 4 = 42
Q.74. Study the bar graph given below and answer the questions that follow.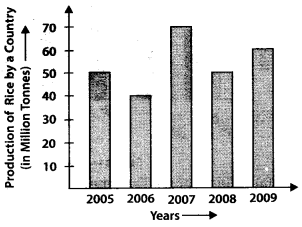
(a) What information does the above bar graph represent?
(b) In which year was production the least?
(c) After which year was the maximum rise in production?
(d) Find the average production of rice during the 5 years.
(e) Find the difference of rice production between the years 2006 and 2008.
Solution:
(a) The bar graph represents the information about the production of rice by a country during the years 2005 to 2009
(b) In 2006, the production was least.
(c) In 2007, there was a maximum rise in the production
∴ After 2006, the production has maximum rise.
(e) Rice production in 2006 = 40 million tonnes
Rice production in 2008 = 50 million tonnes
∴ Difference = (50 – 40) million tonnes = 10 million tonnes
Q.75. Study the bar graph given below and answer the questions that follow: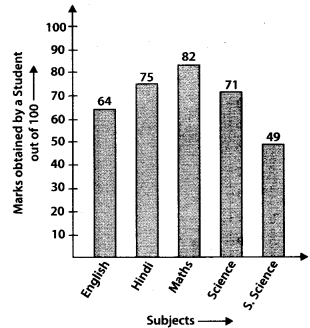
(a) What information is depicted from the bar graph?
(b) in which subject is the student very good?
(c) Calculate the average marks of the student.
(d) If 75 and above marks denote a distinction, then name the subjects in which the student got distinction.
(e) Calculate the percentage of marks the student got out of 500.
Solution:
(a) The bar graph depicts the information about marks obtained by a student in 5 different subjects.
(b) Since, student get highest marks in Maths i.e., 82
∴ The student is very good in Maths.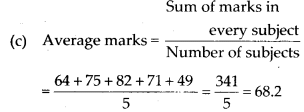
(d) The student got 75 marks in Hindi and 82 marks in Maths.
∴ In Hindi and Maths, the student got distinction.
(e) Total marks obtained by the student = 64 + 75 + 82 + 71 + 49 = 341
∴ Percentage marks =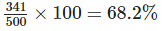
Q.76. The bar graph given below represents the circulation of newspapers (dailies) in a town in six languages (the figures are approximated to hundreds).
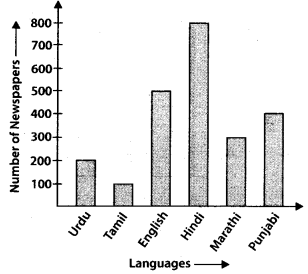
Study the bar graph and answer the following questions:
(a) Find the total number of newspapers read in Hindi, Punjabi, Urdu, Marathi and Tamil.
(b) Find the excess number of newspapers read in Hindi than those in English.
(c) Name the language in which the least number of newspapers are read.
(d) Write the total circulation of newspapers in the town.
Solution: (a) Total number of newspapers read in Hindi, Punjabi, Urdu, Marathi and Tamil = 800 + 400 + 200 + 300 + 100 = 1800
(b) Number of newspapers read in Hindi = 800
Number of newspapers read in English = 500
∴ 800 – 500 = 300 excess newspapers read in Hindi than in English.
(c) The least number of newspapers are read in Tamil language.
(d) Total number of newspapers in the town = 200 + 100 + 500 + 800 + 300 + 400 = 2300
Q.77. Study the double bar graph given below and answer the following questions: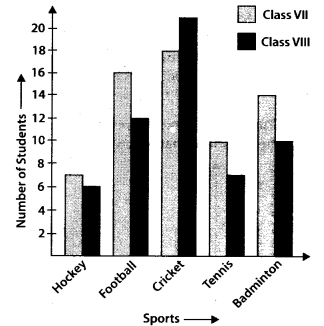
(a) Which sport is liked the most by Class VIII students?
