NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science - Heat
Exercises
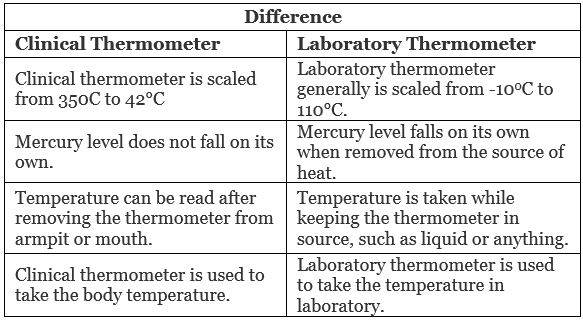
Q1. State similarities and differences between the laboratory thermometer and the clinical thermometer.
Ans:
Similarities:
- Both thermometers are used to measure temperature.
- both laboratory and clinical thermometers have long, narrow, uniform glass tubes.
- They both contain mercury (or alcohol in some cases) that expands or contracts with temperature changes.
- Both have a scale to read the temperature and both are graduated generally on Celsius Scale.
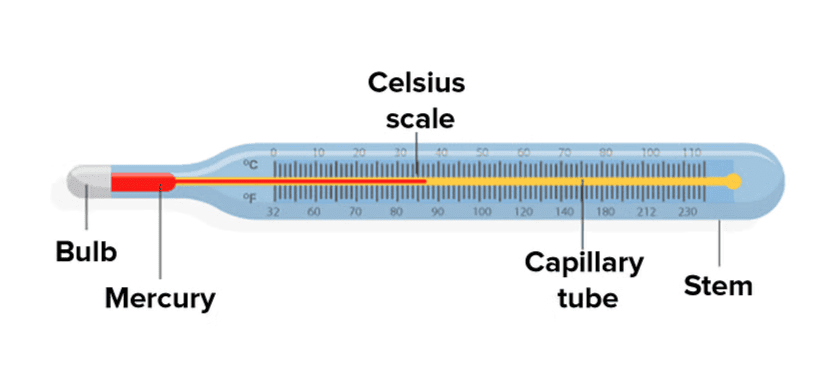 Clinical Thermometer
Clinical Thermometer
 Laboratory Thermometers
Laboratory Thermometers
Differences in Thermometers:
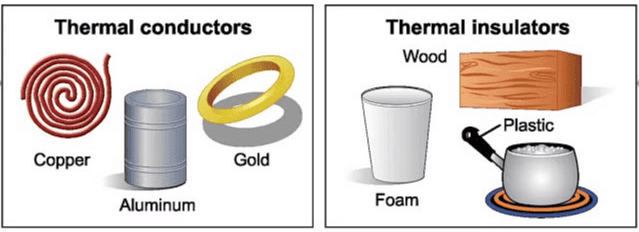
Q2. Give two examples each of conductors and insulators of heat.
Ans:
Conductors:
- Copper
- Aluminum
Insulators:
- Rubber
- Glass
 Thermal Conductors & InsulatorsQ3. Fill in the blanks:
Thermal Conductors & InsulatorsQ3. Fill in the blanks:
(a) The hotness of an object is determined by its ________.
Ans: Temperature.
 View Answer
View Answer 
- Temperature is a measure of how hot or cold an object is.
- It quantifies the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance.
- Higher temperatures indicate that the particles are moving faster, which corresponds to greater thermal energy.
(b) Temperature of boiling water cannot be measured by a ________ thermometer.
Ans: Clinical Thermometer
 View Answer
View Answer 
- Clinical thermometers are designed to measure body temperature and typically have a limited range (around 35°C to 42°C).
- The boiling point of water is 100°C at standard atmospheric pressure, which exceeds the range of a clinical thermometer.
- Instead, a laboratory or alcohol thermometer, which can measure higher temperatures, is used for boiling water.
(c) Temperature is measured in degree ________.
Ans: Celsius
 View Answer
View Answer 
- The Celsius scale (°C) is a temperature scale used in most of the world, where 0°C is the freezing point of water and 100°C is the boiling point at standard atmospheric pressure.
- It is widely used in science and everyday life for temperature measurement.
(d) No medium is required for transfer of heat by the process of __________.
Ans: Radiation
 View Answer
View Answer 
- Radiation is the transfer of heat in the form of electromagnetic waves (such as infrared radiation) and does not require a physical medium (like air, water, or solids) to travel through.
