Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Question Answers - Gravitation
| Table of contents |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
| Activity-Based Questions |

|
| Value-Based Questions |

|
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What is the S.I. unit of thrust?
Ans: Newton.
Q2: What is the S.I. unit of pressure?
Ans: The S.I. unit of pressure = N/m2 = Pascal.
Q3: Define thrust.
Ans: The net force exerted by a body in a particular direction is called thrust.
Q4: Define pressure.
Ans: The force exerted per unit area is called pressure.
Q5: Why is it easier to swim in seawater than in river water?
Ans: The density of seawater is more due to dissolved salts in it as compared to the density of river water. Hence the buoyant force exerted on the swimmer by the sea water is more which helps in floating and makes swimming easier.
Q6: Why a truck or a motorbike has much wider tyres?
Ans: The pressure exerted by it can be distributed to more area, and avoid the wear and tear of tyres.
Q7: Why are knives sharp?
Ans: To increase the pressure, area is reduced,
As pressure ∝ 1/Area hence the pressure or force exerted on a body increases.
Q8: Why is the wall of dam reservoir thicker at the bottom?
Ans: The pressure of water in dams at the bottom is more, to withstand this pressure the dams have wider walls.
Q9: Why do nails have pointed tips?
Ans: The force exerted when acts on a smaller area, it exerts larger pressure. So the nails have pointed tips.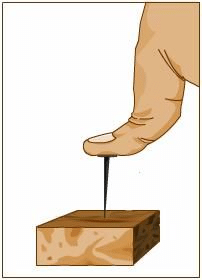
Q10: While swimming why do we feel light?
Ans: The swimmer is exerted by an upward force by water, this phenomenon is called buoyancy and it makes the swimmer feel light.
Q11: Define density and give its unit.
Ans: The density of a substance is defined as mass per unit volume. Its unit is kg/m3.
Q12: What is relative density?
Ans: The relative density of a substance is the ratio of its density to that of water.
Relative density = density of a substance/density of water
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: A ship made of iron does not sink but the iron rod sinks in water, why?
Ans: The iron rod sinks due to high density and less buoyant force exerted by the water on it, but in case of ship the surface area is increased, the upthrust experienced by the body is greater. So it floats on water.
Q2: Camels can walk easily on desert sand but we are not comfortable walking on the sand. State reason.
Ans: Camels feet are broad and the larger area of the feet reduces the force/ pressure exerted by the body on the sand. But when we have to walk on the same sand, we sink because the pressure exerted by our body is not distributed but is directional.
Q3: What is lactometer and hydrometer?
Ans: Lactometer is a device used to find the purity of a given sample of milk. Hydrometer is a device used to find the density of liquids.
Q4: The relative density of silver is 10.8. What does this mean?
Ans: It means that the density of silver is 10.8 times more than that of water. T
Q5: The relative density of gold is 19.3. The density of water is 103 kg/m3? What is the density of gold in S.I. unit?
Ans: Relative density of gold = 19.3
Relative density of gold = Density of gold/Density of water
∴ Density of gold = Relative density of gold x Denisty of water
= 19.3 x 103 Kg/m3
=19300 Kg/m3
Q6: State Archimedes’ principle.
Ans: Archimedes’ principle—When a body is immersed fully or partially in a fluid, it experiences an upward force that is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it.
It is used in designing of ships and submarines.
Q7: Two cork pieces of same size and mass are dipped in two beakers containing water and oil. One cork floats on water but another sinks in oil. Why?
Ans The cork floats on water because the density of cork is less than the density of water, and another cork sinks in the oil because the density of cork is more than the oil.
Q8: What are fluids? Why is Archimedes’ principle applicable only for fluids? Give the application of Archimedes’ principle.
Ans: Fluids are the substances which can flow e.g., gases and liquids are fluids. Archimedes’ principle is based on the upward force exerted by fluids on any object immersed in the fluid.
Hence it is applicable only for fluids.