(b) How many students of Class VII like Hockey and Tennis in all?
(c) How many students are there in Class VII?
(d) For which sport is the number of students of Class VII less than that of Class VIII?
(e) For how many sports students of Class VIII are less than Class VII?
(f) Find the ratio of students who like Badminton in Class VII to students who like Tennis in Class VIII.
Solution:
(a) Cricket has heighest value for Class VIII students in the graph.
∴ Cricket is liked the most by Class VIII students.
(b) Number of students like Hockey of Class VII = 7
Number of students like Tennis of Class VII = 10
∴ 7 + 10 = 17 students of Class VII like Hockey and Tennis.
(c) Total number of students in Class VII = 7 + 16 + 18 + 10 + 14 = 65
(d) For Cricket only, the number of students of Class VII is less than that of Class VIII.
(e) For Hockey Football, Tennis and Badminton i.e., 4 sports, students of Class VIII are less than that of Class VII.
(f) Number of students like Badminton in Class VII = 14
Number of students like Tennis in Class VIII = 7
∴ Required ratio =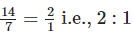
Q.78. Study the double bar graph shown below and answer the questions that follow: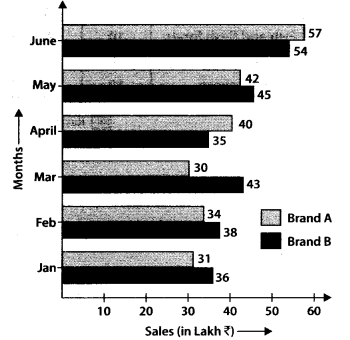
(a) What information is represented by the above double bar graph?
(b) in which month sales of Brand A decreased as compared to the previous month?
(c) What is the difference in sales of both the Brands for the month of June?
(d) Find the average sales of Brand B for the six months.
(e) List all months for which the sales of Brand B was less than that of Brand A.
(f) Find the ratio of sales of Brand A as compared to Brand B for the month of January
Solution:
(a) The double bar graph represents the information about the comparison sales of two brands A and B during January to June.
(b) Sales of Brand A in the month of March is less than sales in the month of February.
∴ In the month of March, sales of Brand A decreased as compared to the previous month.
(c) Sales of Brand A in the month of June = ₹ 57 lakh
Sales of Brand B in the month of June = ₹ 54 lakh.
Difference in sales = ₹ 57 lakh – ₹ 54 lakh = ₹ 3 lakh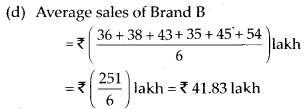
(e) In the month of April and June, the sales of Brand B was less than that of Brand A.
(f) Sales of Brand A in the month of January = ₹ 31 lakh
Sales of Brand B in the month of January = ₹ 36 lakh
∴ Required ratio =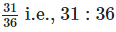
Q.79. Study the double bar graph given below and answer the questions that follow:
(a) What information is compared in the above given double bar graph?
(b) Calculate the ratio of minimum temperatures in the year 2008 to the year 2009 for the month of November.
(c) For how many months was the minimum temperature in the year 2008 greater than that of year 2009? Name those months.
(d) Find the average minimum temperature for the year 2008 for the four months.
(e) in which month is the variation in the two temperatures maximum?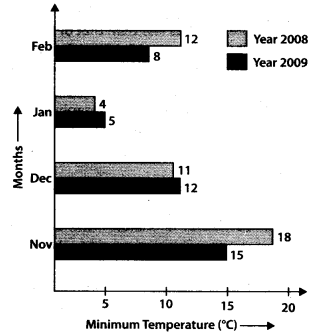
Solution:
(a) The double bar graph compares the information about minimum temperature (oC) of year 2008 and year 2009 during the months November to February
(b) Minimum temperature in the year 2008 for the month of November – 18°C
Minimum temperature in the year 2009 for the month of November = 15°C
∴ Required ratio 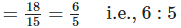
(c) For the month of November and February, i.e., 2 months the minimum temperature in 2008 was greater than that of 2009
(d) Average minimum temperature for 2008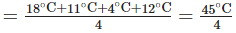
= 11.25°C
(e) In the month of February, the variation in two temperatures is maximum.