- This is how the Sun heats the Earth—through the vacuum of space.
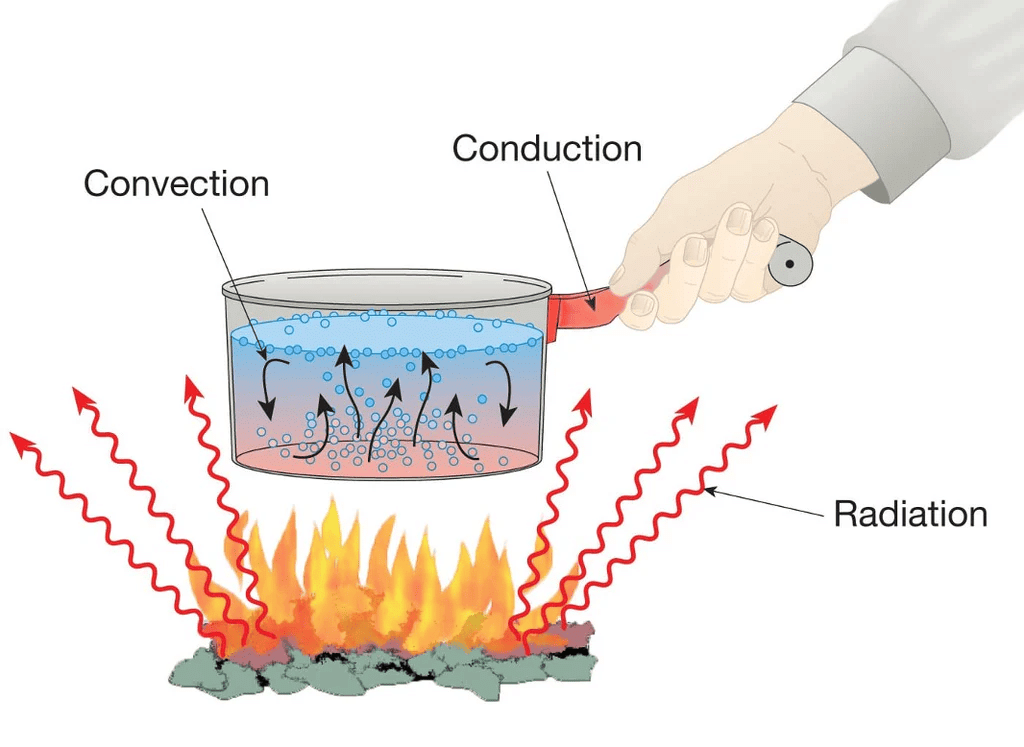 Heat Transfer
Heat Transfer
(e) A cold steel spoon is dipped in a cup of hot milk. It transfers heat to its other end by the process of ________.
Ans: Conduction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
- Conduction is the process of heat transfer through direct contact between materials.
- In this case, the heat from the hot milk transfers to the cold steel spoon, causing the particles in the spoon to gain energy and warm up, thus transferring heat to its other end.
(f) Clothes of ________colours absorb heat better than clothes of light colours.
Ans: Dark
 View Answer
View Answer 
- Dark colors absorb more wavelengths of light compared to light colors, which tend to reflect most of the light that hits them.
- This principle is why wearing dark clothing in the sun makes you feel warmer; the dark fabric absorbs more heat energy.
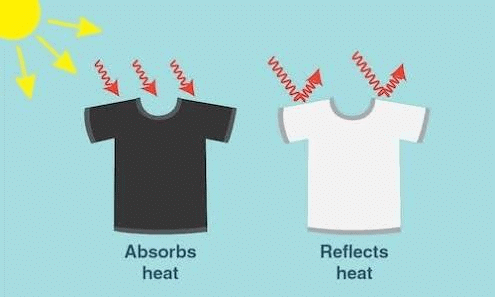 Dark colour clothes absorb Heat
Dark colour clothes absorb Heat
Q4. Match the following: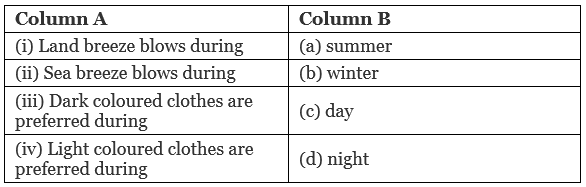 Ans:
Ans: 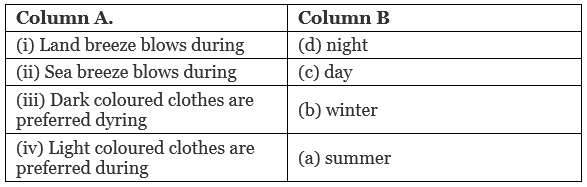
 View Answer
View Answer 
Land breeze blows during (d) night.
