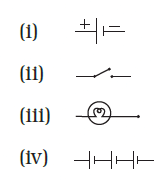NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Electric Current & Its effects | Science Class 7 (Old NCERT) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
| Long Answer Questions |

|
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: When an electric current flows through a copper wire AB as shown in Figure, the wire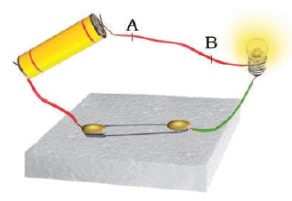
(a) deflects a magnetic needle placed near it.
(b) becomes red hot.
(c) gives an electric shock.
(d) behaves like a fuse.
Ans: a
Explanation:
- A wire carrying an electric current creates a magnetic field around it.
- This magnetic field can deflect a nearby magnetic needle.
- The strength of the magnetic field depends on the current flowing through the wire.
Q2: Choose the statement which is not correct in the case of an electric fuse.
(a) Fuses are inserted in electric circuits of all buildings.
(b) There is a maximum limit on the current which can safely flow through the electric circuits.
(c) There is a minimum limit on the current which can safely flow in the electric circuits.
(d) If a proper fuse is inserted in a circuit it will blow off if current exceeds the safe limit.
Ans: c
Explanation:
- There is only a maximum limit on the current that can safely flow through circuits.
- There is no minimum limit for current flow in these circuits.
- If the current exceeds the safe limit, the fuse will blow to protect the circuit.
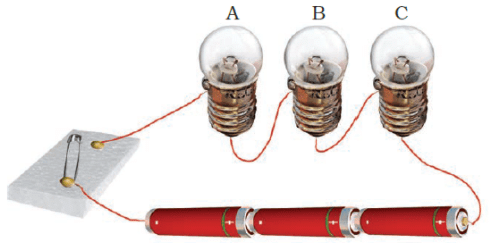
Q3: Three bulbs A, B, C are connected in a circuit as shown in Figure 14.2. When the switch is ‘ON’
(a) bulb C will glow first.
(b) bulb B and C will glow simultaneously and bulb A will glow after some time.
(c) all the bulbs A, B and C will glow at the same time.
(d) the bulbs will glow in the order A, B and C.
Ans: c
Explanation:
- All the bulbs will glow simultaneously when the switch is turned 'ON'.
- This is because there is no delay in the flow of current through the circuit.
Q4: When a switch is in OFF position,
(i) circuit starting from the positive terminal of the cell stops at the switch.
(ii) the circuit is open.
(iii) no current flows through it.
(iv) current flows after some time. Choose the combination of the correct answer from the following.
(a) all are correct
(b) (ii) and (iii) are correct
(c) only (iv) is correct
(d) only (i) and (ii) are correct
Ans: b
Explanation:When the switch is in the OFF position:
- The circuit is incomplete, meaning it is open.
- No current flows through it.
Q5: Which of the following precautions need not be taken while using electric gadgets/appliances/circuit?
(a) We should never touch a lighted electric bulb connected to the mains.
(b) We should never experiment with the electric supply from the mains or a generator or an inverter.
(c) We should never use just any wire or strip of metal in place of a fuse.
(d) We should never turn the switch in ON position.
Ans: d
Explanation
To use electric gadgets/appliances/circuit switch should be turned on, hence statement d) is wrong.
Very Short Answer Questions
Q6: Which property of a conducting wire is utilised in making electric fuse?
Ans: The low melting point of the wire is utilized in making electric fuse.
Q7: Name the device used these days in place of electric fuses in electrical circuits.
Ans: Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB).
Q8: Fill in the blanks:
(i) Our body is a ________________ of electricity.
(ii) An electric cell produces electricity from the __________ ___________ in it.
(iii) In an electric circuit a fuse is a _________ _______ to prevent possible fire.
(iv) A combination of two or more cells is called a _________.
Ans:
(i) Our body is a conductor of electricity.
(ii) An electric cell produces electricity from the Chemicals stored in it.
(iii) In an electric circuit, a fuse is a Safety device to prevent a possible fire.
(iv) A combination of two or more cells is called a battery.
Q9: Unscramble the following words:
(i) TBTAYER
(ii) SFEU
(iii) HTRCO
(iv) HICWTS
Ans:
Battery
Fuse
Torch
Switch
Q10: Paheli does not have a night lamp in her room. She covered the bulb of her room with a towel in the night to get dim light. Has she taken the right step? Give one reason to justify your answer.