Applications of Archimedes’ principle:
1. It is used in designing ships and submarines.
2. It is used in designing a lactometer, used to determine the purity of milk.
3. To make hydrometers, used to determine the density of liquids.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: With the help of an activity prove that the force acting on a smaller area exerts a larger pressure.
Ans: Consider a block of wood kept on a tabletop. The mass of the wooden block is 5 kg. Its dimension is 40 cm x 20 cm x 10 cm.
Now, we have to find the pressure exerted by the wooden block on the tabletop by keeping it vertically and horizontally.
The mass of the wooden block = 5 kg
The weight of the wooden block applies a thrust on the tabletop
∴ Thrust = F = m * g
= 5 kg * 9.8 m/s2 = 49 N
( case a ) — when the wooden box is kept vertically with sides 20 cm * 10 cm.
Area of a side = length * breadth
= 20 cm * 10 cm
= 200 cm2 = 0.02 m2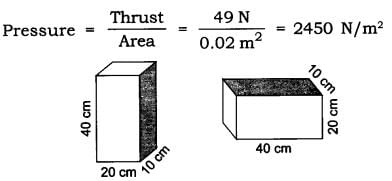
(case b) — When the block is kept horizontally with side 40 cm * 20 cm
Area = length * breadth
= 40 cm * 20 cm
= 800 cm2 = 0.08 m2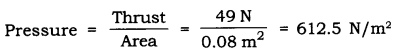
∴ The pressure exerted by the box in case (a) is more as compared to the pressure exerted in case (b).The area is reduced and the pressure exerted is more.
This shows that pressure ∝ 1/area.
Pressure will be larger if the area is reduced.
Application:
• Nails have pointed tips.
• Knives have sharp edges.
• Needles have pointed tips.
Activity-Based Questions
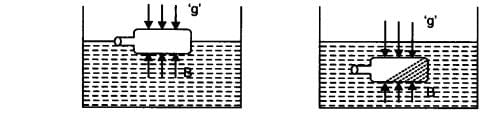
Q1: • Take an empty plastic bottle. Close the mouth of the bottle with an airtight stopper. Put it in a bucket filled with water. You see that the bottle floats.• Push the bottle into the water. You feel an upward push. Try to push it further down. You will find it difficult to push deeper and deeper. This indicates that water exerts a force on the bottle in the upward direction. The upward force exerted by the water goes on increasing as the bottle is pushed deeper till it is completely immersed.
• Now, release the bottle. It bounces back to the surface.
• Does the force due to the gravitational attraction of the earth act on this bottle? If so, why doesn’t the bottle stay immersed in water after it is released? How can you immerse the bottle in water?
Ans: Yes, the bottle is attracted downwards by the earth’s gravitational force. On pushing the bottle with force in the water it does not remain there but comes up because of the upward force exerted by water on the bottle. This upward force is called upthrust or buoyant force. When the upward force or buoyant force is greater than the downward force ‘g’ the bottle will float. But if downward force is greater than upward force, the bottle will sink. The upward force (buoyant force) acting on the bottle can be reduced by increasing the force on the bottle or by filling the bottle with sand, water, etc.
Q2:• Take a beaker filled with water.
• Take an iron nail and place it on the surface of the water.
• Observe what happens.
Ans: The iron nail sinks as the density of nail is more and the downward force exerted on nail is more than the buoyant force.
Q3: • Take a beaker filled with water.
• Take a piece of cork and an iron nail of equal mass.
• Place them on the surface of the water.
• Observe what happens.
Ans: The iron nail sinks as the density of nail is more and the downward force exerted on nail is more than the buoyant force. The cost floats as the density of cost is less and the buoyant force exerted on it is more than the downward force.
Q4: • Take a piece of stone and tie it to one end of a rubber string or a spring balance.
• Suspend the stone by holding the balance or the string as shown in figure (a).
