Class 9 Geography Chapter 1 Question Answers - Contemporary India - I
Q1. Describe the Important features of the Peninsular Plateau.
Ans: The Peninsular Plateau of India lies to the south of the Northern Plains and extends up to the tip of the Indian peninsula. It is a tableland with gently rising, rounded hills and broad, shallow valleys.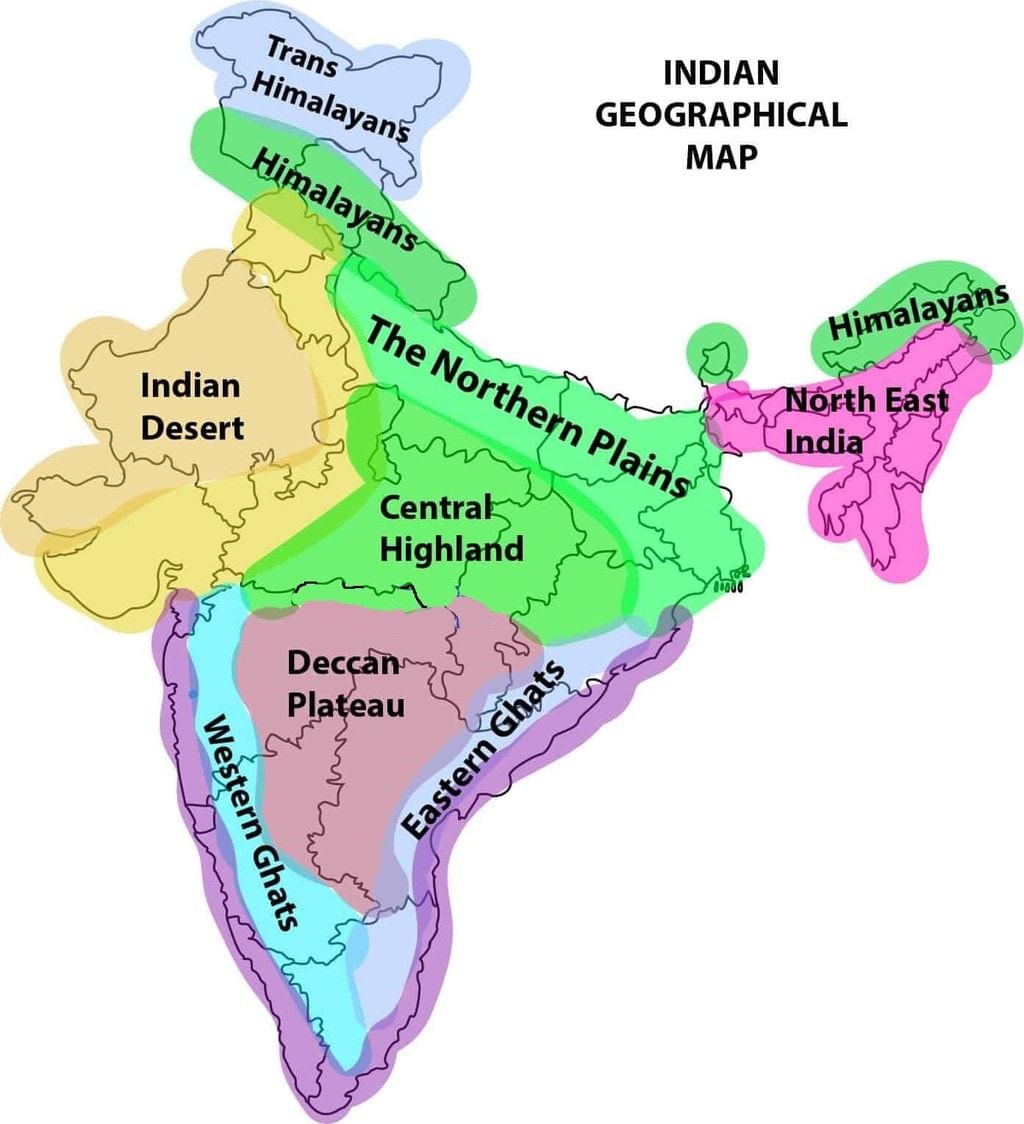
The Peninsular Plateau of India is a triangular-shaped landmass composed of ancient igneous and metamorphic rocks. It has two main parts:
1. Central Highlands (north of the Narmada River) – includes the Malwa Plateau, Bundelkhand, Baghelkhand, and the Vindhya Range. It extends eastward to the Chhota Nagpur Plateau. The Aravalli Hills, old and worn down, lie to the west and northwest.