Ans: No, Paheli's actions are not safe. Here are the reasons:
- The towel can catch fire due to the heat from the bulb.
- Keeping the bulb on wastes energy unnecessarily.
Q11: Why are compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) preferred over electric bulbs?
Ans: Compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) preferred over electric bulbs because CFL’S consume less energy and they will not waste the energy in the form of heat.
Q12: Why is an electric fuse required in all electrical appliances?
Ans: An electric fuse is required for it acts as a safety device and it checks excessive current flow.
Short Answer Questions
Q13: Can we use the same fuse in a geyser and a television set? Explain.
Ans: No, we cannot use the same fuse in a geyser and television because a geyser and a television set require a different amount of current. Therefore the fuse used in these will be of different ratings.
Q14: Name two electric devices for each were (i) heating effect of current is used and (ii) magnetic effect of current is used.
Ans:
Heating effect – Geyser, room heater.Magnetic effect – Electric bell, Cranes to lift magnetic material.
Q15: Boojho made an electromagnet by winding 50 turns of wire over an iron screw. Paheli also made an electromagnet by winding 100 turns over a similar iron screw. Which electromagnet will attract more pins? Give reason.
Ans: Paheli’s electromagnet will attract more pins as it has more number of turns of wire on it and thus a stronger electromagnet.
Long Answer Questions
Q16: Your teacher has shown you the following activity.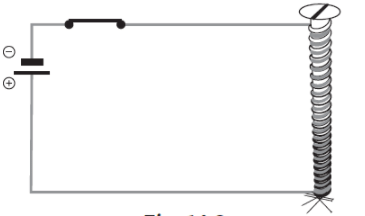
Activity: Teacher has wound a long insulated piece of wire around an iron nail in the form of a coil. Free ends of the wire are connected to a cell through a switch as shown in Figure. The current is switched on and some pins are placed near the ends of the nail.
Write down any three questions that come to your mind about this activity.
Ans:
(i) Why does the nail attract the pins?
(ii) What will happen if we connect more cells in the circuit?
(iii) What will happen if we use some other material like a straw in place of the nail?
(iv) What will happen if we wrap the wire on the nail more tightly?
Q17: Paheli took a wire of length 10 cm. Boojho took a wire of 5 cm of the same material and thickness. Both of them connected the wires as shown in the circuit given in Figure. The current flowing in both circuits is the same.
- Will the heat produced in both the cases be equal? Explain.
- Will, the heat produced be the same if the wires taken by them are of equal lengths but of different thickness? Explain.
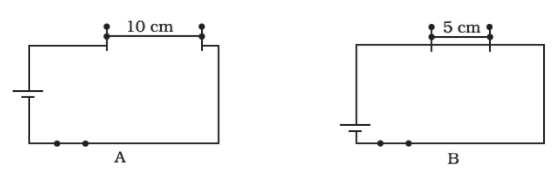
Ans:
(i) No, the amount of heat produced in both the cases will not be equal because the length of the wire decides the amount of heat produced in a wire
(ii) No, Thickness of the wire decides the amount of heat produced by the wire.
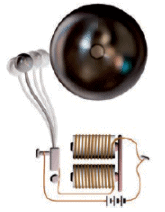
Q18: How does the magnetic effect of electric current help in the working of an electric bell? Explain with the help of a diagram.
Ans: Electric bell consists of a coil of wire wound on an iron piece. The coil acts as an electromagnet. An iron strip with a hammer at one end is kept close to the electromagnet. There is a contact screw near the iron strip. When the iron strip is in contact with the screw, the current flows through the coil which becomes an electromagnet. It, then, pulls the iron strip. In the process, the hammer at the end of the strip strikes the gong of the bell to produce a sound.
Q19: Draw the symbols of the following circuit components.
(i) electric cell
(ii) switch in off position
(iii) electric bulb
(iv) battery
Ans:
|
112 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Electric Current & Its effects - Science Class 7 (Old NCERT)
| 1. What is electric current and its effects? |  |
| 2. How is electric current measured? |  |
| 3. What are the factors that affect the resistance of a conductor? |  |
| 4. How does electric current flow in a circuit? |  |
| 5. What are the safety precautions to be taken while dealing with electric current? |  |