Q.80. The following table shows the average intake of nutrients in calories by rural and urban groups in a particular year. Using a suitable scale for the given data, draw a double bar graph to compare the data.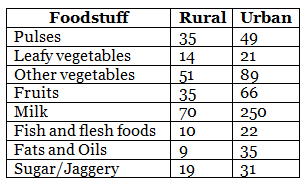
Solution: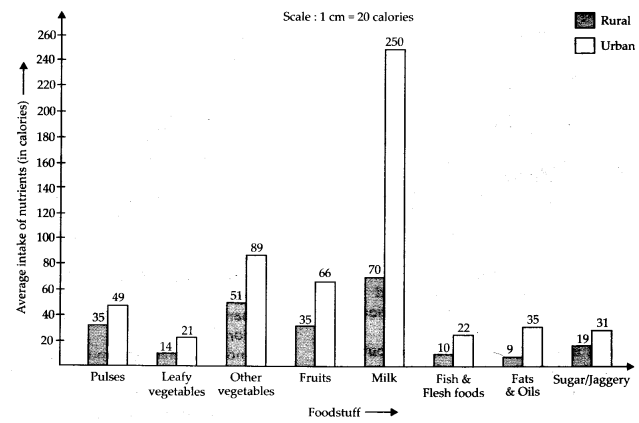
Q.81. Study the double bar graph and answer the questions that follow: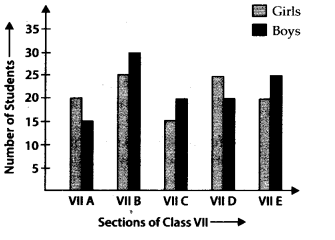
(a) What information does the double bar graph represent?
(b) Find the total number of boys in all sections of Class VII.
(c) in which sections, the number of girls is greater than the number of boys?
(d) In which section, the number of boys is the maximum?
(e) in which section, the number of girls is the least?
Solution:
(a) The double bar graph represents the information about the number of girls and boys in different sections of Class VII
(b) Total number of boys in all sections of Class VIII = 15 + 30 + 20 + 20 + 25 =110
(c) In sections A and D, the number of girls is greater than the number of boys.
(d) In section B, the number of boys is the maximum.
(e) In section C, the number of girls is the least.
Q.82. In a public library, the following observations were recorded by the librarian in a particular week: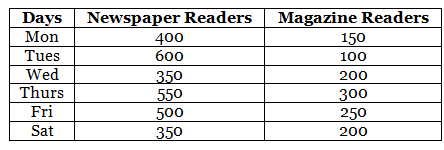
(a) Draw a double bar graph choosing an appropriate scale.
(b) On which day, the number of readers in the library was maximum?
(c) What is the mean number of magazine readers?
Solution: (a)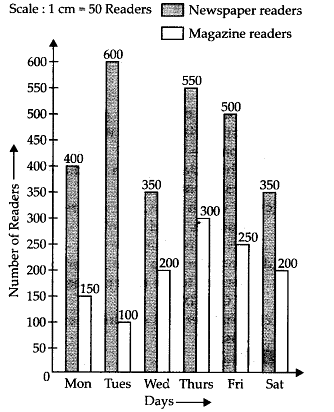
(b) Number of readers on Monday = 400 + 150 = 550
Number of readers on Tuesday = 600 + 100 = 700
Number of readers on Wednesday = 350 + 200 = 550
Number of readers on Thursday = 550 + 300 = 850
Number of readers on Friday = 500 + 250 = 750
Number of readers on Saturday = 350 + 200 = 550
Hence, on Thursday, the number of readers in the library was maximum.