2. Deccan Plateau (south of the Narmada River) – has a broad base in the north and narrows towards the south. It is formed from volcanic lava, mostly made of basalt rocks. The Satpura Range is to its north, while the Mahadev, Kaimur, and Maikal hills extend to the east. It is bordered by the Western Ghats (900-1600 meters high) and the Eastern Ghats (600 meters high). The plateau slopes from west to east. The black soil area here is called the Deccan Trap.
Q2. Write a note on the different parts of the Great Himalayan range.
Ans: The Himalayas are one of the highest and roughest mountain ranges in the world. They stretch from the Indus River in the west to the Brahmaputra River in the east, forming India’s northern border.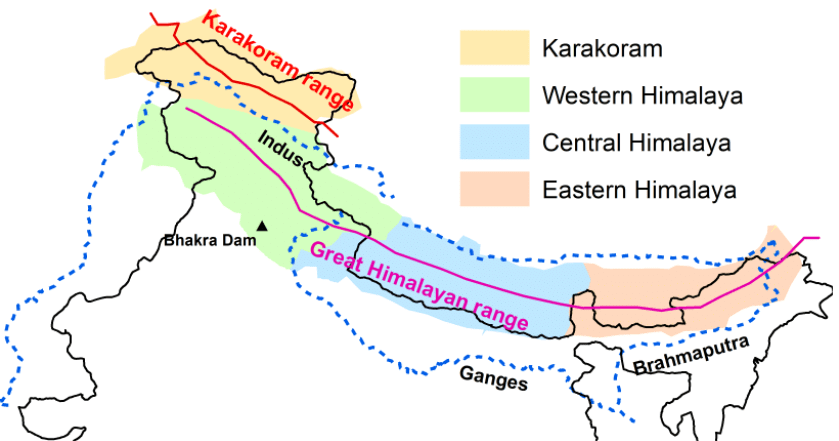
The Himalayan region has three main mountain ranges running parallel from west to east:
1. Greater or Inner Himalayas (Himadri):
- This is the northernmost and highest section, with an average height of 6000 meters.
- It is covered in snow and glaciers, containing the tallest peaks like Mount Everest (8848 m) etc
2. Lesser Himalayas (Himachal):
- Located south of Himadri, these rugged ranges have an average height of 3700-4500 meters.
- Important ranges include Pir Panjal, Dhaula Dhar, and the Mahabharat ranges, with valleys like Kashmir, Kangra, and Kullu.
3. Outer Himalayas (Shivaliks):
- The outermost and youngest range, with a height of 900-1100 meters.
- These ranges are made of loose sediments, with valleys called "duns" like Dehra Dun lying between them and the Lesser Himalayas.
Q3. Explain about Barchans.
Ans: Barchans are crescent-shaped dunes that form in arid or desert regions with a predominant wind direction. They have the following characteristics:
Shape and Formation: Barchans have a curved or crescent shape, with the open side facing the direction of the prevailing wind. They form when the wind blows consistently from one direction, causing sand to accumulate on the leeward side of an obstacle or in a region where the wind’s speed decreases.
Movement: Barchans migrate slowly across the desert as the wind continually moves sand from the windward side to the leeward side. The movement is gradual and can lead to the shifting of these dunes over time.
Size and Scale: Barchans can vary in size from small hills to large dunes. Their size and shape are influenced by the availability of sand and the intensity of the wind.