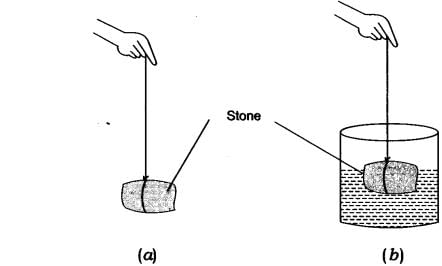
• Note the elongation of the string or the reading on the spring balance due to the weight of the stone.
• Now, slowly dip the stone in the water in a container as shown in Fig. (b).
• Observe what happens to the elongation of the string or the reading on the balance.
Observations :
• In Fig. (a) the elongation of the string is 6 cm.
• In Fig. (b) when the stone is dipped in water the length of the string is reduced to 5 cm.
• The length of the string in case (b) decreases due to the upward force exerted by water on the stone called buoyant force.
Value-Based Questions
Q 1: A milkman sold his milk in the city and always carried a lactometer with him. The customers trusted him and his business flourished.
(a) What is a lactometer?
(b) What is the principle of working of a lactometer?
(c) What value of milkman is seen in this case?
Ans:
(a) A lactometer is an instrument used to measure the purity of milk. It helps determine the specific gravity of milk, which can indicate whether it has been diluted with water or not.
(b) The principle of working of the lactometer is based on Archimedes' Principle. The lactometer floats in milk, and the level at which it floats depends on the density or specific gravity of the milk. If the milk is pure, the lactometer will float at a certain level. If the milk is diluted with water, the specific gravity decreases, and the lactometer will float higher in the liquid.
(c) The value of the milkman reflected in this case is honesty and integrity. He uses the lactometer to ensure that the milk he sells is pure, earning the trust of his customers and helping his business grow.
Q 2: Reeta was wearing a high heel shoes for a beach party, her friend told her to wear flat shoes as she will be tired soon with high heels and would not feel comfortable,
(a) Why would one feel tired with high-heeled shoes on the beach?
(b) Give the unit of pressure.
(c) What value of Reeta’s friend is seen in the above act?
Ans:
(a) One would feel tired with high-heeled shoes on the beach because high heels concentrate the weight on a small area of the feet. On a soft surface like sand, the high heel does not distribute the body weight evenly, leading to more pressure on the feet. This makes it harder to walk and causes discomfort and fatigue.
(b) The unit of pressure is the Pascal (Pa). It is defined as one newton per square meter (N/m²).
(c) The value of Reeta's friend reflected in this case is concern and care. Her friend is looking out for Reeta’s comfort and well-being by advising her to wear flat shoes that would be more suitable for walking on the beach, helping to avoid unnecessary discomfort.
Q 3: In the school fair, there was a game in which one need to find the heaviest ball without holding them in hand. Three balls were given and few disposable glasses were kept. Tarun saw his friend struggling to win the game but he was unable to find the heaviest ball. Tarun helped him by dipping the three balls one by one in the glasses full of water upto the brim and finally they won the game.
(a) Why did Tarun told his friend to dip the balls one by one in completely filled glass of water?
(b) Name the principle used here.
(c) What value of Tarun is reflected in this case?
Ans:
(a) Tarun told his friend to dip the balls one by one in completely filled glasses of water because the heaviest ball would displace more water due to its greater volume. The one that displaces the most water is the heaviest.
(b) The principle used here is Archimedes' Principle, which states that the upward buoyant force exerted on a body submerged in a fluid is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body.
(c) The value of Tarun reflected in this case is helpfulness and problem-solving ability. He used his knowledge to assist his friend and help them win the game.
|
84 videos|541 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Question Answers - Gravitation
| 1. What is the law of universal gravitation? |  |
| 2. How does gravity affect the motion of objects on Earth? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between mass and weight? |  |
| 4. How does the distance between two objects affect gravitational force? |  |
| 5. Can gravity be considered a force in the same way as other forces? |  |
