(c) Total number of magazine readers = 150 + 100 + 200 + 300 + 250 + 200 = 1200
Q.83. Observe the following data: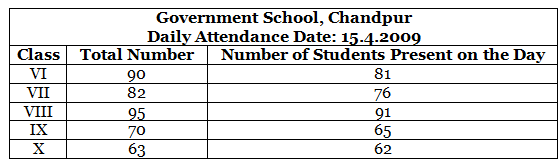
(a) Draw a double bar graph choosing an appropriate scale. What do you infer from the bar graph?
(b) Which class has the maximum number of students?
(c) in which class, the difference of total students and the number of students present is minimum?
(d) Find the ratio of the number of students present to the total number of students of Class IX.
(e) What percent of Class VI students were absent?
Solution: (a)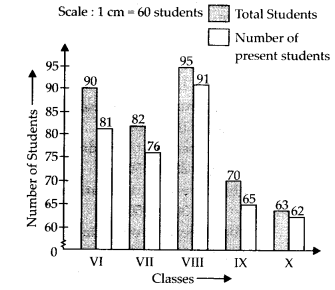
The double bar graph gives information about total number of students and number of students present from Class VI to Class X.
(b) Class VIII has the maximum number of students.
(c) Difference of total students and number of students present in Class VI = 90 – 81 = 9
Difference of total students and number of students present in Class VII = 82 – 76 = 6
Difference of total students and number of students present in Class VIII = 95 – 91 = 4
Difference of total students and number of students present in Class IX = 70 – 65 = 5
Difference of total students and number of students present in Class X = 63 – 62 = 1
Hence, in Class X, the difference of total students and number of students present is minimum.
(d) Total number of students in Class IX = 70
Number of present students in Class IX = 65
∴ Required ratio= 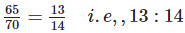
(e) Total number of students in Class VI = 90
Number of students present in Class VI = 81
∴ Number of students absent in Class VI = 90 – 81 = 9
∴ Percentage of students who were absent 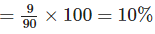
Q.84. Observe the given data: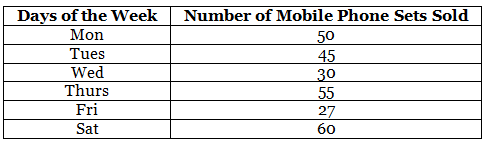
(a) Draw a bar graph to represent the above given information.
(b) On which day of the week was the sales maximum?
(c) Find the total sales during the week.
(d) Find the ratio of the minimum sale to the maximum sale.
(e) Calculate the average sale during the week.
(f) On how many days of the week was the sale above the average sale?
Solution:
(a)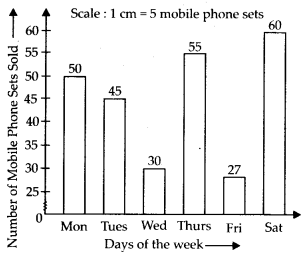
(b) On Saturday, the sales was maximum.
(c) Total sale during the week = 50 + 45 + 30 + 55 + 27 + 60 = 267
(d) Maximum sale = 60
Minimum sale = 27
∴ Required ratio 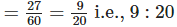
(e) Total sales during the week = 50 + 45 +30 + 55+ 27 +60 = 267
∴ Average sale 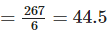
(f) Average sale is 44.5.
∴ 4 days of the week i.e., Monday, Tuesday, Thursday and Saturday has the sale above the average sale.
Q.85. Below is a list of 10 tallest buildings in India. This list ranks buildings in India that stand at least 150 m (492 ft.) tall, based on standard height measurement. This includes spires and architectural details but does not include antenna marks.
Following data is given as per the available information till 2009.
Since new buildings are always under construction, go on-line to check new taller buildings.