Q4. Describe the causes of the Shiwalik Ranges’ vulnerability to earthquakes and landslides.
Ans: The Shiwalik Ranges are particularly prone to landslides and earthquakes due to several factors:
Tectonic Activity: The Shiwalik Ranges lie at the boundary between the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayan foothills. This region is tectonically active due to the ongoing collision between the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate, which causes significant seismic activity. The tectonic movements and fault lines in this region increase the likelihood of earthquakes.
Geological Composition: The Shiwalik Ranges are composed of loose, unconsolidated sediments and debris. This loose material is less stable compared to solid rock, making it more susceptible to erosion and landslides, especially during periods of heavy rainfall or seismic activity.
Steep Slopes: The steep slopes and rugged terrain increase landslide risk. Rainfall can cause the soil to become saturated, increasing its weight and reducing stability, leading to landslides.
Human Activities: Deforestation, construction, and other human activities in the region disturb the natural stability of the slopes. These activities can weaken the ground and trigger landslides, particularly in areas where the natural vegetation has been removed.
Q5. Which part of the Himalayas is known as Purvanchal? Write a short note on the Purvanchal Himalayas. (Important)
Ans: The eastern hills and mountains of the Himalayas running along the eastern boundary of India are known as Purvanchal.
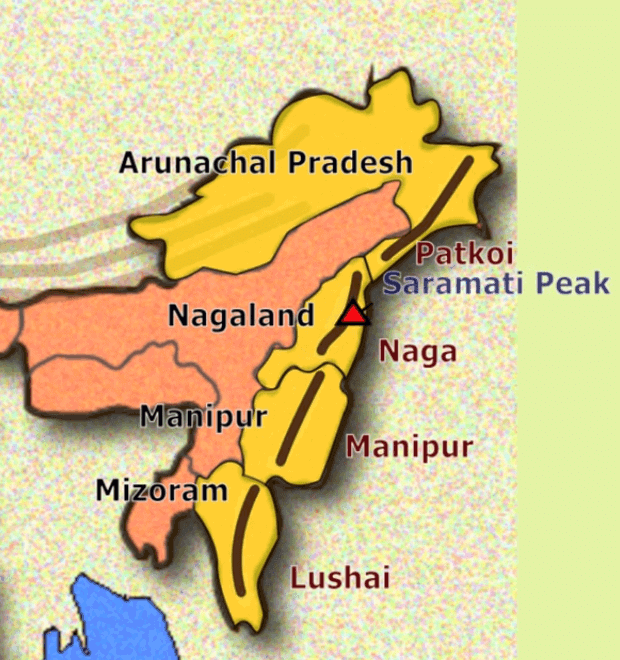
- They are located in the northeastern states of India. The river Brahmaputra marks the easternmost boundary of the Himalayas. Beyond the Dihang gorge, the Himalayas bend sharply to the south and spread along India’s eastern border. They are known as Purvanchal.
- They run mostly as parallel ranges with valleys in between. They are mostly composed of strong sandstone, a sedimentary rock. The Purvanchal are less spectacular than the Himalayas and are of medium height. The hills and ranges are covered with dense forests.
- Some important hills of the Purvanchal are:
(i) the Patkai Bum and Naga hills.
(ii) the Mizo hills and Manipur hills.
(iii) the Garo, Khasi and Jaintia hills along the Meghalaya-Bangladesh border.
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Geography Chapter 1 Question Answers - Contemporary India - I
| 1. भारत के भौतिक विशेषताएँ क्या हैं ? |  |
| 2. हिमालय पर्वत की विशेषताएँ क्या हैं ? |  |
| 3. भारत के प्रमुख नदी प्रणालियाँ कौन सी हैं ? |  |
| 4. डेक्कन पठार के विशेषताएँ क्या हैं ? |  |
| 5. भारत के तटीय क्षेत्र की विशेषताएँ क्या हैं ? |  |






