Explanation: A land breeze occurs at night when the land cools down more quickly than the sea. The cooler, denser air over the land moves towards the sea, creating a breeze from the land.Sea breeze blows during (c) day.
Explanation: A sea breeze happens during the day when the land heats up faster than the sea. The warm air over the land rises, causing cooler air from the sea to move in, resulting in a sea breeze.Dark colored clothes are preferred during (b) winter.
Explanation: Dark-colored clothes absorb more heat from sunlight, making them a good choice in winter to help keep the wearer warm.Light colored clothes are preferred during (a) summer.
Explanation: Light-colored clothes reflect sunlight, which helps to keep the wearer cooler in hot weather, making them ideal for summer.
Q5. Discuss why wearing more layers of clothing during winter keeps us warmer than wearing just one thick piece of clothing?
Ans:
- By wearing more layers of clothing, air gets trapped between different layers.
- As air is a bad conductor of heat, it does not allow the escape of the heat from the body.
- On the other hand, wearing just one piece of clothing creates just one insulator layer and is less effective in beating the cold.
Q6. Look at Fig. (in NCERT Text Book). Mark where the heat is being transferred by conduction, by convection and by radiation. Ans:
Ans:
Q7. In places of hot climate it is advised that the outer walls of houses be painted white. Explain.
Ans:
- White colour reflects most of the heat falling on it.
- This makes the house colder.
- Thus, in places of hot climate, it is advised that the outer walls of the house be painted white.
Q8. One litre of water at 30°C is mixed with one litre of water at 50°C. The temperature of the mixture will be
(a) 80°C
(b) more than 50°C but less than 80°C
(c) 20°C
(d) between 30°C and 50°C
Ans: (d)
 View Answer
View Answer 
- The temperature of the mixture will be between 30°C and 50°C because hot water loses heat and simultaneously cold water gains heat.
- This keeps the temperature between 30°C and 50°C.
Q9. An iron ball at 40°C is dropped in a mug containing water at 40°C. The heat will
(a) flow from iron ball to water.
(b) not flow from iron ball to water or from water to iron ball.
(c) flow from water to iron ball.
(d) increase the temperature of both.
Ans: (b)
 View Answer
View Answer 
- Heat transfer occurs only when there is a temperature difference between two objects.
- In this case, both the iron ball and the water are at the same temperature of 40°C.
- Therefore, there is no heat flow between them, as thermal energy only transfers from a hotter object to a cooler one.
Q10. A wooden spoon is dipped in a cup of ice cream. Its other end
(a) becomes cold by the process of conduction.
(b) becomes cold by the process of convection.
(c) becomes cold by the process of radiation.
(d) does not become cold.
Ans: (d)
 View Answer
View Answer 
- Wood is a poor conductor of heat (insulator).
- A bad conductor does not support the transfer of energy or heat.
- Therefore, the other end of the spoon remains warm and does not get cold.
Q11. Stainless steel pans are usually provided with copper bottoms. The reason for this could be that
(a) copper bottom makes the pan more durable.
(b) such pans appear colourful.
(c) copper is a better conductor of heat than stainless steel.
(d) copper is easier to clean than stainless steel.
Ans: (c)
 View Answer
View Answer 
- Copper is an excellent heat conductor, providing even heat distribution.
- This property helps in cooking food more efficiently.
- Stainless steel adds durability and resistance to corrosion, but it doesn’t conduct heat as well.
- Combining both materials optimizes cooking performance while ensuring longevity.
|
112 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science - Heat
| 1. What is heat and how is it different from temperature? |  |
| 2. What are the three methods of heat transfer? |  |
| 3. How does conduction occur in solids? |  |
| 4. What is the role of insulators in heat transfer? |  |
| 5. Why does hot air rise and cold air sink? |  |

