Use the information given in the table about skyscrapers to answer the following questions: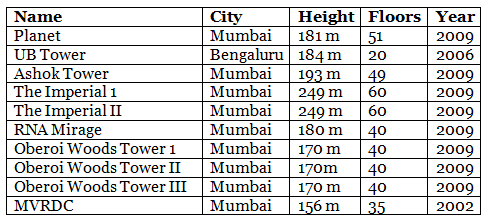
(a) Find the height of each storey of the three tallest buildings and write them in the following table:
(b) The average height of one storey for the buildings given in (a) is ______
(c) Which city in this list has the largest percentage of sky scrappers? What is the percentage?
(d) What is the range of data?
(e) Find the median of the data.
(f) Draw a bar graph for given data.
Solution:
(a)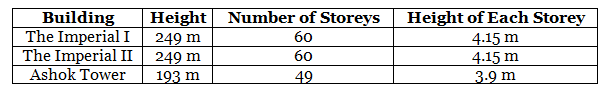
(b) Average height of one storey for three tallest buildings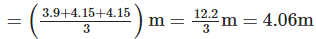
(c) Mumbai has the largest percentage of skys crappers
Total number of sky scrappers = 10
Total number sky scrappers in Mumbai = 9
∴ Percentage of skyscrappers in Mumbai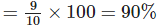
(d) Range = Highest value – Lowest value
= 249 m – 156 m = 93 m
(e) Arranging the height (inm) in ascending order, we get
156, 170, 170, 170, 180, 181, 184, 193, 249, 249
Since, observations are even in number.
∴ Median = Mean of two middle most observations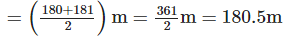
(f)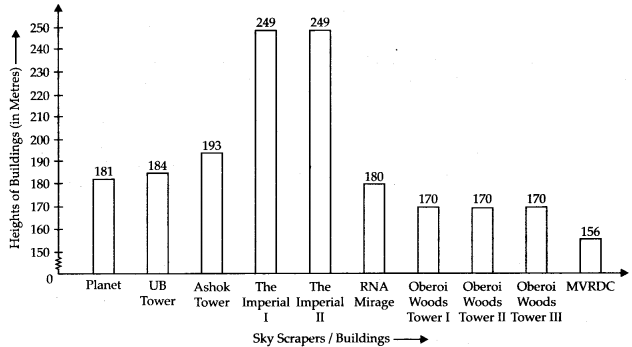
Q.86. The marks out of 100 obtained by Kunal and Soni in the Half Yearly Examination are given below: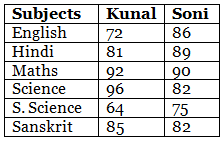
(a) Draw a double bar graph by choosing an appropriate scale.
(b) Calculate the total percentage of marks obtained by Soni.
(c) Calculate the total percentage of marks obtained by Kunal.
(d) Compare the percentages of marks obtained by Kunal and Soni.
(e) In how many subjects did Soni get more marks than Kunal? Which are those subjects?
(f) Who got more marks in S. Science and what was the difference of marks?
(g) in which subject the difference of marks was maximum and by how much?
Solution:
(a)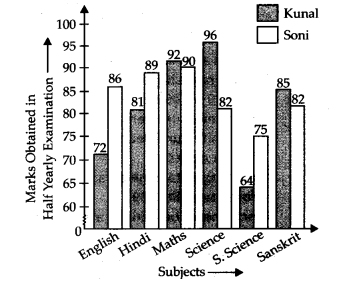
(b) Total marks obtained by Soni = 86 + 89 + 90 + 82 + 75 + 82 = 504
Total maximum marks = 6 × 100=600
∴ Percentage of marks obtained by Soni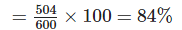
(c) Total marks obtained by Kunal = 72 + 81 + 92 +96 + 64 + 85 = 490
Total maximum marks – 6 × 100 = 600
∴ Percentage of marks obtained by Kunal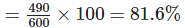
(d) Required ratio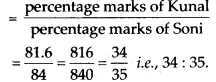
(e) In English, Hindi and S. Science i.e., 3 subjects Soni get more marks than Kunal.
