Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Notes > Subject-Wise Mind Maps for Class 11 (Science) > Mind Map: Mineral Nutrition (Old NCERT)
Mind Map: Mineral Nutrition (Old NCERT) | Subject-Wise Mind Maps for Class 11 (Science) PDF Download
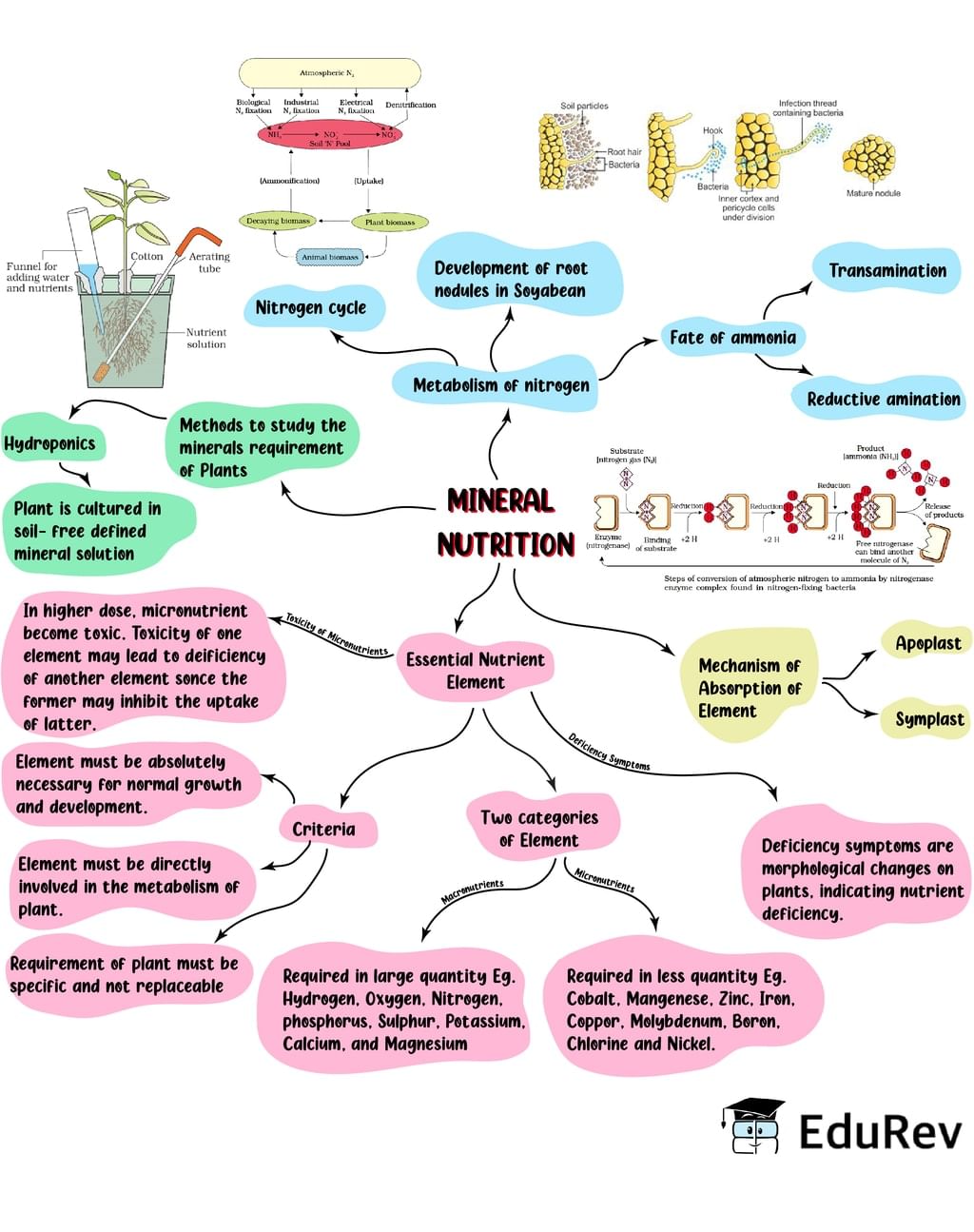
The document Mind Map: Mineral Nutrition (Old NCERT) | Subject-Wise Mind Maps for Class 11 (Science) is a part of the Class 11 Course Subject-Wise Mind Maps for Class 11 (Science).
All you need of Class 11 at this link: Class 11
FAQs on Mind Map: Mineral Nutrition (Old NCERT) - Subject-Wise Mind Maps for Class 11 (Science)
| 1. What are minerals in the context of plant nutrition? |  |
Ans. Minerals in the context of plant nutrition refer to inorganic nutrients that are essential for the growth and development of plants. These minerals are obtained from the soil and play crucial roles in various plant processes such as photosynthesis, enzyme activation, and structural support.
| 2. How do plants acquire minerals from the soil? |  |
Ans. Plants acquire minerals from the soil through their root system. The roots have specialized structures called root hairs, which increase the surface area for absorption. The minerals are taken up by active transport or through passive diffusion, depending on the concentration gradient between the soil and the root.
| 3. What are the essential macronutrients for plants? |  |
Ans. The essential macronutrients for plants are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and sulfur (S). These macronutrients are required in relatively large amounts by plants and are involved in various physiological processes such as protein synthesis, energy transfer, and cell division.
| 4. What are the essential micronutrients for plants? |  |
Ans. The essential micronutrients for plants are iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), boron (B), and chlorine (Cl). Although required in smaller quantities compared to macronutrients, these micronutrients are equally important for plant growth and development. They act as cofactors or activators of enzymes and participate in various metabolic reactions.
| 5. What are the consequences of mineral deficiencies in plants? |  |
Ans. Mineral deficiencies in plants can have various consequences. For example, nitrogen deficiency can lead to stunted growth and yellowing of leaves, while phosphorus deficiency can result in poor root development and delayed flowering. Potassium deficiency may cause weak stems and increased susceptibility to diseases. Different mineral deficiencies can manifest in specific symptoms, and if left unaddressed, they can severely impact the overall health and productivity of plants.
Related Searches

