(f) Soni got more marks in S. Science and difference of marks = 75 – 64 = 11
(g) Difference of marks in English = 86 – 72 = 14
Difference of marks in Hindi = 89 – 81 = 8
Difference of marks in Maths = 92 – 90 = 2
Difference of marks in Science = 96 – 82 – 14
Difference of marks in S. Science = 75 – 64 = 11
Difference of marks in Sanskrit = 85 – 82 = 3
Hence, in English and Science, the difference of marks was maximum by 14 marks.
Q.87. The students of Class VII have to choose one club from Music, Dance, Yoga, Dramatics, Fine arts and Electronics clubs. The data given below shows the choices made by girls and boys of the class. Study the table and answer the questions that follow: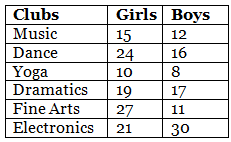
(a) Draw a double bar graph using an appropriate scale to depict the above data.
(b) How many students are there in Class VII?
(c) Which is the most preferred club by boys?
(d) Which is the least preferred club by girls?
(e) For which club the difference between boys and girls is the least?
(f) For which club is the difference between boys and girls the maximum?
Solution:
(a)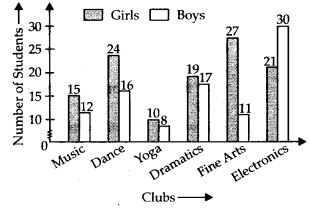
(b) Total number of girls in Class VII = 15 + 24 + 10 + 19 + 27 + 21 = 116
Total number of boys in Class VII = 12 + 16 + 8 + 17 + 11 + 30 = 94
∴ Total number of students in Class VII = 116 + 94 = 210
(c) Electronics club is the most preferred by boys.
(d) Yoga club is the least preferred by girls.
(e) Difference between the number of boys and girls for Music club 15 – 12 = 3
Difference between the number of boys and girls for Dance club = 24 – 16 = 8
Difference between the number of boys and girls for Yoga club = 10 – 8 = 2
Difference between the number of boys and girls for Dramatics club = 19 – 17 = 2
Difference between the number of boys and girls for Fine Arts = 27 – 11 = 16
Difference between the number of boys and girls for Electronics club = 30 – 21 = 9
Hence, for Dramatics club and Yoga club the difference between the number of boys and girls is the least.
(f) For Fine Arts club, the difference between the number of boys and girls is the maximum.
Q.88. The data given below shows the production of motor bikes in a factory for some months of two consecutive years.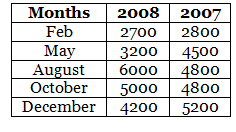
Study the table given above and answer the following questions:
(a) Draw a double bar graph using an appropriate scale to depict the above information and compare them.
(b) In which year was the total output the maximum?
(c) Find the mean production for the year 2007.
(d) for which month was the difference between the production for the two years the maximum?
(e) in which month for the year 2008, the production was the maximum?
(f) In which month for the year 2007, the production was the least?
Solution:
(a)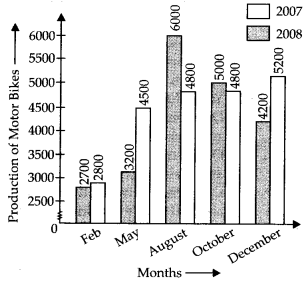
(b) Total output in year 2007 = 2800+ 4500 + 4800 + 4800 + 5200 = 22100
Total output in year 2008 = 2700+ 3200 + 6000 + 5000 + 4200 = 21100
Thus, in year 2007, the total output was the maximum.
(c) Total production for the year 2007 = 22100
∴ Mean production 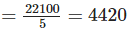
(d) Difference between the production for February = 2800 – 2700 = 100
Difference between the production for May = 4500 – 3200 = 1300
Difference between the production for August = 6000 – 4800 = 1200
Difference between the production for October = 5000 – 4800 = 200
Difference between the production for December = 5200 – 4200 – 1000
Thus, in the month of May the difference between the production for two years was the maximum.
(e) In the month of August for the year 2008, the production was the maximum.
(f) In the month of February for the year 2007, the production was the least.
Q.89. The table below compares the population in hundreds) of 4 towns over two years: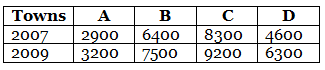
Study the table and answer the following questions:
(a) Draw a double bar graph using an appropriate scale to depict the above information.
(b) In which town was the population growth maximum?
(c) in which town was the population growth least?
Solution:
(a)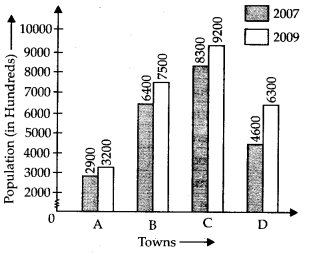
(b) Population growth in town A = 3200 – 2900 = 300
Population growth in town B = 7500 – 6400 = 1100
Population growth in town C = 9200 – 8300 = 900
Population growth in town D = 6300 – 4600 = 1700
Hence, in town the population growth was maximum.
(c) In town A, the population growth was the least.
Q.90. The table below gives the data of tourists visiting 5 hill stations over two consecutive years. Study the table and answer the questions that follow: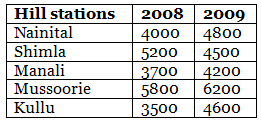
(a) Draw a double bar graph to depict the above information using appropriate scale.
(b) Which hill station was visited by the maximum number of tourists in 2008?
(c) Which hill station was visited by the least number of tourists in 2009?
(d) In which hill stations was there increase in number of tourists in the year 2009?
Solution:
(a)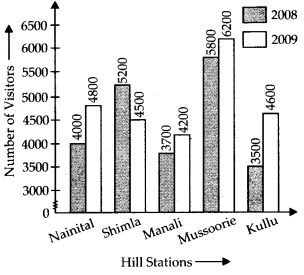
(b) The hill station Mussoorie was visited by the maximum number of tourists in 2008.
(c) The hill station Manali was visited by the least number of tourists in 2009.
(d) In the hill stations Nainital, Manali, Mussoorie and Kullu, there was increase in number of tourists in the year 2009.
Q.91. The table below gives the flavours of ice cream liked by children (boys and girls) of a society.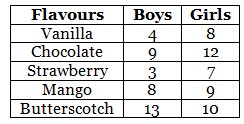
Study the table and answer the following questions:
(a) Draw a double bar graph using an appropriate scale to represent the above information.
(b) Which flavour is liked the most by the boys?
(c) How many girls are there in all?
(d) How many children like the chocolate flavour of ice cream?
(e) Find the ratio of children who like strawberry flavour to vanilla flavour of ice cream.
Solution:
(a)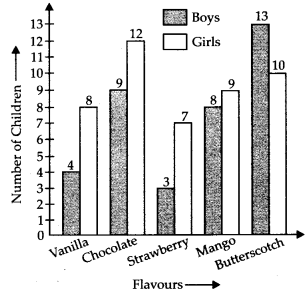
(b) Butterscotch flavour is liked the most by the boys.
(c) Total number of girls = 8 + 12 + 7 + 9 + 10 = 46
(d) Number of girls, like chocolate flavour = 12
Number of boys, like chocolate flavour = 9
Thus, 12 + 9 = 21 children like chocolate flavour of ice cream.
(e) Total number of children who like strawberry flavour = 3 + 7 = 10
Total number of children who like vanilla flavour = 4 + 8 = 12
∴ Required ratio 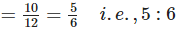
|
76 videos|452 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Data Handling - Mathematics (Maths) Class 7 (Old NCERT)
| 1. What is data handling in mathematics? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of data in data handling? |  |
| 3. How can data be represented in data handling? |  |
| 4. What is the importance of data handling in real-life applications? |  |
| 5. What are the key steps involved in data handling? |  |

















